160:
Phosphatidylinositol-(4,5)-bisphosphate (PIP2) serves as a signal sequence that binds and is recognized by AP2. PIP2 can be found within liposomes containing cargo, which interact with AP2 to then bind clathrin and execute its function. In the closed form, the PIP2 binding site is exposed, allowing for the conformational regulation to occur. Because of this, a certain order of slight conformational changes bring about the fully open conformation, beginning with PIP2 binding, then cargo sequence binding, and finally clathrin binding. A family of proteins called muniscins are thought to be the primary allosteric activators of the AP2 adaptor complex, due to their prevalence in AP2 associated pits and their inhibition resulting in the decrease in AP2 mediated endocytosis. Additionally, the complex has been found to be regulated and activated by phosphorylation of its (mu) subunit.
125:
their respective interactions to occur. In its inactive state, the complex experiences a conformational change that causes both sites to be covered, preventing its primary functions. The α and β heavy chains of the complex make up about 60% of the polypeptide sequence of AP2 and are tightly structured into 14 HEAT repeats which form zigzagging α-helical structures that interact with the helical "legs" of the clathrin trimer.
129:
28:
168:
Deactivation, or change into the "closed" conformation, is still unclear. NECAPs are thought the play a role in it, by binding to the α subunit of AP2. Not much is known, but the open conformation of AP2, which is phosphorylated, appears to be necessary for NECAP1 to bind within its core. The process
150:
The regulation of AP2 activity is primarily done through conformational rearrangements of the structure into two distinct (and a potential third and fourth) conformations. The "open" conformation is the active state of the complex, as the "pits" or active binding sites for clathrins and the cargo are
177:
AP2 has been identified to intimately participate in autophagic cellular pathways, responsible for the degradation of aggregated protein. In fact, it's seen to complex with phosphatidylinositol clathrin assembly lymphoid-myeloid leukemia (PICALM), which would serve as an important receptor group for
124:
The AP2 adaptor complex exists in two primary conformations: the open conformation (active state) and the closed conformation (inactive state). In its active state, the clathrin binding site found on the β subunit and the cargo binding site found on the μ subunit are exposed to the cytosol, allowing
141:
AP2 facilitates the assembly of clathrin lattices when endocytosis needs to occur, by aggregating together with other AP2 complexes, in their active conformation. These AP2 aggregates interact with individual clathrin proteins by their β-active sites, orienting them into the clathrin "cages" that
159:
The presence of clathrins have been found to induce binding to cargo, and similarly, presence of cargo appears to induce clathrin binding. This is thought to occur by a secondary stabilization of the complex structure, which would allow partial activation, or access, to the respective pits.
59:
which give rise to a structure that has a core domain and two appendage domains attached to the core domain by polypeptide linkers. These appendage domains are sometimes called 'ears'. The core domain binds to the membrane and to cargo destined for
182:). LC3 has an important role in some autophagic pathways. Because of this, there is suspicion that AP2 deficiency or dysfunction may be a precursor for the development of familial Alzheimer's Disease.
969:
Dhingra A, Alexander D, Reyes-Reveles J, Sharp R, Boesze-Battaglia K (2018). "Microtubule-Associated
Protein 1 Light Chain 3 (LC3) Isoforms in RPE and Retina".
1033:
1028:
986:
169:
of action is still unknown, but this interaction causes the dephosphorylation of the AP2 adaptor complex, thus deactivating it.
79:
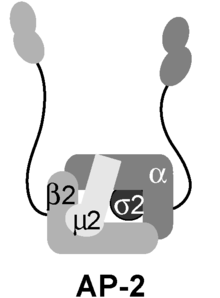
The AP-2 complex is a heterotetramer consisting of two large adaptins (α and β), a medium adaptin (μ), and a small adaptin (σ):
920:"Adaptor complex AP2/PICALM, through interaction with LC3, targets Alzheimer's APP-CTF for terminal degradation via autophagy"
132:
AP2 Adaptor
Complex Cryo-EM Structure. Red - alpha subunits. Blue - beta subunit. Green - mu subunit. Yellow - sigma subunit.
151:
uncovered. On the other hand, the "closed" conformation is denoted by the closing or inaccessibility of these same sites.
1013:
868:"Phosphorylation of the AP2 mu subunit by AAK1 mediates high affinity binding to membrane protein sorting signals"
670:"Syp1 is a conserved endocytic adaptor that contains domains involved in cargo selection and membrane tubulation"
61:
69:
817:"AP-1 binding to sorting signals and release from clathrin-coated vesicles is regulated by phosphorylation"
526:
Ehrlich M, Boll W, Van Oijen A, Hariharan R, Chandran K, Nibert ML, Kirchhausen T (September 2004).
668:
Reider A, Barker SL, Mishra SK, Im YJ, Maldonado-Báez L, Hurley JH, et al. (October 2009).
567:
Rapoport I, Miyazaki M, Boll W, Duckworth B, Cantley LC, Shoelson S, Kirchhausen T (May 1997).
992:
982:
951:
897:
848:
797:
748:
699:
650:
598:
549:
508:
456:
405:
351:
297:
248:
974:
941:
931:
887:
879:
838:
828:
787:
779:
738:
730:
689:
681:
640:
632:
588:
580:
539:
498:
490:
446:
436:
395:
387:
341:
331:
287:
240:
569:"Regulatory interactions in the recognition of endocytic sorting signals by AP-2 complexes"
621:"Regulation of clathrin-mediated endocytosis by hierarchical allosteric activation of AP2"
717:
Henne WM, Boucrot E, Meinecke M, Evergren E, Vallis Y, Mittal R, McMahon HT (June 2010).
619:
Kadlecova Z, Spielman SJ, Loerke D, Mohanakrishnan A, Reed DK, Schmid SL (January 2017).
423:
Partlow EA, Baker RW, Beacham GM, Chappie JS, Leschziner AE, Hollopeter G (August 2019).
231:
Pearse BM, Smith CJ, Owen DJ (April 2000). "Clathrin coat construction in endocytosis".
946:
919:
892:
867:
843:
816:
792:
767:
743:
718:
694:
669:
645:
620:
593:
568:
503:
478:
451:
424:
400:
375:
346:
319:
425:"A structural mechanism for phosphorylation-dependent inactivation of the AP2 complex"
292:
275:
244:
1022:
44:
973:. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Vol. 1074. pp. 609–616.
376:"Molecular structure, function, and dynamics of clathrin-mediated membrane traffic"
68:. Their interactions allow the temporal and spatial regulation of the assembly of
978:
391:
191:
73:
52:
924:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
783:
544:
527:
584:
128:
936:
734:
528:"Endocytosis by random initiation and stabilization of clathrin-coated pits"
211:
17:
996:
955:
901:
852:
801:
752:
703:
685:
654:
553:
512:
460:
409:
355:
301:
252:
883:
833:
636:
602:
276:"Molecular Architecture and Functional Model of the Endocytic AP2 Complex"
27:
179:
65:
64:. The alpha and beta appendage domains bind to accessory proteins and to
48:
441:
336:
56:
40:
866:
Ricotta D, Conner SD, Schmid SL, von Figura K, Honing S (March 2002).
494:
614:
612:
479:"Conformational regulation of AP1 and AP2 clathrin adaptor complexes"
206:
320:"NECAPs are negative regulators of the AP2 clathrin adaptor complex"
918:
Tian Y, Chang JC, Fan EY, Flajolet M, Greengard P (October 2013).
201:
196:
127:
110:
104:
98:
92:
86:
26:
719:"FCHo proteins are nucleators of clathrin-mediated endocytosis"
318:
Beacham GM, Partlow EA, Lange JJ, Hollopeter G (January 2018).
274:
Collins BM, McCoy AJ, Kent HM, Evans PR, Owen DJ (2002-05-17).
768:"The first five seconds in the life of a clathrin-coated pit"
766:
Cocucci E, Aguet F, Boulant S, Kirchhausen T (August 2012).
477:
Beacham GM, Partlow EA, Hollopeter G (October 2019).
178:microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (
374:Kirchhausen T, Owen D, Harrison SC (May 2014).
8:
380:Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology
945:
935:
891:
842:
832:
791:
742:
693:
644:
592:
543:
502:
450:
440:
399:
345:
335:
291:
223:
913:
911:
233:Current Opinion in Structural Biology
7:
472:
470:
369:
367:
365:
313:
311:
269:
267:
265:
815:Ghosh P, Kornfeld S (March 2003).
25:
55:. It is a stable complex of four
1:
1014:Adaptor models and structures
971:Retinal Degenerative Diseases
293:10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00735-3
245:10.1016/S0959-440X(00)00071-3
1034:Vesicular transport proteins
1029:Peripheral membrane proteins
979:10.1007/978-3-319-75402-4_74
872:The Journal of Cell Biology
821:The Journal of Cell Biology
625:The Journal of Cell Biology
392:10.1101/cshperspect.a016725
1050:
784:10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.047
545:10.1016/j.cell.2004.08.017
142:form the endocytic coat.
70:clathrin-coated vesicles
47:to internalize cargo in
937:10.1073/pnas.1315110110
735:10.1126/science.1188462
585:10.1093/emboj/16.9.2240
258:(subscription required)
686:10.1038/emboj.2009.248
133:
32:
884:10.1083/jcb.200111068
834:10.1083/jcb.200211080
637:10.1083/jcb.201608071
131:
30:
930:(42): 17071–17076.
729:(5983): 1281–1284.
442:10.7554/eLife.50003
337:10.7554/eLife.32242
37:AP2 adaptor complex
134:
43:that works on the
33:
988:978-3-319-75401-7
680:(20): 3103–3116.
495:10.1111/tra.12677
173:Medical Relevance
16:(Redirected from
1041:
1001:
1000:
966:
960:
959:
949:
939:
915:
906:
905:
895:
863:
857:
856:
846:
836:
812:
806:
805:
795:
763:
757:
756:
746:
714:
708:
707:
697:
674:The EMBO Journal
665:
659:
658:
648:
616:
607:
606:
596:
579:(9): 2240–2250.
573:The EMBO Journal
564:
558:
557:
547:
523:
517:
516:
506:
474:
465:
464:
454:
444:
420:
414:
413:
403:
371:
360:
359:
349:
339:
315:
306:
305:
295:
271:
260:
259:
256:
228:
39:is a multimeric
21:
1049:
1048:
1044:
1043:
1042:
1040:
1039:
1038:
1019:
1018:
1010:
1005:
1004:
989:
968:
967:
963:
917:
916:
909:
865:
864:
860:
814:
813:
809:
765:
764:
760:
716:
715:
711:
667:
666:
662:
618:
617:
610:
566:
565:
561:
525:
524:
520:
489:(10): 741–751.
476:
475:
468:
422:
421:
417:
373:
372:
363:
317:
316:
309:
273:
272:
263:
257:
230:
229:
225:
220:
188:
175:
166:
157:
148:
139:
122:
62:internalisation
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1047:
1045:
1037:
1036:
1031:
1021:
1020:
1017:
1016:
1009:
1008:External links
1006:
1003:
1002:
987:
961:
907:
878:(5): 791–795.
858:
827:(5): 699–708.
807:
778:(3): 495–507.
758:
709:
660:
631:(1): 167–179.
608:
559:
538:(5): 591–605.
518:
466:
415:
386:(5): a016725.
361:
307:
286:(4): 523–535.
261:
239:(2): 220–228.
222:
221:
219:
216:
215:
214:
209:
204:
199:
194:
187:
184:
174:
171:
165:
162:
156:
153:
147:
144:
138:
135:
121:
118:
117:
116:
115:
114:
108:
102:
96:
90:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1046:
1035:
1032:
1030:
1027:
1026:
1024:
1015:
1012:
1011:
1007:
998:
994:
990:
984:
980:
976:
972:
965:
962:
957:
953:
948:
943:
938:
933:
929:
925:
921:
914:
912:
908:
903:
899:
894:
889:
885:
881:
877:
873:
869:
862:
859:
854:
850:
845:
840:
835:
830:
826:
822:
818:
811:
808:
803:
799:
794:
789:
785:
781:
777:
773:
769:
762:
759:
754:
750:
745:
740:
736:
732:
728:
724:
720:
713:
710:
705:
701:
696:
691:
687:
683:
679:
675:
671:
664:
661:
656:
652:
647:
642:
638:
634:
630:
626:
622:
615:
613:
609:
604:
600:
595:
590:
586:
582:
578:
574:
570:
563:
560:
555:
551:
546:
541:
537:
533:
529:
522:
519:
514:
510:
505:
500:
496:
492:
488:
484:
480:
473:
471:
467:
462:
458:
453:
448:
443:
438:
434:
430:
426:
419:
416:
411:
407:
402:
397:
393:
389:
385:
381:
377:
370:
368:
366:
362:
357:
353:
348:
343:
338:
333:
329:
325:
321:
314:
312:
308:
303:
299:
294:
289:
285:
281:
277:
270:
268:
266:
262:
254:
250:
246:
242:
238:
234:
227:
224:
217:
213:
210:
208:
205:
203:
200:
198:
195:
193:
190:
189:
185:
183:
181:
172:
170:
163:
161:
154:
152:
145:
143:
136:
130:
126:
119:
112:
109:
106:
103:
100:
97:
94:
91:
88:
85:
84:
82:
81:
80:
77:
75:
71:
67:
63:
58:
54:
50:
46:
45:cell membrane
42:
38:
29:
19:
970:
964:
927:
923:
875:
871:
861:
824:
820:
810:
775:
771:
761:
726:
722:
712:
677:
673:
663:
628:
624:
576:
572:
562:
535:
531:
521:
486:
482:
432:
428:
418:
383:
379:
327:
323:
283:
279:
236:
232:
226:
176:
167:
164:Deactivation
158:
149:
140:
123:
78:
36:
34:
31:AP-2 complex
18:AP2 adaptors
192:Amphiphysin
74:endocytosis
53:endocytosis
1023:Categories
435:: e50003.
330:: e32242.
218:References
155:Activation
146:Regulation
95:(α unit 2)
89:(α unit 1)
83:complex 2
72:and their
51:-mediated
212:Muniscins
120:Structure
997:29721994
956:24067654
902:11877457
853:12604586
802:22863004
753:20448150
704:19713939
655:28003333
554:15339664
513:31313456
461:31464684
410:24789820
356:29345618
302:12086608
253:10753805
186:See also
137:Function
113:(σ unit)
107:(μ unit)
101:(β unit)
66:clathrin
57:adaptins
49:clathrin
947:3801056
893:2173304
844:2173368
793:3413093
744:2883440
723:Science
695:2771086
646:5223608
603:9171339
594:1169826
504:6774827
483:Traffic
452:6739873
401:3996469
347:5785209
41:protein
995:
985:
954:
944:
900:
890:
851:
841:
800:
790:
751:
741:
702:
692:
653:
643:
601:
591:
552:
511:
501:
459:
449:
408:
398:
354:
344:
300:
251:
207:Exomer
429:eLife
324:eLife
202:Epsin
197:AP180
111:AP2S1
105:AP2M1
99:AP2B1
93:AP2A2
87:AP2A1
993:PMID
983:ISBN
952:PMID
898:PMID
849:PMID
798:PMID
772:Cell
749:PMID
700:PMID
651:PMID
599:PMID
550:PMID
532:Cell
509:PMID
457:PMID
406:PMID
352:PMID
298:PMID
280:Cell
249:PMID
35:The
975:doi
942:PMC
932:doi
928:110
888:PMC
880:doi
876:156
839:PMC
829:doi
825:160
788:PMC
780:doi
776:150
739:PMC
731:doi
727:328
690:PMC
682:doi
641:PMC
633:doi
629:216
589:PMC
581:doi
540:doi
536:118
499:PMC
491:doi
447:PMC
437:doi
396:PMC
388:doi
342:PMC
332:doi
288:doi
284:109
241:doi
180:LC3
1025::
991:.
981:.
950:.
940:.
926:.
922:.
910:^
896:.
886:.
874:.
870:.
847:.
837:.
823:.
819:.
796:.
786:.
774:.
770:.
747:.
737:.
725:.
721:.
698:.
688:.
678:28
676:.
672:.
649:.
639:.
627:.
623:.
611:^
597:.
587:.
577:16
575:.
571:.
548:.
534:.
530:.
507:.
497:.
487:20
485:.
481:.
469:^
455:.
445:.
431:.
427:.
404:.
394:.
382:.
378:.
364:^
350:.
340:.
326:.
322:.
310:^
296:.
282:.
278:.
264:^
247:.
237:10
235:.
76:.
999:.
977::
958:.
934::
904:.
882::
855:.
831::
804:.
782::
755:.
733::
706:.
684::
657:.
635::
605:.
583::
556:.
542::
515:.
493::
463:.
439::
433:8
412:.
390::
384:6
358:.
334::
328:7
304:.
290::
255:.
243::
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.