1265:, and it becomes more difficult for it to activate in future. This mechanism prevents inappropriate responses to self, as self-peptides will not usually be presented with suitable co-stimulation. Once a T cell has been appropriately activated (i.e. has received signal one and signal two) it alters its cell surface expression of a variety of proteins. Markers of T cell activation include CD69, CD71 and CD25 (also a marker for Treg cells), and HLA-DR (a marker of human T cell activation). CTLA-4 expression is also up-regulated on activated T cells, which in turn outcompetes CD28 for binding to the B7 proteins. This is a checkpoint mechanism to prevent over activation of the T cell. Activated T cells also change their cell surface glycosylation profile.
513:β-selection is the first checkpoint, where thymocytes that are able to form a functional pre-TCR (with an invariant alpha chain and a functional beta chain) are allowed to continue development in the thymus. Next, positive selection checks that thymocytes have successfully rearranged their TCRα locus and are capable of recognizing MHC molecules with appropriate affinity. Negative selection in the medulla then eliminates thymocytes that bind too strongly to self-antigens expressed on MHC molecules. These selection processes allow for tolerance of self by the immune system. Typical naive T cells that leave the thymus (via the corticomedullary junction) are self-restricted, self-tolerant, and single positive.
40:
1383:(Caspase activation and recruitment domains) domains; that then binds TRAF6, which is ubiquitinated at K63. This form of ubiquitination does not lead to degradation of target proteins. Rather, it serves to recruit NEMO, IKKα and -β, and TAB1-2/ TAK1. TAK 1 phosphorylates IKK-β, which then phosphorylates IκB allowing for K48 ubiquitination: leads to proteasomal degradation. Rel A and p50 can then enter the nucleus and bind the NF-κB response element. This coupled with NFAT signaling allows for complete activation of the IL-2 gene.
768:
1442:
901:) differ from the other memory subsets in that they do not originate following a strong clonal expansion event. Thus, although this population as a whole is abundant within the peripheral circulation, individual virtual memory T cell clones reside at relatively low frequencies. One theory is that homeostatic proliferation gives rise to this T cell population. Although CD8 virtual memory T cells were the first to be described, it is now known that CD4 virtual memory cells also exist.
1719:
studies have suggested that it is possible to predict relapse of leukemia based on expression of inhibitory receptors PD-1 and TIM-3 by T cells. Many experiments and clinical trials have focused on immune checkpoint blockers in cancer therapy, with some of these approved as valid therapies that are now in clinical use. Inhibitory receptors targeted by those medical procedures are vital in T cell exhaustion and blocking them can reverse these changes.
551:
403:α-chain, signals are produced which cease rearrangement of the β-chain (and silence the alternate allele). Although these signals require the pre-TCR at the cell surface, they are independent of ligand binding to the pre-TCR. If the chains successfully pair a pre-TCR forms, and the cell downregulates CD25 and is termed a DN4 cell (CD25CD44). These cells then undergo a round of proliferation, and begin to re-arrange the TCRα locus during the
999:
recognition of peptide antigens in the context of the MHC molecule. Overall, there are three large populations of unconventional T cells: NKT cells, MAIT cells, and gammadelta T cells. Now, their functional roles are already being well established in the context of infections and cancer. Furthermore, these T cell subsets are being translated into many therapies against malignancies such as leukemia, for example.
1166:
52:
1594:
378:
must be tested to make sure they work at all. First, the thymocytes attempt to create a functional beta chain, testing it against a 'mock' alpha chain. Then they attempt to create a functional alpha chain. Once a working TCR has been produced, the cells then must test if their TCR will identify threats correctly, and to do this it is required to recognize the body’s
818:
thought to belong to either the effector or central memory subtypes, each with their own distinguishing set of cell surface markers (see below). Subsequently, numerous new populations of memory T cells were discovered including tissue-resident memory T (Trm) cells, stem memory TSCM cells, and virtual memory T cells. The single unifying theme for all
1233:, like dendritic cells, B cells, and macrophages, to name a few. The peptides presented to CD8 T cells by MHC class I molecules are 8–13 amino acids in length; the peptides presented to CD4 cells by MHC class II molecules are longer, usually 12–25 amino acids in length, as the ends of the binding cleft of the MHC class II molecule are open.
1119:. In rabbits, sheep, and chickens, the number of γδ T cells can be as high as 60% of total T cells. The antigenic molecules that activate γδ T cells are still mostly unknown. However, γδ T cells are not MHC-restricted and seem to be able to recognize whole proteins rather than requiring peptides to be presented by MHC molecules on
1690:
encounter anti-inflammatory cytokines and pro-apoptotic proteins take over to protect the body from damage. Sepsis also carries high antigen load and inflammation. In this stage of sepsis T cell exhaustion increases. Currently there are studies aiming to utilize inhibitory receptor blockades in treatment of sepsis.
1699:
role in tolerance of a graft mainly by depletion of alloreactive CD8 T cells. Several studies showed positive effect of chronic infection on graft acceptance and its long-term survival mediated partly by T cell exhaustion. It was also shown that recipient T cell exhaustion provides sufficient conditions for
1698:
While during infection T cell exhaustion can develop following persistent antigen exposure after graft transplant similar situation arises with alloantigen presence. It was shown that T cell response diminishes over time after kidney transplant. These data suggest T cell exhaustion plays an important
521:
About 98% of thymocytes die during the development processes in the thymus by failing either positive selection or negative selection, whereas the other 2% survive and leave the thymus to become mature immunocompetent T cells. The thymus contributes fewer cells as a person ages. As the thymus shrinks
1689:
cells can be a source of IL-10 and TGF-β and therefore they can play a role in T cell exhaustion. Furthermore, T cell exhaustion is reverted after depletion of Treg cells and blockade of PD1. T cell exhaustion can also occur during sepsis as a result of cytokine storm. Later after the initial septic
1664:
T cell exhaustion can be triggered by several factors like persistent antigen exposure and lack of CD4 T cell help. Antigen exposure also has effect on the course of exhaustion because longer exposure time and higher viral load increases the severity of T cell exhaustion. At least 2–4 weeks exposure
1355:
into the cytosol. Low calcium in the endoplasmic reticulum causes STIM1 clustering on the ER membrane and leads to activation of cell membrane CRAC channels that allows additional calcium to flow into the cytosol from the extracellular space. This aggregated cytosolic calcium binds calmodulin, which
1718:
During cancer T cell exhaustion plays a role in tumor protection. According to research some cancer-associated cells as well as tumor cells themselves can actively induce T cell exhaustion at the site of tumor. T cell exhaustion can also play a role in cancer relapses as was shown on leukemia. Some
817:
after they encounter their cognate antigen within the context of an MHC molecule on the surface of a professional antigen presenting cell (e.g. a dendritic cell). Appropriate co-stimulation must be present at the time of antigen encounter for this process to occur. Historically, memory T cells were
530:
T cells are grouped into a series of subsets based on their function. CD4 and CD8 T cells are selected in the thymus, but undergo further differentiation in the periphery to specialized cells which have different functions. T cell subsets were initially defined by function, but also have associated
1421:
on their cell surface and although the T cell antigen receptor can interact with at least a subset of these self pMHC, the T cell generally ignores these healthy cells. However, when these very same cells contain even minute quantities of pathogen derived pMHC, T cells are able to become activated
459:
Negative selection removes thymocytes that are capable of strongly binding with "self" MHC molecules. Thymocytes that survive positive selection migrate towards the boundary of the cortex and medulla in the thymus. While in the medulla, they are again presented with a self-antigen presented on the
402:
and constant region genes in an attempt to create a functional TCRβ chain. As the developing thymocyte progresses through to the DN3 stage (CD44CD25), the thymocyte expresses an invariant α-chain called pre-Tα alongside the TCRβ gene. If the rearranged β-chain successfully pairs with the invariant
377:
A thymocyte can only become an active T cell when it survives the process of developing a functional TCR. The TCR consists of two major components, the alpha and beta chains. These both contain random elements designed to produce a wide variety of different TCRs, but due to this huge variety they
1225:
production. Optimal CD8 T cell response relies on CD4 signalling. CD4 cells are useful in the initial antigenic activation of naive CD8 T cells, and sustaining memory CD8 T cells in the aftermath of an acute infection. Therefore, activation of CD4 T cells can be beneficial to the action of CD8 T
822:
subtypes is that they are long-lived and can quickly expand to large numbers of effector T cells upon re-exposure to their cognate antigen. By this mechanism they provide the immune system with "memory" against previously encountered pathogens. Memory T cells may be either CD4 or CD8 and usually
1627:
T cell exhaustion is a poorly defined or ambiguous term. There are three approaches to its definition. "The first approach primarily defines as exhausted the cells that present the same cellular dysfunction (typically, the absence of an expected effector response). The second approach primarily
427:
on MHC molecules, which reside on the surface of cortical epithelial cells. Only thymocytes that interact well with MHC-I or MHC-II will receive a vital "survival signal", while those that cannot interact strongly enough will receive no signal and die from neglect. This process ensures that the
945:
Regulatory T cells can develop either during normal development in the thymus, and are then known as thymic Treg cells, or can be induced peripherally and are called peripherally derived Treg cells. These two subsets were previously called "naturally occurring" and "adaptive" (or "induced"),
998:
represent some subsets of T cells that behave differently in immunity. They trigger rapid immune responses, regardless of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) expression, unlike their conventional counterparts (CD4 T helper cells and CD8 cytotoxic T cells), which are dependent on the
203:. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the
1628:
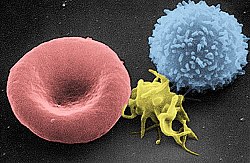
defines as exhausted the cells that are produced by a given cause (typically, but not necessarily, chronic exposure to an antigen). Finally, the third approach primarily defines as exhausted the cells that present the same molecular markers (typically, programmed cell death protein 1 )."
1111:(γδ T cells) represent a small subset of T cells which possess a γδ TCR rather than the αβ TCR on the cell surface. The majority of T cells express αβ TCR chains. This group of T cells is much less common in humans and mice (about 2% of total T cells) and are found mostly in the gut
5645:
Liu L, Chang YJ, Xu LP, Zhang XH, Wang Y, Liu KY, Huang XJ (May 2018). "T cell exhaustion characterized by compromised MHC class I and II restricted cytotoxic activity associates with acute B lymphoblastic leukemia relapse after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation".
1386:
While in most cases activation is dependent on TCR recognition of antigen, alternative pathways for activation have been described. For example, cytotoxic T cells have been shown to become activated when targeted by other CD8 T cells leading to tolerization of the latter.
1127:γδ T cells recognize MHC class IB molecules. Human γδ T cells that use the Vγ9 and Vδ2 gene fragments constitute the major γδ T cell population in peripheral blood. These cells are unique in that they specifically and rapidly respond to a set of nonpeptidic phosphorylated
1036:. Once activated, these cells can perform functions ascribed to both helper and cytotoxic T cells: cytokine production and release of cytolytic/cell killing molecules. They are also able to recognize and eliminate some tumor cells and cells infected with herpes viruses.
428:
surviving thymocytes will have an 'MHC affinity' that means they can serve useful functions in the body, responding to MHC molecules to assist immune responses. The vast majority of developing thymocytes will not pass positive selection, and die during this process.
2202:
Pekalski ML, García AR, Ferreira RC, Rainbow DB, Smyth DJ, Mashar M, Brady J, Savinykh N, Dopico XC, Mahmood S, Duley S, Stevens HE, Walker NM, Cutler AJ, Waldron-Lynch F, Dunger DB, Shannon-Lowe C, Coles AJ, Jones JL, Wallace C, Todd JA, Wicker LS (August 2017).
1422:
and initiate immune responses. The ability of T cells to ignore healthy cells but respond when these same cells contain pathogen (or cancer) derived pMHC is known as antigen discrimination. The molecular mechanisms that underlie this process are controversial.
439:
molecules mature into CD8 "killer" cells. A thymocyte becomes a CD4 cell by down-regulating expression of its CD8 cell surface receptors. If the cell does not lose its signal, it will continue downregulating CD8 and become a CD4, both CD8 and CD4 cells are now
3595:
Kjer-Nielsen L, Patel O, Corbett AJ, Le Nours J, Meehan B, Liu L, Bhati M, Chen Z, Kostenko L, Reantragoon R, Williamson NA, Purcell AW, Dudek NL, McConville MJ, O'Hair RA, Khairallah GN, Godfrey DI, Fairlie DP, Rossjohn J, McCluskey J (November 2012).
488:
molecules (positively selected CD4 cells must interact with these MHC class II molecules, thus APCs, which possess MHC class II, must be present for CD4 T-cell negative selection). Thymocytes that interact too strongly with the self-antigen receive an
5452:
Woo SR, Turnis ME, Goldberg MV, Bankoti J, Selby M, Nirschl CJ, Bettini ML, Gravano DM, Vogel P, Liu CL, Tangsombatvisit S, Grosso JF, Netto G, Smeltzer MP, Chaux A, Utz PJ, Workman CJ, Pardoll DM, Korman AJ, Drake CG, Vignali DA (February 2012).
264:" response. For this reason, these regulatory T cells have also been called "suppressor" T cells. These same regulatory T cells can also be co-opted by cancer cells to prevent the recognition of, and an immune response against, tumor cells.
1703:
transfer. While there are data showing that induction of T cell exhaustion can be beneficial for transplantation it also carries disadvantages among which can be counted increased number of infections and the risk of tumor development.
369:
A critical step in T cell maturation is making a functional T cell receptor (TCR). Each mature T cell will ultimately contain a unique TCR that reacts to a random pattern, allowing the immune system to recognize many different types of
1339:); PI3K also acts on PIP2, phosphorylating it to produce phosphatidlyinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3). DAG binds and activates some PKCs. Most important in T cells is PKC-θ, critical for activating the transcription factors
798:
molecules, present on the surface of all nucleated cells. Cytotoxic T cells also produce the key cytokines IL-2 and IFNγ. These cytokines influence the effector functions of other cells, in particular macrophages and NK cells.
5353:
Shi XL, de Mare-Bredemeijer EL, Tapirdamaz Ö, Hansen BE, van Gent R, van
Campenhout MJ, Mancham S, Litjens NH, Betjes MG, van der Eijk AA, Xia Q, van der Laan LJ, de Jonge J, Metselaar HJ, Kwekkeboom J (September 2015).
1236:
The second signal comes from co-stimulation, in which surface receptors on the APC are induced by a relatively small number of stimuli, usually products of pathogens, but sometimes breakdown products of cells, such as
522:
by about 3% a year throughout middle age, a corresponding fall in the thymic production of naive T cells occurs, leaving peripheral T cell expansion and regeneration to play a greater role in protecting older people.
374:. This process is essential in developing immunity to threats that the immune system has not encountered before, since due to random variation there will always be at least one TCR to match any new pathogen.
297:. The process of differentiation then proceeds to a common lymphoid progenitor (CLP), which can only differentiate into T, B or NK cells. These CLP cells then migrate via the blood to the thymus, where they
1147:) and corresponding mononucleotide conjugates, in addition to IPP and DMAPP. Plant cells produce both types of phosphoantigens. Drugs activating human Vγ9/Vδ2 T cells comprise synthetic phosphoantigens and
1631:
Dysfunctional T cells are characterized by progressive loss of function, changes in transcriptional profiles and sustained expression of inhibitory receptors. At first, cells lose their ability to produce
2806:
Marusina AI, Ono Y, Merleev AA, Shimoda M, Ogawa H, Wang EA, Kondo K, Olney L, Luxardi G, Miyamura Y, Yilma TD, Villalobos IB, Bergstrom JW, Kronenberg DG, Soulika AM, Adamopoulos IE, Maverakis E (2017).
1417:
A unique feature of T cells is their ability to discriminate between healthy and abnormal (e.g. infected or cancerous) cells in the body. Healthy cells typically express a large number of self derived
234:, to recruit other types of cells when mounting an immune response. A different population of T cells, the CD4+ T cells, function as "helper cells". Unlike CD8+ killer T cells, the CD4+ helper T (T
5080:
Wei Z, Li P, Yao Y, Deng H, Yi S, Zhang C, Wu H, Xie X, Xia M, He R, Yang XP, Tang ZH (July 2018). "Alpha-lactose reverses liver injury via blockade of Tim-3-mediated CD8 apoptosis in sepsis".
3403:
Bianchini E, De Biasi S, Simone AM, Ferraro D, Sola P, Cossarizza A, Pinti M (March 2017). "Invariant natural killer T cells and mucosal-associated invariant T cells in multiple sclerosis".
1169:
The T lymphocyte activation pathway: T cells contribute to immune defenses in two major ways; some direct and regulate immune responses; others directly attack infected or cancerous cells.
1272:
exists as a complex of several proteins. The actual T cell receptor is composed of two separate peptide chains, which are produced from the independent T cell receptor alpha and beta (
612:
that regulate or assist the immune response. These cells can differentiate into one of several subtypes, which have different roles. Cytokines direct T cells into particular subtypes.
1640:, which is followed by the loss of high proliferative capacity and cytotoxic potential, and eventually leads to their deletion. Exhausted T cells typically indicate higher levels of
3706:
Janssen EM, Lemmens EE, Wolfe T, Christen U, von
Herrath MG, Schoenberger SP (February 2003). "CD4+ T cells are required for secondary expansion and memory in CD8+ T lymphocytes".
975:
cells, which are thought to originate during an immune response and act by producing suppressive molecules. Tr1 cells are associated with IL-10, and Th3 cells are associated with
2856:
Abbas AK, Benoist C, Bluestone JA, Campbell DJ, Ghosh S, Hori S, Jiang S, Kuchroo VK, Mathis D, Roncarolo MG, Rudensky A, Sakaguchi S, Shevach EM, Vignali DA, Ziegler SF (2013).
1078:
bacterially-infected cells. MAIT cells can also be activated through MR1-independent signaling. In addition to possessing innate-like functions, this T cell subset supports the
320:
co-receptor. The newly arrived CLP cells are CD4CD8CD44CD25ckit cells, and are termed early thymic progenitor (ETP) cells. These cells will then undergo a round of division and
5271:
de Mare-Bredemeijer EL, Shi XL, Mancham S, van Gent R, van der Heide-Mulder M, de Boer R, Heemskerk MH, de Jonge J, van der Laan LJ, Metselaar HJ, Kwekkeboom J (August 2015).
6254:
5033:"Frontline Science: Defects in immune function in patients with sepsis are associated with PD-1 or PD-L1 expression and can be restored by antibodies targeting PD-1 or PD-L1"
4933:
Boomer JS, To K, Chang KC, Takasu O, Osborne DF, Walton AH, Bricker TL, Jarman SD, Kreisel D, Krupnick AS, Srivastava A, Swanson PE, Green JM, Hotchkiss RS (December 2011).
2277:
Haynes BF, Markert ML, Sempowski GD, Patel DD, Hale LP (2000). "The role of the thymus in immune reconstitution in aging, bone marrow transplantation, and HIV-1 infection".
5172:
Halloran PF, Chang J, Famulski K, Hidalgo LG, Salazar ID, Merino Lopez M, Matas A, Picton M, de
Freitas D, Bromberg J, Serón D, Sellarés J, Einecke G, Reeve J (July 2015).
2809:"CD4+ virtual memory: Antigen-inexperienced T cells reside in the naïve, regulatory, and memory T cell compartments at similar frequencies, implications for autoimmunity"
230:– this means that they are able to directly kill virus-infected cells, as well as cancer cells. CD8+ T cells are also able to use small signalling proteins, known as
4830:
Penaloza-MacMaster P, Kamphorst AO, Wieland A, Araki K, Iyer SS, West EE, O'Mara L, Yang S, Konieczny BT, Sharpe AH, Freeman GJ, Rudensky AY, Ahmed R (August 2014).
1656:. Exhaustion can develop during chronic infections, sepsis and cancer. Exhausted T cells preserve their functional exhaustion even after repeated antigen exposure.
1285:
1261:
and ICOS, but these largely depend upon CD28 for their expression. The second signal licenses the T cell to respond to an antigen. Without it, the T cell becomes
1229:
The first signal is provided by binding of the T cell receptor to its cognate peptide presented on MHCII on an APC. MHCII is restricted to so-called professional
133:
2505:
Sallusto F, Lenig D, Förster R, Lipp M, Lanzavecchia A (1999). "Two subsets of memory T lymphocytes with distinct homing potentials and effector functions".
1368:
that activates the transcription of a pleiotropic set of genes, most notable, IL-2, a cytokine that promotes long-term proliferation of activated T cells.
386:, called negative selection. If both positive and negative selection are successful, the TCR becomes fully operational and the thymocyte becomes a T cell.
3856:
Jennifer
Rolland and Robyn O'Hehir, "Turning off the T cells: Peptides for treatment of allergic Diseases," Today's life science publishing, 1999, Page 32
246:
cell depends on its subtype (such as T-helper1, T-helper2, T-helper17, regulatory T-cell), which is distinguished by the types of cytokines they secrete.
2606:
5312:
Gassa A, Jian F, Kalkavan H, Duhan V, Honke N, Shaabani N, Friedrich SK, Dolff S, Wahlers T, Kribben A, Hardt C, Lang PA, Witzke O, Lang KS (2016).
260:
are able to distinguish invading cells from "self". This prevents immune cells from inappropriately reacting against one's own cells, known as an "
6247:
5840:
1375:. DAG activates PKC-θ, which then phosphorylates CARMA1, causing it to unfold and function as a scaffold. The cytosolic domains bind an adapter
415:
The process of positive selection takes 3 to 4 days and occurs in the thymic cortex. Double-positive thymocytes (CD4/CD8) migrate deep into the
5356:"CMV Primary Infection Is Associated With Donor-Specific T Cell Hyporesponsiveness and Fewer Late Acute Rejections After Liver Transplantation"
5884:
5830:
4246:
3927:
2481:
1135:, which are produced by virtually all living cells. The most common phosphoantigens from animal and human cells (including cancer cells) are
3438:
Serriari NE, Eoche M, Lamotte L, Lion J, Fumery M, Marcelo P, Chatelain D, Barre A, Nguyen-Khac E, Lantz O, Dupas JL, Treiner E (May 2014).
3042:"Invariant and noninvariant natural killer T cells exert opposite regulatory functions on the immune response during murine schistosomiasis"
4442:"Hepatitis B Virus-Specific CD8+ T Cells Maintain Functional Exhaustion after Antigen Reexposure in an Acute Activation Immune Environment"
3040:
Mallevaey T, Fontaine J, Breuilh L, Paget C, Castro-Keller A, Vendeville C, Capron M, Leite-de-Moraes M, Trottein F, Faveeuw C (May 2007).
5273:"Cytomegalovirus-Induced Expression of CD244 after Liver Transplantation Is Associated with CD8+ T Cell Hyporesponsiveness to Alloantigen"
2011:"Distinct phases in the positive selection of CD8+ T cells distinguished by intrathymic migration and T-cell receptor signaling patterns"
6103:
1477:
1214:
1045:
4632:
Okagawa T, Konnai S, Nishimori A, Maekawa N, Goto S, Ikebuchi R, Kohara J, Suzuki Y, Yamada S, Kato Y, Murata S, Ohashi K (June 2018).
3986:
Milstein O, Hagin D, Lask A, Reich-Zeliger S, Shezen E, Ophir E, Eidelstein Y, Afik R, Antebi YE, Dustin ML, Reisner Y (January 2011).
1245:. The only co-stimulatory receptor expressed constitutively by naive T cells is CD28, so co-stimulation for these cells comes from the
6240:
1577:
4734:"Cell-intrinsic transforming growth factor-beta signaling mediates virus-specific CD8+ T cell deletion and viral persistence in vivo"
328:(DN1) cells. To become T cells, the thymocytes must undergo multiple DN stages as well as positive selection and negative selection.
2261:
1993:
1769:
461:
451:. The potentially autoimmune cells are removed by the following process of negative selection, which occurs in the thymic medulla.
877:
stands for terminally differentiated effector memory cells re-expressing CD45RA, which is a marker usually found on naive T cells.
6586:
6139:
1728:
1465:
1316:
1029:
424:
379:
140:
5730:
5683:"PD-1(hi)TIM-3(+) T cells associate with and predict leukemia relapse in AML patients post allogeneic stem cell transplantation"
5174:"Disappearance of T Cell-Mediated Rejection Despite Continued Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Late Kidney Transplant Recipients"
4832:"Interplay between regulatory T cells and PD-1 in modulating T cell exhaustion and viral control during chronic LCMV infection"
1682:
554:
Depiction of the various key subsets of CD4-positive T cells with corresponding associated cytokines and transcription factors.
2946:
Godfrey DI, Uldrich AP, McCluskey J, Rossjohn J, Moody DB (November 2015). "The burgeoning family of unconventional T cells".
6581:
3943:
Wu H, Arron JR (November 2003). "TRAF6, a molecular bridge spanning adaptive immunity, innate immunity and osteoimmunology".
1572:
1305:
880:
1473:
854:
and in the peripheral circulation. (Note- CD44 expression is usually used to distinguish murine naive from memory T cells).
505:
and serves to prevent the formation of self-reactive T cells that are capable of inducing autoimmune diseases in the host.
6524:
6062:
1485:
839:
395:
382:(MHC) in a process known as positive selection. The thymocyte must also ensure that it does not react adversely to "self"
128:
3196:
Eckle SB, Corbett AJ, Keller AN, Chen Z, Godfrey DI, Liu L, Mak JY, Fairlie DP, Rossjohn J, McCluskey J (December 2015).
2153:
1776:. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. 17 June 2001. Archived from
1493:
6184:
6154:
6134:
1685:
are also able to trigger exhaustion. Last known factors that can play a role in T cell exhaustion are regulatory cells.
1257:
protein, (B7.1 and B7.2, respectively) on the APC. Other receptors are expressed upon activation of the T cell, such as
431:
A thymocyte's fate is determined during positive selection. Double-positive cells (CD4/CD8) that interact well with MHC
242:
and cytotoxic T cells, which leads to a larger immune response. The specific adaptive immune response regulated by the T
1460:
of T cells and/or defects on function of individual T cells. Complete insufficiency of T cell function can result from
873:. These memory T cells lack lymph node-homing receptors and are thus found in the peripheral circulation and tissues. T
6172:
6167:
6007:
5455:"Immune inhibitory molecules LAG-3 and PD-1 synergistically regulate T-cell function to promote tumoral immune escape"
5223:"Exhaustive differentiation of alloreactive CD8+ T cells: critical for determination of graft acceptance or rejection"
1637:
1522:
1395:
1312:
1301:
1140:
782:
cells, CTLs, T-killer cells, killer T cells) destroy virus-infected cells and tumor cells, and are also implicated in
719:
1653:
5502:
Zelle-Rieser C, Thangavadivel S, Biedermann R, Brunner A, Stoitzner P, Willenbacher E, et al. (November 2016).
6410:
1554:
1391:
1331:. PLC-γ cleaves PI(4,5)P2 on the inner leaflet of the membrane to create the active intermediaries diacylglycerol (
1210:
1116:
1091:
887:) occupy tissues (skin, lung, etc.) without recirculating. One cell surface marker that has been associated with T
5877:
1559:
1328:
1202:
1136:
1070:
metabolites to MAIT cells. After the presentation of foreign antigen by MR1, MAIT cells secrete pro-inflammatory
967:
Several other types of T cells have suppressive activity, but do not express FOXP3 constitutively. These include
923:. Their major role is to shut down T cell–mediated immunity toward the end of an immune reaction and to suppress
3757:
Shedlock DJ, Shen H (April 2003). "Requirement for CD4 T cell help in generating functional CD8 T cell memory".
1665:
is needed to establish exhaustion. Another factor able to induce exhaustion are inhibitory receptors including
1120:
968:
278:
188:
169:
116:
104:
3810:"CD4+ T cells are required for the maintenance, not programming, of memory CD8+ T cells after acute infection"
5970:
4036:
3866:
Maverakis E, Kim K, Shimoda M, Gershwin M, Patel F, Wilken R, Raychaudhuri S, Ruhaak LR, Lebrilla CB (2015).
6590:
6348:
6211:
5757:"Control of Toxoplasma reactivation by rescue of dysfunctional CD8+ T-cell response via PD-1-PDL-1 blockade"
1666:
1406:
1230:
1190:
920:
790:
protein on their cell surface. Cytotoxic T cells recognize their targets by binding to short peptides (8-11
605:
481:
1822:
1402:
mission to study how "deficiencies in the human immune system are affected by a microgravity environment".
767:
39:
6693:
6612:
6330:
6266:
6054:
4262:
2363:"T Helper (Th) Cell Profiles in Pregnancy and Recurrent Pregnancy Losses: Th1/Th2/Th9/Th17/Th22/Tfh Cells"
1500:
1336:
1079:
1021:
894:
289:. The HSC then differentiate into multipotent progenitors (MPP) which retain the potential to become both
4542:"Progressive loss of memory T cell potential and commitment to exhaustion during chronic viral infection"
1602:
1347:
is released from the membrane by PLC-γ and diffuses rapidly to activate calcium channel receptors on the
6559:
6415:
6393:
6093:
6070:
6046:
5555:"Cancer-associated fibroblasts induce antigen-specific deletion of CD8 T Cells to protect tumour cells"
1489:
1348:
1344:
1013:
1008:
286:
181:
1284:
proteins: CD3εγ and CD3εδ heterodimers and, most important, a CD3ζ homodimer, which has a total of six
1082:
immune response and has a memory-like phenotype. Furthermore, MAIT cells are thought to play a role in
394:
At the DN2 stage (CD44CD25), cells upregulate the recombination genes RAG1 and RAG2 and re-arrange the
5851:
3658:
2205:"Neonatal and adult recent thymic emigrants produce IL-8 and express complement receptors CR1 and CR2"
121:
6688:
6576:
6509:
6420:
6344:
6117:
5934:
5870:
5768:
5566:
5405:"Recipient T Cell Exhaustion and Successful Adoptive Transfer of Haploidentical Natural Killer Cells"
4493:"CD4+ T cells are required to sustain CD8+ cytotoxic T-cell responses during chronic viral infection"
3766:
3715:
3612:
3500:
3305:"MR1-Restricted Mucosal-Associated Invariant T Cells and Their Activation during Infectious Diseases"
2907:"Modulation of autoimmune diseases by interleukin (IL)-17 producing regulatory T helper (Th17) cells"
2514:
2022:
1547:
1505:
1461:
1365:
1051:
1025:
947:
654:
Produce an inflammatory response, key for defense against intracellular bacteria, viruses and cancer.
465:
6232:
5610:
Conforti L (February 2012). "The ion channel network in T lymphocytes, a target for immunotherapy".
3489:"MR1 antigen presentation to mucosal-associated invariant T cells was highly conserved in evolution"
3356:"Mucosal-associated invariant T cells in autoimmunity, immune-mediated diseases and airways disease"
1441:
435:
molecules will eventually become CD4 "helper" cells, whereas thymocytes that interact well with MHC
6698:
6636:
6571:
6554:
6388:
6306:
6126:
5965:
3988:"CTLs respond with activation and granule secretion when serving as targets for T cell recognition"
1748:
1733:
1700:
1242:
1017:
924:
399:
210:
One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes:
3597:
6456:
6098:
6085:
5403:
Williams RL, Cooley S, Bachanova V, Blazar BR, Weisdorf DJ, Miller JS, Verneris MR (March 2018).
5385:
5253:
5105:
4881:"The late phase of sepsis is characterized by an increased microbiological burden and death rate"
4614:
4440:
Wang Q, Pan W, Liu Y, Luo J, Zhu D, Lu Y, Feng X, Yang X, Dittmer U, Lu M, Yang D, Liu J (2018).
3968:
3790:
3739:
3636:
3577:
3440:"Innate mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells are activated in inflammatory bowel diseases"
2989:
de Araújo ND, Gama FM, de Souza Barros M, Ribeiro TL, Alves FS, Xabregas LA, et al. (2021).
2971:
2887:
2639:
2587:
2538:
2184:
2152:
Hinterberger M, Aichinger M, Prazeres da Costa O, Voehringer D, Hoffmann R, Klein L (June 2010).
2134:
1352:
1108:
1103:
1087:
1083:
958:
4879:
Otto GP, Sossdorf M, Claus RA, Rödel J, Menge K, Reinhart K, Bauer M, Riedemann NC (July 2011).
1563:
2659:"Multiparameter flow cytometric analysis of CD4 and CD8 T cell subsets in young and old people"
2607:"Molecular signatures distinguish human central memory from effector memory CD8 T cell subsets"
1831:
T cells ... derive their from the organs in which they develop. T cells develop in the thymus
6504:
6270:
6149:
6030:
5949:
5929:
5826:
5796:
5712:
5663:
5627:
5592:
5535:
5484:
5434:
5377:
5335:
5294:
5245:
5203:
5154:
5097:
5062:
5013:
4964:
4912:
4861:
4812:
4763:
4714:
4665:
4606:
4571:
4522:
4473:
4422:
4373:
4324:
4242:
4236:
4194:
4145:
4093:
4017:
3960:
3923:
3897:
3839:
3782:
3731:
3688:
3628:
3569:
3528:
3469:
3420:
3385:
3336:
3280:
3229:
3178:
3129:
3071:
3022:
2963:
2928:
2879:
2838:
2788:
2739:
2690:
2631:
2579:
2530:
2487:
2477:
2446:
2394:
2343:
2294:
2257:
2234:
2176:
2126:
2085:
2068:
Starr TK, Jameson SC, Hogquist KA (2003-01-01). "Positive and negative selection of T cells".
2050:
1989:
1966:
1917:
1876:
1686:
1607:
1567:
1481:
1453:
1436:
916:
911:
578:
502:
249:
5504:"T cells in multiple myeloma display features of exhaustion and senescence at the tumor site"
4982:
Shindo Y, McDonough JS, Chang KC, Ramachandra M, Sasikumar PG, Hotchkiss RS (February 2017).
3684:
2081:
593:
glycoprotein on their surfaces. Helper T cells become activated when they are presented with
6683:
6624:
6564:
6536:
6531:
6499:
6486:
6476:
6022:
5998:
5786:
5776:
5702:
5694:
5655:
5619:
5582:
5574:
5525:
5515:
5474:
5466:
5424:
5416:
5367:
5325:
5284:
5237:
5222:
5193:
5185:
5144:
5136:
5089:
5052:
5044:
5003:
4995:
4954:
4946:
4902:
4892:
4851:
4843:
4802:
4794:
4753:
4745:
4704:
4696:
4655:
4645:
4598:
4561:
4553:
4512:
4504:
4463:
4453:
4412:
4404:
4363:
4355:
4314:
4304:
4184:
4176:
4135:
4127:
4083:
4073:
4007:
3999:
3952:
3887:
3879:
3829:
3821:
3774:
3723:
3680:
3620:
3559:
3518:
3508:
3459:
3451:
3412:
3375:
3367:
3326:
3316:
3270:
3260:
3219:
3209:
3198:"Recognition of Vitamin B Precursors and Byproducts by Mucosal Associated Invariant T Cells"
3168:
3160:
3119:
3109:
3061:
3053:
3012:
3002:
2955:
2918:
2869:
2828:
2820:
2778:
2770:
2729:
2721:
2680:
2670:
2621:
2569:
2522:
2469:
2436:
2428:
2384:
2374:
2333:
2325:
2286:
2224:
2216:
2168:
2116:
2077:
2040:
2030:
1956:
1948:
1907:
1866:
1856:
1743:
1713:
1372:
1281:
814:
783:
775:
762:
468:
positive (AIRE) to properly express self-antigens from all tissues of the body on their MHC
253:
211:
161:
1054:, effector-like qualities. In humans, MAIT cells are found in the blood, liver, lungs, and
6519:
6014:
1543:
1534:
1457:
1418:
1269:
1174:
1160:
1148:
1055:
972:
961:
364:
204:
177:
4342:
Blank CU, Haining WN, Held W, Hogan PG, Kallies A, Lugli E, et al. (November 2019).
4215:
2154:"Autonomous role of medullary thymic epithelial cells in central CD4(+) T cell tolerance"
1777:
5772:
5570:
5129:
Philosophical
Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences
4683:
Brooks DG, Trifilo MJ, Edelmann KH, Teyton L, McGavern DB, Oldstone MB (November 2006).
3770:
3719:
3616:
3504:
2518:
2026:
1937:"Impaired CD8 T cell memory and CD4 T cell primary responses in IL-7R alpha mutant mice"
6546:
6491:
6432:
6352:
6325:
5820:
5791:
5756:
5707:
5682:
5587:
5554:
5530:
5503:
5479:
5454:
5429:
5404:
5198:
5173:
5149:
5124:
5057:
5032:
5008:
4983:
4959:
4934:
4907:
4880:
4856:
4831:
4807:
4782:
4758:
4733:
4709:
4684:
4660:
4633:
4566:
4541:
4468:
4441:
4417:
4392:
4368:
4343:
4319:
4292:
4189:
4164:
4140:
4115:
4088:
4061:
4012:
3987:
3892:
3867:
3834:
3809:
3523:
3488:
3464:
3439:
3380:
3355:
3331:
3304:
3275:
3248:
3224:
3197:
3173:
3148:
3124:
3097:
3066:
3041:
3017:
2990:
2923:
2906:
2833:
2808:
2783:
2758:
2734:
2709:
2685:
2658:
2441:
2416:
2389:
2362:
2338:
2313:
2229:
2204:
2045:
2010:
1961:
1936:
1935:
Osborne LC, Dhanji S, Snow JW, Priatel JJ, Ma MC, Miners MJ, et al. (March 2007).
1871:
1844:
1678:
1469:
1201:. The signalling pathways downstream from co-stimulatory molecules usually engages the
1194:
1132:
477:
294:
57:
4517:
4492:
3487:
Huang S, Martin E, Kim S, Yu L, Soudais C, Fremont DH, Lantz O, Hansen TH (May 2009).
2121:
2105:"The MHC reactivity of the T cell repertoire prior to positive and negative selection"
2104:
1193:. Both are required for production of an effective immune response; in the absence of
550:
252:
are yet another distinct population of T cells that provide the critical mechanism of
51:
6677:
6514:
6403:
6221:
6203:
6041:
6003:
5924:
4508:
4408:
4116:"Quantitative challenges in understanding ligand discrimination by alphabeta T cells"
2290:
1633:
1511:
1222:
819:
808:
574:
558:
545:
493:
signal that leads to cell death. However, some of these cells are selected to become
336:
239:
215:
165:
80:
5257:
5109:
4618:
3972:
3794:
3581:
2975:
2891:
2643:
2591:
2188:
2138:
711:
Defense against helminths (parasitic worms) and cell-dependent allergic inflammation
281:(HSC) which reside in the bone marrow. In some cases, the origin might be the fetal
6481:
6466:
6461:
6398:
6296:
6036:
5939:
5389:
5031:
Patera AC, Drewry AM, Chang K, Beiter ER, Osborne D, Hotchkiss RS (December 2016).
3640:
2991:"Translating Unconventional T Cells and Their Roles in Leukemia Antitumor Immunity"
2542:
1399:
1254:
1028:. Unlike conventional T cells that recognize protein peptide antigens presented by
601:
501:, also known as recent thymic emigrants. This process is an important component of
498:
473:
448:
321:
290:
261:
257:
227:
75:
5681:
Kong Y, Zhang J, Claxton DF, Ehmann WC, Rybka WB, Zhu L, et al. (July 2015).
5470:
3743:
2468:. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Vol. 841. pp. 209–230.
673:
Immunologically important against extracellular pathogens, such as worm infections
5314:"IL-10 Induces T Cell Exhaustion During Transplantation of Virus Infected Hearts"
4749:
4309:
4131:
4003:
3164:
1912:
1895:
109:
6216:
5919:
5914:
5241:
3416:
2626:
2574:
2557:
2473:
1738:
1612:
1380:
1357:
1332:
1165:
1059:
795:
570:
298:
192:
173:
5761:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
5659:
5623:
5578:
5420:
5093:
3883:
3671:
Williams MA, Bevan MJ (2007-01-01). "Effector and memory CTL differentiation".
3493:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
2857:
2824:
2015:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
1803:
771:
Superresolution image of a group of cytotoxic T cells surrounding a cancer cell
17:
6604:
6357:
6263:
5893:
5520:
4999:
4650:
4359:
4078:
3249:"Mucosal-associated invariant T-cells: new players in anti-bacterial immunity"
2432:
2220:
2009:
Ross JO, Melichar HJ, Au-Yeung BB, Herzmark P, Weiss A, Robey EA (June 2014).
1649:
1324:
1308:, which allows the aggregation of signalling complexes around these proteins.
1128:
1067:
1063:
980:
866:
851:
843:
791:
582:
5289:
5272:
5048:
4458:
4180:
3321:
3265:
3114:
2774:
2379:
846:(CD62L). Central memory T cells also have intermediate to high expression of
747:
Pathogenesis of allergic airway diseases and predominantly anti-inflammatory
6662:
6367:
6189:
6144:
5992:
5781:
4935:"Immunosuppression in patients who die of sepsis and multiple organ failure"
4220:
3868:"Glycans in the immune system and The Altered Glycan Theory of Autoimmunity"
3778:
3513:
3214:
3098:"The Role of Mucosal Associated Invariant T Cells in Antimicrobial Immunity"
2035:
1297:
1173:
Activation of CD4 T cells occurs through the simultaneous engagement of the
700:
490:
302:
5800:
5716:
5667:
5631:
5596:
5539:
5488:
5438:
5381:
5339:
5298:
5249:
5207:
5189:
5158:
5140:
5101:
5066:
5017:
4968:
4950:
4916:
4865:
4816:
4767:
4718:
4669:
4610:
4575:
4477:
4426:
4377:
4328:
4198:
4149:
4097:
4021:
3964:
3901:
3843:
3786:
3735:
3692:
3632:
3573:
3532:
3473:
3424:
3389:
3340:
3284:
3233:
3182:
3149:"Mucosal associated invariant T cells and the immune response to infection"
3133:
3075:
3026:
3007:
2967:
2932:
2883:
2842:
2792:
2743:
2694:
2657:
Koch S, Larbi A, Derhovanessian E, Özcelik D, Naumova E, Pawelec G (2008).
2635:
2558:"Loss of CD45R and gain of UCHL1 reactivity is a feature of primed T cells"
2534:
2491:
2450:
2398:
2347:
2298:
2238:
2180:
2089:
2054:
1970:
1921:
1880:
4526:
2675:
2583:
2314:"APC-derived cytokines and T cell polarization in autoimmune inflammation"
2130:
1861:
331:
Double negative thymocytes can be identified by the surface expression of
6652:
6437:
6425:
6383:
6337:
6301:
5958:
5909:
4847:
4557:
3564:
3547:
3057:
1952:
1517:
1445:
1340:
1238:
1071:
976:
638:
609:
371:
231:
61:
5698:
5221:
Steger U, Denecke C, Sawitzki B, Karim M, Jones ND, Wood KJ (May 2008).
4293:"Immunological exhaustion: How to make a disparate concept operational?"
3727:
3624:
218:
T cells. (These are named for the presence of the cell surface proteins
6657:
6471:
6320:
6291:
6177:
3956:
1186:
1124:
643:
597:
594:
420:
383:
5372:
5355:
5330:
5313:
4798:
3455:
3371:
2725:
1032:(MHC) molecules, NKT cells recognize glycolipid antigens presented by
146:
6629:
6362:
6313:
5944:
5901:
5125:"The role of peripheral T-cell deletion in transplantation tolerance"
2329:
1670:
1539:
1262:
1198:
1144:
1112:
566:
416:
200:
196:
5731:"U.S. FDA Approved Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors and Immunotherapies"
5553:
Lakins MA, Ghorani E, Munir H, Martins CP, Shields JD (March 2018).
4897:
4602:
2959:
2905:
Singh B, Schwartz JA, Sandrock C, Bellemore SM, Nikoopour E (2013).
2874:
2605:
Willinger T, Freeman T, Hasegawa H, McMichael AJ, Callan MF (2005).
2172:
4700:
4540:
Angelosanto JM, Blackburn SD, Crawford A, Wherry EJ (August 2012).
3825:
1821:
Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P (2002).
1802:
Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P (2002).
308:
The earliest cells which arrived in the thymus are commonly termed
4685:"Interleukin-10 determines viral clearance or persistence in vivo"
3654:
2858:"Regulatory T cells: recommendations to simplify the nomenclature"
2526:
1440:
1376:
1293:
1218:
1182:
1164:
1075:
957:
gene can prevent regulatory T cell development, causing the fatal
950:
766:
649:
549:
282:
92:
2556:
Akbar AN, Terry L, Timms A, Beverley PC, Janossy G (April 1988).
1896:"One Niche to Rule Both Maintenance and Loss of Stemness in HSCs"
1143:(DMPP). Many microbes produce the active compound hydroxy-DMAPP (
199:
gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the
1674:
1645:
1641:
1361:
1320:
1258:
1250:
1246:
1206:
1185:) on the T cell by the major histocompatibility complex (MHCII)
1178:
1033:
870:
847:
824:
681:
494:
344:
6236:
5866:
2464:
Jia L, Wu C (2014). "The
Biology and Functions of Th22 Cells".
1476:. Causes of partial insufficiencies of T cell function include
813:
Antigen-naive T cells expand and differentiate into memory and
5862:
5822:
Immunobiology 5 : the immune system in health and disease
1587:
1289:
927:
that escaped the process of negative selection in the thymus.
787:
662:
590:
348:
340:
332:
317:
313:
223:
219:
5735:
Medical Writer Agency | 香港醫學作家 | MediPR | MediPaper Hong Kong
4732:
Tinoco R, Alcalde V, Yang Y, Sauer K, Zuniga EI (July 2009).
2361:
Wang W, Sung N, Gilman-Sachs A, Kwak-Kim J (18 August 2020).
1288:
motifs. The ITAM motifs on the CD3ζ can be phosphorylated by
565:
cells) assist other lymphocytes, including the maturation of
3598:"MR1 presents microbial vitamin B metabolites to MAIT cells"
1315:
recruits SLP-76 to the membrane, where it can then bring in
786:
rejection. These cells are defined by the expression of the
4393:"T-cell exhaustion: characteristics, causes and conversion"
1648:
and inhibitory receptors combined with lower expression of
447:
This process does not filter for thymocytes that may cause
5819:
Janeway Jr CA, Travers P, Walport M, Shlomchik MJ (2001).
4268:. The Leukemia & Lymphoma Society. May 2006. p. 2
1058:, defending against microbial activity and infection. The
953:
which can be used to identify the cells. Mutations of the
484:(APCs), allowing for presentation of self-antigens on MHC
4037:"SpaceX ready for CRS-3 Dragon launch and new milestones"
3096:
Napier RJ, Adams EJ, Gold MC, Lewinsohn DM (2015-07-06).
1499:
The main pathogens of concern in T cell deficiencies are
1488:(CBSs), and B cell and T cell combined disorders such as
946:
respectively. Both subsets require the expression of the
3548:"Bacteria, mucosal-associated invariant T cells and MR1"
1525:
are also more common and severe in T cell deficiencies.
608:(APCs). Once activated, they divide rapidly and secrete
351:
is expressed. Expression of both CD4 and CD8 makes them
1094:, although definitive evidence is yet to be published.
4781:
Veiga-Parga T, Sehrawat S, Rouse BT (September 2013).
4491:
Matloubian M, Concepcion RJ, Ahmed R (December 1994).
4165:"An induced rebinding model of antigen discrimination"
865:
cells) express CD45RO but lack expression of CCR7 and
5848:
National
Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
1066:, is responsible for presenting bacterially-produced
850:. This memory subpopulation is commonly found in the
692:
Defense against gut pathogens and at mucosal barriers
497:
cells. The remaining cells exit the thymus as mature
273:
Origin, early development and migration to the thymus
226:.) CD8+ T cells, also known as "killer T cells", are
4230:
4228:
3913:
3911:
1364:, which then translocates to the nucleus. NFAT is a
1050:
Mucosal associated invariant T (MAIT) cells display
869:. They also have intermediate to high expression of
6645:
6603:
6545:
6446:
6376:
6284:
6277:
6202:
6125:
6116:
6084:
5979:
5900:
5755:Bhadra R, Gigley JP, Weiss LM, Khan IA (May 2011).
4783:"Role of regulatory T cells during virus infection"
1988:(8th ed.). Garland Science. pp. 301–305.
1280:) genes. The other proteins in the complex are the
127:
115:
103:
91:
86:
74:
69:
32:
4634:"+ T cells during bovine leukemia virus infection"
4291:Kaminski H, Lemoine M, Pradeu T (September 2021).
4235:Jones J, Bannister BA, Gillespie SH, eds. (2006).
4060:Belikov AV, Schraven B, Simeoni L (October 2015).
3247:Ussher JE, Klenerman P, Willberg CB (2014-10-08).
2410:
2408:
4928:
4926:
4109:
4107:
604:molecules, which are expressed on the surface of
5123:Wells AD, Li XC, Strom TB, Turka LA (May 2001).
4984:"Anti-PD-L1 peptide improves survival in sepsis"
4114:Feinerman O, Germain RN, Altan-Bonnet G (2008).
3808:Sun JC, Williams MA, Bevan MJ (September 2004).
2466:T Helper Cell Differentiation and Their Function
4210:
4208:
1843:Luckheeram RV, Zhou R, Verma AD, Xia B (2012).
1829:(4th ed.). Garland Science. p. 1367.
1546:, and accounts for perhaps one in ten cases of
1296:. Lck and/or ZAP-70 can also phosphorylate the
64:(center), and a T lymphocyte (right); colorized
3303:Howson LJ, Salio M, Cerundolo V (2015-06-16).
2759:"Alternative memory in the CD8 T cell lineage"
2256:(8th ed.). Garland Science. p. 297.
1797:
1795:
1197:, T cell receptor signalling alone results in
750:Crohn's Disease, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Tumors
355:, and matures into either CD4+ or CD8+ cells.
6248:
5878:
5178:Journal of the American Society of Nephrology
8:
4589:Wherry EJ (June 2011). "T cell exhaustion".
4286:
4284:
4282:
1845:"CD4⁺T cells: differentiation and functions"
1677:(LAG3). Soluble molecules such as cytokines
5825:(5th ed.). New York: Garland Science.
5409:Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation
2103:Zerrahn J, Held W, Raulet DH (March 1997).
1601:It has been suggested that this section be
343:. Still during the double negative stages,
6281:
6255:
6241:
6233:
6122:
5985:
5885:
5871:
5863:
2415:Saravia J, Chapman NM, Chi H (July 2019).
1823:"Helper t Cells and Lymphocyte Activation"
1804:"Helper T Cells and Lymphocyte Activation"
1480:(AIDS), and hereditary conditions such as
172:. T cells can be distinguished from other
50:
38:
5790:
5780:
5706:
5586:
5529:
5519:
5478:
5428:
5371:
5329:
5288:
5197:
5148:
5056:
5007:
4958:
4906:
4896:
4855:
4806:
4757:
4708:
4659:
4649:
4565:
4516:
4467:
4457:
4416:
4367:
4318:
4308:
4188:
4139:
4087:
4077:
4011:
3918:Tatham P, Gomperts BD, Kramer IM (2003).
3891:
3833:
3563:
3522:
3512:
3463:
3379:
3330:
3320:
3274:
3264:
3223:
3213:
3172:
3123:
3113:
3065:
3016:
3006:
2922:
2873:
2832:
2782:
2733:
2684:
2674:
2625:
2573:
2440:
2388:
2378:
2337:
2228:
2120:
2044:
2034:
1960:
1911:
1870:
1860:
1550:. The main forms of T cell lymphoma are:
1300:on many other molecules, not least CD28,
1217:that are essential for the activation of
1151:, which upregulate endogenous IPP/DMAPP.
195:. Developing T cells then migrate to the
3685:10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141548
2757:Lee YJ, Jameson SC, Hogquist KA (2011).
2082:10.1146/annurev.immunol.21.120601.141107
1673:, T cell membrane protein-3 (TIM3), and
1253:proteins, which together constitute the
1161:T-cell receptor § Signaling pathway
1020:of the innate immune system) bridge the
891:is the intern αeβ7, also known as CD103.
614:
3659:"Understanding the Immune System (pdf)"
1849:Clinical & Developmental Immunology
1761:
423:. These self-antigens are expressed by
238:) cells function by further activating
4391:Yi JS, Cox MA, Zajac AJ (April 2010).
4238:Infection: Microbiology and Management
3922:. Amsterdam: Elsevier Academic Press.
3298:
3296:
3294:
3091:
3089:
3087:
3085:
1394:(TCAS) experiment was launched to the
1209:at the plasma membrane and recruiting
144:
29:
27:White blood cells of the immune system
4062:"T cells and reactive oxygen species"
3147:Gold MC, Lewinsohn DM (August 2011).
1605:out into another article titled
1016:(NKT cells – not to be confused with
531:gene or protein expression patterns.
419:, where they are presented with self-
277:All T cells originate from c-kitSca1
7:
5508:Journal of Hematology & Oncology
5318:Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry
4836:The Journal of Experimental Medicine
3546:Chua WJ, Hansen TH (November 2010).
3444:Clinical and Experimental Immunology
2708:Shin H, Iwasaki A (September 2013).
1941:The Journal of Experimental Medicine
1675:lymphocyte activation gene 3 protein
1213:containing signaling molecules like
1189:and co-stimulatory molecules on the
1177:and a co-stimulatory molecule (like
1040:Mucosal associated invariant T cells
695:MS, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriasis
6104:Mucosal associated invariant T cell
5360:American Journal of Transplantation
4163:Dushek O, van der Merwe PA (2014).
3202:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
2421:Cellular & Molecular Immunology
1660:During chronic infection and sepsis
1478:acquired immune deficiency syndrome
1046:Mucosal associated invariant T cell
919:are crucial for the maintenance of
733:Asthma and other allergic diseases
676:Asthma and other allergic diseases
1578:Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma
1405:T cell activation is modulated by
1360:. Calcineurin, in turn, activates
305:, the immature stage of a T cell.
160:are one of the important types of
56:Scanning electron micrograph of a
25:
1335:), inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate (
934:cells have been described—FOXP3 T
462:medullary thymic epithelial cells
6140:Lymphokine-activated killer cell
5850:. September 2003. Archived from
4988:The Journal of Surgical Research
4509:10.1128/JVI.68.12.8056-8063.1994
4409:10.1111/j.1365-2567.2010.03255.x
4241:. Wiley-Blackwell. p. 435.
2710:"Tissue-resident memory T cells"
2291:10.1146/annurev.immunol.18.1.529
1810:(4th ed.). Garland Science.
1729:Chimeric antigen receptor T cell
1592:
1466:severe combined immunodeficiency
1030:major histocompatibility complex
585:. These cells are also known as
425:thymic cortical epithelial cells
380:major histocompatibility complex
141:Anatomical terms of microanatomy
2417:"Helper T cell differentiation"
1667:programmed cell death protein 1
1351:, which induces the release of
1131:precursors, collectively named
730:Help B cells produce antibodies
301:. Henceforth they are known as
168:and play a central role in the
6582:Immunoglobulin class switching
4344:"Defining 'T cell exhaustion'"
2995:Journal of Immunology Research
1573:Anaplastic large cell lymphoma
1486:chromosomal breakage syndromes
983:have been added to this list.
881:Tissue-resident memory T cells
312:, as they express neither the
1:
5471:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1620
4066:Journal of Biomedical Science
2122:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81905-4
1827:Molecular Biology of the Cell
1808:Molecular Biology of the Cell
1770:"5. Hematopoietic Stem Cells"
840:C-C chemokine receptor type 7
535:Conventional adaptive T cells
6185:Type 3 innate lymphoid cells
6173:Type 2 innate lymphoid cells
6168:Type 1 innate lymphoid cells
6155:Uterine natural killer cells
6135:Cytokine-induced killer cell
5037:Journal of Leukocyte Biology
4750:10.1016/j.immuni.2009.06.015
4310:10.1371/journal.ppat.1009892
4132:10.1016/j.molimm.2007.03.028
4004:10.1182/blood-2010-05-283770
3165:10.1016/j.micinf.2011.03.007
2312:Gutcher I, Becher B (2007).
1913:10.1016/j.immuni.2016.12.003
1371:PLC-γ can also initiate the
5242:10.1097/TP.0b013e31816dd64a
3673:Annual Review of Immunology
3552:Immunology and Cell Biology
3417:10.1016/j.imlet.2017.01.009
2627:10.4049/jimmunol.175.9.5895
2575:10.4049/jimmunol.140.7.2171
2474:10.1007/978-94-017-9487-9_8
2070:Annual Review of Immunology
1396:International Space Station
1141:dimethylallyl pyrophosphate
1117:intraepithelial lymphocytes
794:in length) associated with
616:CD4+ Helper T cell subsets
6715:
6411:Polyclonal B cell response
5660:10.1016/j.clim.2018.02.009
5624:10.1016/j.clim.2011.11.009
5579:10.1038/s41467-018-03347-0
5421:10.1016/j.bbmt.2017.11.022
5094:10.1016/j.clim.2018.04.010
4348:Nature Reviews. Immunology
3884:10.1016/j.jaut.2014.12.002
2825:10.1016/j.jaut.2016.11.001
1711:
1560:Cutaneous T cell lymphomas
1555:Extranodal T cell lymphoma
1532:
1434:
1392:T-Cell Activation in Space
1158:
1101:
1092:inflammatory bowel disease
1043:
1006:
930:Two major classes of CD4 T
909:
857:Effector memory T cells (T
806:
760:
543:
362:
6163:
5988:
5521:10.1186/s13045-016-0345-3
5000:10.1016/j.jss.2016.08.099
4651:10.1186/s13567-018-0543-9
4360:10.1038/s41577-019-0221-9
4079:10.1186/s12929-015-0194-3
2433:10.1038/s41423-019-0220-6
2221:10.1172/jci.insight.93739
1894:Kondo M (December 2016).
1474:cartilage–hair hypoplasia
1137:isopentenyl pyrophosphate
1115:, within a population of
834:Central memory T cells (T
472:peptides. Some mTECs are
279:haematopoietic stem cells
139:
49:
37:
5290:10.4049/jimmunol.1500440
5049:10.1189/jlb.4hi0616-255r
4459:10.3389/fimmu.2018.00219
4181:10.1016/j.it.2014.02.002
3322:10.3389/fimmu.2015.00303
3266:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00450
3115:10.3389/fimmu.2015.00344
2775:10.1016/j.it.2010.12.004
2380:10.3389/fimmu.2020.02025
2252:Murphy, Kenneth (2011).
1984:Murphy, Kenneth (2011).
1494:Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome
1231:antigen-presenting cells
830:Memory T cell subtypes:
627:Key Transcription Factor
606:antigen-presenting cells
482:antigen presenting cells
189:hematopoietic stem cells
170:adaptive immune response
6212:Hematopoietic stem cell
5971:Lymphoplasmacytoid cell
5782:10.1073/pnas.1015298108
4035:Graham W (2014-04-14).
3779:10.1126/science.1082305
3514:10.1073/pnas.0903196106
3309:Frontiers in Immunology
3253:Frontiers in Immunology
3215:10.1074/jbc.R115.685990
3102:Frontiers in Immunology
2813:Journal of Autoimmunity
2367:Frontiers in Immunology
2254:Janeway's Immunobiology
2036:10.1073/pnas.1408482111
1986:Janeway's Immunobiology
1501:intracellular pathogens
1407:reactive oxygen species
921:immunological tolerance
906:Regulatory CD4+ T cells
838:cells) express CD45RO,
509:TCR development summary
480:; this makes them AIRE
464:(mTECs). mTECs must be
6525:Tolerance in pregnancy
6267:adaptive immune system
5190:10.1681/ASN.2014060588
5141:10.1098/rstb.2001.0845
4951:10.1001/jama.2011.1829
3153:Microbes and Infection
3046:Infection and Immunity
1694:During transplantation
1449:
1413:Antigen discrimination
1170:
1022:adaptive immune system
1014:Natural killer T cells
996:unconventional T cells
895:Virtual memory T cells
772:
757:Cytotoxic CD8+ T cells
630:Role in immune defense
555:
478:thymic dendritic cells
187:T cells are born from
6560:Somatic hypermutation
6394:Polyclonal antibodies
6389:Monoclonal antibodies
6118:Innate lymphoid cells
6094:Natural killer T cell
5559:Nature Communications
5277:Journal of Immunology
4787:Immunological Reviews
3354:Hinks TS (May 2016).
2714:Immunological Reviews
2676:10.1186/1742-4933-5-6
2663:Immunity & Ageing
2614:Journal of Immunology
1774:Stem Cell Information
1542:of T cells is termed
1533:Further information:
1490:ataxia-telangiectasia
1462:hereditary conditions
1444:
1426:Clinical significance
1168:
1139:(IPP) and its isomer
1009:Natural killer T cell
1003:Natural killer T cell
770:
686:IL-17F, IL-17A, IL-22
553:
390:TCR β-chain selection
347:expression stops and
324:c-kit and are termed
287:embryonic development
176:by the presence of a
6577:Junctional diversity
6345:Antigen presentation
5687:Blood Cancer Journal
4848:10.1084/jem.20132577
4558:10.1128/JVI.00889-12
3565:10.1038/icb.2010.104
3058:10.1128/IAI.01178-06
3008:10.1155/2021/6633824
2763:Trends in Immunology
1953:10.1084/jem.20061871
1548:non-Hodgkin lymphoma
1506:Herpes simplex virus
1390:In spring 2014, the
1366:transcription factor
1292:and in turn recruit
1149:aminobisphosphonates
1026:innate immune system
1018:natural killer cells
948:transcription factor
925:autoreactive T cells
657:MS, Type 1 diabetes
589:as they express the
577:, and activation of
466:Autoimmune regulator
6572:V(D)J recombination
6555:Affinity maturation
6307:Antigenic variation
6086:Innate-like T cells
5966:Transitional B cell
5841:"The Immune System"
5773:2011PNAS..108.9196B
5699:10.1038/bcj.2015.58
5648:Clinical Immunology
5612:Clinical Immunology
5571:2018NatCo...9..948L
5082:Clinical Immunology
4638:Veterinary Research
4546:Journal of Virology
4497:Journal of Virology
4041:NASAspaceflight.com
3920:Signal transduction
3771:2003Sci...300..337S
3728:10.1038/nature01441
3720:2003Natur.421..852J
3625:10.1038/nature11605
3617:2012Natur.491..717K
3505:2009PNAS..106.8290H
2519:1999Natur.401..708S
2027:2014PNAS..111E2550R
2021:(25): E2550–E2558.
1862:10.1155/2012/925135
1749:Parafollicular cell
1734:Gut-specific homing
1243:heat shock proteins
1205:pathway generating
1109:Gamma delta T cells
1098:Gamma delta T cells
1084:autoimmune diseases
1074:and are capable of
992:Innate-like T cells
987:Innate-like T cells
714:Multiple Sclerosis
617:
540:Helper CD4+ T cells
400:V-D-J recombination
326:double-negative one
44:Animation of T cell
3957:10.1002/bies.10352
3405:Immunology Letters
2911:Indian J. Med. Res
2279:Annu. Rev. Immunol
1780:on 29 October 2016
1751:also called C cell
1450:
1356:can then activate
1171:
1104:Gamma delta T cell
1088:multiple sclerosis
959:autoimmune disease
917:Regulatory T cells
773:
624:Cytokines Produced
615:
556:
455:Negative selection
411:Positive selection
250:Regulatory T cells
122:H2.00.04.1.02007
6671:
6670:
6599:
6598:
6349:professional APCs
6230:
6229:
6198:
6197:
6112:
6111:
5832:978-0-8153-3642-6
5767:(22): 9196–9201.
5373:10.1111/ajt.13288
5331:10.1159/000443067
4799:10.1111/imr.12085
4591:Nature Immunology
4248:978-1-4051-2665-6
3929:978-0-12-289632-3
3814:Nature Immunology
3657:resource booklet
3456:10.1111/cei.12277
3372:10.1111/imm.12582
2954:(11): 1114–1123.
2948:Nature Immunology
2726:10.1111/imr.12087
2513:(6754): 708–712.
2483:978-94-017-9486-2
2161:Nature Immunology
1625:
1624:
1620:
1608:T cell exhaustion
1568:Mycosis fungoides
1523:fungal infections
1482:DiGeorge syndrome
1454:T cell deficiency
1437:T cell deficiency
938:cells and FOXP3 T
912:Regulatory T cell
776:Cytotoxic T cells
754:
753:
667:IL-4, IL-5, IL-13
633:Related diseases
579:cytotoxic T cells
503:central tolerance
398:locus, combining
162:white blood cells
155:
154:
150:
16:(Redirected from
6706:
6565:Clonal selection
6537:Immune privilege
6532:Immunodeficiency
6487:Cross-reactivity
6477:Hypersensitivity
6282:
6257:
6250:
6243:
6234:
6150:Adaptive NK cell
6123:
5986:
5887:
5880:
5873:
5864:
5858:
5857:on 25 June 2009.
5856:
5845:
5836:
5805:
5804:
5794:
5784:
5752:
5746:
5745:
5743:
5742:
5727:
5721:
5720:
5710:
5678:
5672:
5671:
5642:
5636:
5635:
5607:
5601:
5600:
5590:
5550:
5544:
5543:
5533:
5523:
5499:
5493:
5492:
5482:
5449:
5443:
5442:
5432:
5400:
5394:
5393:
5375:
5350:
5344:
5343:
5333:
5309:
5303:
5302:
5292:
5268:
5262:
5261:
5227:
5218:
5212:
5211:
5201:
5169:
5163:
5162:
5152:
5135:(1409): 617–23.
5120:
5114:
5113:
5077:
5071:
5070:
5060:
5043:(6): 1239–1254.
5028:
5022:
5021:
5011:
4979:
4973:
4972:
4962:
4945:(23): 2594–605.
4930:
4921:
4920:
4910:
4900:
4876:
4870:
4869:
4859:
4827:
4821:
4820:
4810:
4778:
4772:
4771:
4761:
4729:
4723:
4722:
4712:
4680:
4674:
4673:
4663:
4653:
4629:
4623:
4622:
4586:
4580:
4579:
4569:
4537:
4531:
4530:
4520:
4488:
4482:
4481:
4471:
4461:
4437:
4431:
4430:
4420:
4388:
4382:
4381:
4371:
4339:
4333:
4332:
4322:
4312:
4288:
4277:
4276:
4274:
4273:
4267:
4259:
4253:
4252:
4232:
4223:
4216:T-Cell Disorders
4212:
4203:
4202:
4192:
4160:
4154:
4153:
4143:
4111:
4102:
4101:
4091:
4081:
4057:
4051:
4050:
4048:
4047:
4032:
4026:
4025:
4015:
3983:
3977:
3976:
3951:(11): 1096–105.
3940:
3934:
3933:
3915:
3906:
3905:
3895:
3863:
3857:
3854:
3848:
3847:
3837:
3805:
3799:
3798:
3754:
3748:
3747:
3703:
3697:
3696:
3668:
3662:
3651:
3645:
3644:
3611:(7426): 717–23.
3602:
3592:
3586:
3585:
3567:
3543:
3537:
3536:
3526:
3516:
3484:
3478:
3477:
3467:
3435:
3429:
3428:
3400:
3394:
3393:
3383:
3351:
3345:
3344:
3334:
3324:
3300:
3289:
3288:
3278:
3268:
3244:
3238:
3237:
3227:
3217:
3208:(51): 30204–11.
3193:
3187:
3186:
3176:
3144:
3138:
3137:
3127:
3117:
3093:
3080:
3079:
3069:
3037:
3031:
3030:
3020:
3010:
2986:
2980:
2979:
2943:
2937:
2936:
2926:
2902:
2896:
2895:
2877:
2853:
2847:
2846:
2836:
2803:
2797:
2796:
2786:
2754:
2748:
2747:
2737:
2705:
2699:
2698:
2688:
2678:
2654:
2648:
2647:
2629:
2611:
2602:
2596:
2595:
2577:
2553:
2547:
2546:
2502:
2496:
2495:
2461:
2455:
2454:
2444:
2412:
2403:
2402:
2392:
2382:
2358:
2352:
2351:
2341:
2330:10.1172/JCI31720
2309:
2303:
2302:
2274:
2268:
2267:
2249:
2243:
2242:
2232:
2199:
2193:
2192:
2158:
2149:
2143:
2142:
2124:
2100:
2094:
2093:
2065:
2059:
2058:
2048:
2038:
2006:
2000:
1999:
1981:
1975:
1974:
1964:
1932:
1926:
1925:
1915:
1906:(6): 1177–1179.
1891:
1885:
1884:
1874:
1864:
1840:
1834:
1833:
1818:
1812:
1811:
1799:
1790:
1789:
1787:
1785:
1766:
1744:Immunosenescence
1714:Immunosenescence
1616:
1596:
1595:
1588:
1448:-infected T cell
1327:and potentially
1090:, arthritis and
815:effector T cells
763:Cytotoxic T cell
618:
214:(cytotoxic) and
147:edit on Wikidata
54:
42:
30:
21:
6714:
6713:
6709:
6708:
6707:
6705:
6704:
6703:
6674:
6673:
6672:
6667:
6641:
6595:
6541:
6520:Clonal deletion
6448:
6442:
6372:
6273:
6261:
6231:
6226:
6194:
6159:
6108:
6080:
6074:
6066:
6058:
6050:
6026:
6018:
6011:
5975:
5953:
5896:
5891:
5861:
5854:
5843:
5839:
5833:
5818:
5814:
5812:Further reading
5809:
5808:
5754:
5753:
5749:
5740:
5738:
5729:
5728:
5724:
5680:
5679:
5675:
5644:
5643:
5639:
5609:
5608:
5604:
5552:
5551:
5547:
5501:
5500:
5496:
5459:Cancer Research
5451:
5450:
5446:
5402:
5401:
5397:
5352:
5351:
5347:
5311:
5310:
5306:
5270:
5269:
5265:
5230:Transplantation
5225:
5220:
5219:
5215:
5171:
5170:
5166:
5122:
5121:
5117:
5079:
5078:
5074:
5030:
5029:
5025:
4981:
4980:
4976:
4932:
4931:
4924:
4898:10.1186/cc10332
4878:
4877:
4873:
4829:
4828:
4824:
4780:
4779:
4775:
4731:
4730:
4726:
4689:Nature Medicine
4682:
4681:
4677:
4631:
4630:
4626:
4603:10.1038/ni.2035
4588:
4587:
4583:
4552:(15): 8161–70.
4539:
4538:
4534:
4503:(12): 8056–63.
4490:
4489:
4485:
4439:
4438:
4434:
4390:
4389:
4385:
4354:(11): 665–674.
4341:
4340:
4336:
4303:(9): e1009892.
4290:
4289:
4280:
4271:
4269:
4265:
4263:"The Lymphomas"
4261:
4260:
4256:
4249:
4234:
4233:
4226:
4213:
4206:
4162:
4161:
4157:
4113:
4112:
4105:
4059:
4058:
4054:
4045:
4043:
4034:
4033:
4029:
3985:
3984:
3980:
3942:
3941:
3937:
3930:
3917:
3916:
3909:
3865:
3864:
3860:
3855:
3851:
3807:
3806:
3802:
3765:(5617): 337–9.
3756:
3755:
3751:
3714:(6925): 852–6.
3705:
3704:
3700:
3670:
3669:
3665:
3652:
3648:
3600:
3594:
3593:
3589:
3545:
3544:
3540:
3486:
3485:
3481:
3437:
3436:
3432:
3402:
3401:
3397:
3353:
3352:
3348:
3302:
3301:
3292:
3246:
3245:
3241:
3195:
3194:
3190:
3146:
3145:
3141:
3095:
3094:
3083:
3039:
3038:
3034:
2988:
2987:
2983:
2960:10.1038/ni.3298
2945:
2944:
2940:
2904:
2903:
2899:
2875:10.1038/ni.2554
2855:
2854:
2850:
2805:
2804:
2800:
2756:
2755:
2751:
2707:
2706:
2702:
2656:
2655:
2651:
2620:(9): 5895–903.
2609:
2604:
2603:
2599:
2555:
2554:
2550:
2504:
2503:
2499:
2484:
2463:
2462:
2458:
2414:
2413:
2406:
2360:
2359:
2355:
2318:J. Clin. Invest
2311:
2310:
2306:
2276:
2275:
2271:
2264:
2251:
2250:
2246:
2201:
2200:
2196:
2173:10.1038/ni.1874
2156:
2151:
2150:
2146:
2102:
2101:
2097:
2067:
2066:
2062:
2008:
2007:
2003:
1996:
1983:
1982:
1978:
1934:
1933:
1929:
1893:
1892:
1888:
1842:
1841:
1837:
1820:
1819:
1815:
1801:
1800:
1793:
1783:
1781:
1768:
1767:
1763:
1758:
1725:
1716:
1710:
1696:
1662:
1621:
1597:
1593:
1586:
1564:Sézary syndrome
1544:T-cell lymphoma
1537:
1535:T-cell lymphoma
1531:
1458:lymphocytopenia
1439:
1433:
1428:
1415:
1311:Phosphorylated
1270:T cell receptor
1221:, and eventual
1175:T-cell receptor
1163:
1157:
1133:phosphoantigens
1106:
1100:
1062:-like protein,
1048:
1042:
1011:
1005:
989:
941:
937:
933:
914:
908:
900:
890:
886:
876:
864:
860:
837:
811:
805:
781:
765:
759:
564:
548:
542:
537:
528:
526:Types of T cell
519:
511:
460:MHC complex of
457:
442:single positive
413:
405:double-positive
392:
367:
365:T-cell receptor
361:
359:TCR development
353:double positive
310:double-negative
275:
270:
245:
237:
205:immune response
191:, found in the
180:(TCR) on their
178:T-cell receptor
151:
65:
45:
28:
23:
22:
18:Effector T cell
15:
12:
11:
5:
6712:
6710:
6702:
6701:
6696:
6691:
6686:
6676:
6675:
6669:
6668:
6666:
6665:
6660:
6655:
6649:
6647:
6643:
6642:
6640:
6639:
6634:
6633:
6632:
6622:
6621:
6620:
6609:
6607:
6601:
6600:
6597:
6596:
6594:
6593:
6584:
6579:
6574:
6569:
6568:
6567:
6562:
6551:
6549:
6547:Immunogenetics
6543:
6542:
6540:
6539:
6534:
6529:
6528:
6527:
6522:
6517:
6512:
6507:
6495:
6494:
6492:Co-stimulation
6489:
6484:
6479:
6474:
6469:
6464:
6459:
6452:
6450:
6444:
6443:
6441:
6440:
6435:
6433:Immune complex
6429:
6428:
6423:
6418:
6413:
6408:
6407:
6406:
6401:
6396:
6391:
6380:
6378:
6374:
6373:
6371:
6370:
6365:
6360:
6355:
6353:Dendritic cell
6341:
6340:
6335:
6334:
6333:
6331:Conformational
6328:
6317:
6316:
6311:
6310:
6309:
6304:
6299:
6288:
6286:
6279:
6275:
6274:
6262:
6260:
6259:
6252:
6245:
6237:
6228:
6227:
6225:
6224:
6219:
6214:
6208:
6206:
6200:
6199:
6196:
6195:
6193:
6192:
6187:
6182:
6181:
6180:
6170:
6164:
6161:
6160:
6158:
6157:
6152:
6147:
6142:
6137:
6131:
6129:
6120:
6114:
6113:
6110:
6109:
6107:
6106:
6101:
6096:
6090:
6088:
6082:
6081:
6079:
6078:
6077:
6076:
6072:
6068:
6064:
6060:
6056:
6052:
6048:
6039:
6034:
6024:
6016:
6009:
6001:
5995:
5989:
5983:
5977:
5976:
5974:
5973:
5968:
5963:
5962:
5961:
5951:
5947:
5942:
5937:
5932:
5927:
5922:
5917:
5912:
5906:
5904:
5898:
5897:
5892:
5890:
5889:
5882:
5875:
5867:
5860:
5859:
5837:
5831:
5815:
5813:
5810:
5807:
5806:
5747:
5722:
5673:
5637:
5618:(2): 105–106.
5602:
5545:
5494:
5444:
5415:(3): 618–622.
5395:
5366:(9): 2431–42.
5345:
5324:(3): 1171–81.
5304:
5283:(4): 1838–48.
5263:
5236:(9): 1339–47.
5213:
5184:(7): 1711–20.
5164:
5115:
5072:
5023:
4974:
4922:
4871:
4842:(9): 1905–18.
4822:
4773:
4724:
4701:10.1038/nm1492
4695:(11): 1301–9.
4675:
4624:
4581:
4532:
4483:
4432:
4383:
4334:
4297:PLOS Pathogens
4278:
4254:
4247:
4224:
4204:
4169:Trends Immunol
4155:
4103:
4052:
4027:
3998:(3): 1042–52.
3978:
3935:
3928:
3907:
3858:
3849:
3826:10.1038/ni1105
3800:
3749:
3698:
3663:
3646:
3587:
3538:
3499:(20): 8290–5.
3479:
3430:
3395:
3346:
3290:
3239:
3188:
3159:(8–9): 742–8.
3139:
3081:
3052:(5): 2171–80.
3032:
2981:
2938:
2897:
2848:
2798:
2749:
2700:
2649:
2597:
2548:
2497:
2482:
2456:
2427:(7): 634–643.
2404:
2353:
2324:(5): 1119–27.
2304:
2269:
2262:
2244:
2194:
2167:(6): 512–519.
2144:
2115:(5): 627–636.
2095:
2076:(1): 139–176.
2060:
2001:
1994:
1976:
1947:(3): 619–631.
1927:
1886:
1835:
1813:
1791:
1760:
1759:
1757:
1754:
1753:
1752:
1746:
1741:
1736:
1731:
1724:
1721:
1709:
1706:
1695:
1692:
1661:
1658:
1623:
1622:
1600:
1598:
1591:
1585:
1582:
1581:
1580:
1575:
1570:
1557:
1530:
1527:
1470:Omenn syndrome
1435:Main article:
1432:
1429:
1427:
1424:
1414:
1411:
1195:co-stimulation
1156:
1153:
1102:Main article:
1099:
1096:
1044:Main article:
1041:
1038:
1007:Main article:
1004:
1001:
988:
985:
939:
935:
931:
910:Main article:
907:
904:
903:
902:
898:
892:
888:
884:
878:
874:
862:
858:
855:
835:
807:Main article:
804:
803:Memory T cells
801:
779:
761:Main article:
758:
755:
752:
751:
748:
745:
742:
739:
735:
734:
731:
728:
725:
722:
716:
715:
712:
709:
706:
703:
697:
696:
693:
690:
687:
684:
678:
677:
674:
671:
668:
665:
659:
658:
655:
652:
647:
641:
635:
634:
631:
628:
625:
622:
575:memory B cells
562:
559:T helper cells
544:Main article:
541:
538:
536:
533:
527:
524:
518:
515:
510:
507:
456:
453:
412:
409:
391:
388:
363:Main article:
360:
357:
295:lymphoid cells
274:
271:
269:
266:
243:
240:memory B cells
235:
153:
152:
143:
137:
136:
131:
125:
124:
119:
113:
112:
107:
101:
100:
95:
89:
88:
84:
83:
78:
72:
71:
67:
66:
58:red blood cell
55:
47:
46:
43:
35:
34:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
6711:
6700:
6697:
6695:
6694:Immune system
6692:
6690:
6687:
6685:
6682:
6681:
6679:
6664:
6661:
6659:
6656:
6654:
6651:
6650:
6648:
6644:
6638:
6635:
6631:
6628:
6627:
6626:
6623:
6619:
6616:
6615:
6614:
6611:
6610:
6608:
6606:
6602:
6592:
6588:
6585:
6583:
6580:
6578:
6575:
6573:
6570:
6566:
6563:
6561:
6558:
6557:
6556:
6553:
6552:
6550:
6548:
6544:
6538:
6535:
6533:
6530:
6526:
6523:
6521:
6518:
6516:
6515:Clonal anergy
6513:
6511:
6508:
6506:
6503:
6502:
6501:
6497:
6496:
6493:
6490:
6488:
6485:
6483:
6480:
6478:
6475:
6473:
6470:
6468:
6465:
6463:
6460:
6458:
6454:
6453:
6451:
6445:
6439:
6436:
6434:
6431:
6430:
6427:
6424:
6422:
6419:
6417:
6414:
6412:
6409:
6405:
6404:Microantibody
6402:
6400:
6397:
6395:
6392:
6390:
6387:
6386:
6385:
6382:
6381:
6379:
6375:
6369:
6366:
6364:
6361:
6359:
6356:
6354:
6350:
6346:
6343:
6342:
6339:
6336:
6332:
6329:
6327:
6324:
6323:
6322:
6319:
6318:
6315:
6312:
6308:
6305:
6303:
6300:
6298:
6295:
6294:
6293:
6290:
6289:
6287:
6283:
6280:
6276:
6272:
6268:
6265:
6258:
6253:
6251:
6246:
6244:
6239:
6238:
6235:
6223:
6222:Prolymphocyte
6220:
6218:
6215:
6213:
6210:
6209:
6207:
6205:
6204:Lymphopoiesis
6201:
6191:
6188:
6186:
6183:
6179:
6176:
6175:
6174:
6171:
6169:
6166:
6165:
6162:
6156:
6153:
6151:
6148:
6146:
6143:
6141:
6138:
6136:
6133:
6132:
6130:
6128:
6124:
6121:
6119:
6115:
6105:
6102:
6100:
6097:
6095:
6092:
6091:
6089:
6087:
6083:
6075:
6069:
6067:
6061:
6059:
6053:
6051:
6045:
6044:
6043:
6042:Memory T cell
6040:
6038:
6035:
6032:
6028:
6020:
6012:
6005:
6002:
6000:
5999:Cytotoxic CD8
5996:
5994:
5991:
5990:
5987:
5984:
5982:
5978:
5972:
5969:
5967:
5964:
5960:
5957:
5956:
5955:
5948:
5946:
5943:
5941:
5938:
5936:
5935:Marginal zone
5933:
5931:
5928:
5926:
5923:
5921:
5918:
5916:
5913:
5911:
5908:
5907:
5905:
5903:
5899:
5895:
5888:
5883:
5881:
5876:
5874:
5869:
5868:
5865:
5853:
5849:
5842:
5838:
5834:
5828:
5824:
5823:
5817:
5816:
5811:
5802:
5798:
5793:
5788:
5783:
5778:
5774:
5770:
5766:
5762:
5758:
5751:
5748:
5736:
5732:
5726:
5723:
5718:
5714:
5709:
5704:
5700:
5696:
5692:
5688:
5684:
5677:
5674:
5669:
5665:
5661:
5657:
5653:
5649:
5641:
5638:
5633:
5629:
5625:
5621:
5617:
5613:
5606:
5603:
5598:
5594:
5589:
5584:
5580:
5576:
5572:
5568:
5564:
5560:
5556:
5549:
5546:
5541:
5537:
5532:
5527:
5522:
5517:
5513:
5509:
5505:
5498:
5495:
5490:
5486:
5481:
5476:
5472:
5468:
5465:(4): 917–27.
5464:
5460:
5456:
5448:
5445:
5440:
5436:
5431:
5426:
5422:
5418:
5414:
5410:
5406:
5399:
5396:
5391:
5387:
5383:
5379:
5374:
5369:
5365:
5361:
5357:
5349:
5346:
5341:
5337:
5332:
5327:
5323:
5319:
5315:
5308:
5305:
5300:
5296:
5291:
5286:
5282:
5278:
5274:
5267:
5264:
5259:
5255:
5251:
5247:
5243:
5239:
5235:
5231:
5224:
5217:
5214:
5209:
5205:
5200:
5195:
5191:
5187:
5183:
5179:
5175:
5168:
5165:
5160:
5156:
5151:
5146:
5142:
5138:
5134:
5130:
5126:
5119:
5116:
5111:
5107:
5103:
5099:
5095:
5091:
5087:
5083:
5076:
5073:
5068:
5064:
5059:
5054:
5050:
5046:
5042:
5038:
5034:
5027:
5024:
5019:
5015:
5010:
5005:
5001:
4997:
4993:
4989:
4985:
4978:
4975:
4970:
4966:
4961:
4956:
4952:
4948:
4944:
4940:
4936:
4929:
4927:
4923:
4918:
4914:
4909:
4904:
4899:
4894:
4890:
4886:
4885:Critical Care
4882:
4875:
4872:
4867:
4863:
4858:
4853:
4849:
4845:
4841:
4837:
4833:
4826:
4823:
4818:
4814:
4809:
4804:
4800:
4796:
4793:(1): 182–96.
4792:
4788:
4784:
4777:
4774:
4769:
4765:
4760:
4755:
4751:
4747:
4744:(1): 145–57.
4743:
4739:
4735:
4728:
4725:
4720:
4716:
4711:
4706:
4702:
4698:
4694:
4690:
4686:
4679:
4676:
4671:
4667:
4662:
4657:
4652:
4647:
4643:
4639:
4635:
4628:
4625:
4620:
4616:
4612:
4608:
4604:
4600:
4596:
4592:
4585:
4582:
4577:
4573:
4568:
4563:
4559:
4555:
4551:
4547:
4543:
4536:
4533:
4528:
4524:
4519:
4514:
4510:
4506:
4502:
4498:
4494:
4487:
4484:
4479:
4475:
4470:
4465:
4460:
4455:
4451:
4447:
4446:Front Immunol
4443:
4436:
4433:
4428:
4424:
4419:
4414:
4410:
4406:
4403:(4): 474–81.
4402:
4398:
4394:
4387:
4384:
4379:
4375:
4370:
4365:
4361:
4357:
4353:
4349:
4345:
4338:
4335:
4330:
4326:
4321:
4316:
4311:
4306:
4302:
4298:
4294:
4287:
4285:
4283:
4279:
4264:
4258:
4255:
4250:
4244:
4240:
4239:
4231:
4229:
4225:
4222:
4218:
4217:
4211:
4209:
4205:
4200:
4196:
4191:
4186:
4182:
4178:
4174:
4170:
4166:
4159:
4156:
4151:
4147:
4142:
4137:
4133:
4129:
4126:(3): 619–31.
4125:
4121:
4117:
4110:
4108:
4104:
4099:
4095:
4090:
4085:
4080:
4075:
4071:
4067:
4063:
4056:
4053:
4042:
4038:
4031:
4028:
4023:
4019:
4014:
4009:
4005:
4001:
3997:
3993:
3989:
3982:
3979:
3974:
3970:
3966:
3962:
3958:
3954:
3950:
3946:
3939:
3936:
3931:
3925:
3921:
3914:
3912:
3908:
3903:
3899:
3894:
3889:
3885:
3881:
3877:
3873:
3869:
3862:
3859:
3853:
3850:
3845:
3841:
3836:
3831:
3827:
3823:
3820:(9): 927–33.
3819:
3815:
3811:
3804:
3801:
3796:
3792:
3788:
3784:
3780:
3776:
3772:
3768:
3764:
3760:
3753:
3750:
3745:
3741:
3737:
3733:
3729:
3725:
3721:
3717:
3713:
3709:
3702:
3699:
3694:
3690:
3686:
3682:
3679:(1): 171–92.
3678:
3674:
3667:
3664:
3660:
3656:
3650:
3647:
3642:
3638:
3634:
3630:
3626:
3622:
3618:
3614:
3610:
3606:
3599:
3591:
3588:
3583:
3579:
3575:
3571:
3566:
3561:
3557:
3553:
3549:
3542:
3539:
3534:
3530:
3525:
3520:
3515:
3510:
3506:
3502:
3498:
3494:
3490:
3483:
3480:
3475:
3471:
3466:
3461:
3457:
3453:
3450:(2): 266–74.
3449:
3445:
3441:
3434:
3431:
3426:
3422:
3418:
3414:
3410:
3406:
3399:
3396:
3391:
3387:
3382:
3377:
3373:
3369:
3365:
3361:
3357:
3350:
3347:
3342:
3338:
3333:
3328:
3323:
3318:
3314:
3310:
3306:
3299:
3297:
3295:
3291:
3286:
3282:
3277:
3272:
3267:
3262:
3258:
3254:
3250:
3243:
3240:
3235:
3231:
3226:
3221:
3216:
3211:
3207:
3203:
3199:
3192:
3189:
3184:
3180:
3175:
3170:
3166:
3162:
3158:
3154:
3150:
3143:
3140:
3135:
3131:
3126:
3121:
3116:
3111:
3107:
3103:
3099:
3092:
3090:
3088:
3086:
3082:
3077:
3073:
3068:
3063:
3059:
3055:
3051:
3047:
3043:
3036:
3033:
3028:
3024:
3019:
3014:
3009:
3004:
3000:
2996:
2992:
2985:
2982:
2977:
2973:
2969:
2965:
2961:
2957:
2953:
2949:
2942:
2939:
2934:
2930:
2925:
2920:
2916:
2912:
2908:
2901:
2898:
2893:
2889:
2885:
2881:
2876:
2871:
2867:
2863:
2859:
2852:
2849:
2844:
2840:
2835:
2830:
2826:
2822:
2818:
2814:
2810:
2802:
2799:
2794:
2790:
2785:
2780:
2776:
2772:
2768:
2764:
2760:
2753:
2750:
2745:
2741:
2736:
2731:
2727:
2723:
2720:(1): 165–81.
2719:
2715:
2711:
2704:
2701:
2696:
2692:
2687:
2682:
2677:
2672:
2668:
2664:
2660:
2653:
2650:
2645:
2641:
2637:
2633:
2628:
2623:
2619:
2615:
2608:
2601:
2598:
2593:
2589:
2585:
2581:
2576:
2571:
2568:(7): 2171–8.
2567:
2563:
2559:
2552:
2549:
2544:
2540:
2536:
2532:
2528:
2527:10.1038/44385
2524:
2520:
2516:
2512:
2508:
2501:
2498:
2493:
2489:
2485:
2479:
2475:
2471:
2467:
2460:
2457:
2452:
2448:
2443:
2438:
2434:
2430:
2426:
2422:
2418:
2411:
2409:
2405:
2400:
2396:
2391:
2386:
2381:
2376:
2372:
2368:
2364:
2357:
2354:
2349:
2345:
2340:
2335:
2331:
2327:
2323:
2319:
2315:
2308:
2305:
2300:
2296:
2292:
2288:
2284:
2280:
2273:
2270:
2265:
2263:9780815342434
2259:
2255:
2248:
2245:
2240:
2236:
2231:
2226:
2222:
2218:
2214:
2210:
2206:
2198:
2195:
2190:
2186:
2182:
2178:
2174:
2170:
2166:
2162:
2155:
2148:
2145:
2140:
2136:
2132:
2128:
2123:
2118:
2114:
2110:
2106:
2099:
2096:
2091:
2087:
2083:
2079:
2075:
2071:
2064:
2061:
2056:
2052:
2047:
2042:
2037:
2032:
2028:
2024:
2020:
2016:
2012:
2005:
2002:
1997:
1995:9780815342434
1991:
1987:
1980:
1977:
1972:
1968:
1963:
1958:
1954:
1950:
1946:
1942:
1938:
1931:
1928:
1923:
1919:
1914:
1909:
1905:
1901:
1897:
1890:
1887:
1882:
1878:
1873:
1868:
1863:
1858:
1854:
1850:
1846:
1839:
1836:
1832:
1828:
1824:
1817:
1814:
1809:
1805:
1798:
1796:
1792:
1779:
1775:
1771:
1765:
1762:
1755:
1750:
1747:
1745:
1742:
1740:
1737:
1735:
1732:
1730:
1727:
1726:
1722:
1720:
1715:
1708:During cancer
1707:
1705:
1702:
1693:
1691:
1688:
1684:
1680:
1676:
1672:
1668:
1659:
1657:
1655:
1651:
1647:
1643:
1639:
1635:
1629:
1619:
1614:
1610:
1609:
1604:
1599:
1590:
1589:
1583:
1579:
1576:
1574:
1571:
1569:
1565:
1561:
1558:
1556:
1553:
1552:
1551:
1549:
1545:
1541:
1536:
1528:
1526:
1524:
1520:
1519:
1514:
1513:
1512:Mycobacterium
1508:
1507:
1502:
1497:
1495:
1491:
1487:
1483:
1479:
1475:
1471:
1467:
1463:
1459:
1455:
1447:
1443:
1438:
1430:
1425:
1423:
1420:
1412:
1410:
1408:
1403:
1401:
1397:
1393:
1388:
1384:
1382:
1378:
1374:
1373:NF-κB pathway
1369:
1367:
1363:
1359:
1354:
1350:
1346:
1342:
1338:
1334:
1330:
1326:
1322:
1318:
1314:
1309:
1307:
1303:
1299:
1295:
1291:
1287:
1283:
1279:
1275:
1271:
1266:
1264:
1260:
1256:
1252:
1248:
1244:
1240:
1234:
1232:
1227:
1224:
1220:
1216:
1212:
1208:
1204:
1200:
1196:
1192:
1188:
1184:
1180:
1176:
1167:
1162:
1154:
1152:
1150:
1146:
1142:
1138:
1134:
1130:
1126:
1122:
1118:
1114:
1110:
1105:
1097:
1095:
1093:
1089:
1085:
1081:
1077:
1073:
1069:
1065:
1061:
1057:
1053:
1047:
1039:
1037:
1035:
1031:
1027:
1023:
1019:
1015:
1010:
1002:
1000:
997:
993:
986:
984:
982:
978:
974:
970:
965:
963:
960:
956:
952:
949:
943:
928:
926:
922:
918:
913:
905:
896:
893:
882:
879:
872:
868:
856:
853:
849:
845:
841:
833:
832:
831:
828:
826:
821:
820:memory T cell
816:
810:
809:Memory T cell
802:
800:
797:
793:
789:
785:
777:
769:
764:
756:
749:
746:
743:
740:
737:
736:
732:
729:
726:
723:
721:
718:
717:
713:
710:
707:
704:
702:
699:
698:
694:
691:
688:
685:
683:
680:
679:
675:
672:
669:
666:
664:
661:
660:
656:
653:
651:
648:
645:
642:
640:
637:
636:
632:
629:
626:
623:
620:
619:
613:
611:
607:
603:
599:
596:
592:
588:
584:
580:
576:
572:
568:
560:
552:
547:
546:T helper cell
539:
534:
532:
525:
523:
517:Thymic output
516:
514:
508:
506:
504:
500:
499:naive T cells
496:
492:
487:
483:
479:
475:
471:
467:
463:
454:
452:
450:
445:
443:
438:
434:
429:
426:
422:
418:
417:thymic cortex
410:
408:
406:
401:
397:
389:
387:
385:
381:
375:
373:
366:
358:
356:
354:
350:
346:
342:
338:
334:
329:
327:
323:
319:
315:
311:
306:
304:
300:
296:
292:
288:
284:
280:
272:
267:
265:
263:
259:
255:
251:
247:
241:
233:
229:
225:
221:
217:
216:CD4+ "helper"
213:
212:CD8+ "killer"
208:
206:
202:
198:
194:
190:
185:
183:
179:
175:
171:
167:
166:immune system
163:
159:
148:
142:
138:
135:
132:
130:
126:
123:
120:
118:
114:
111:
108:
106:
102:
99:
98:lymphocytus T
96:
94:
90:
85:
82:
81:Immune system
79:
77:
73:
68:
63:
59:
53:
48:
41:
36:
31:
19:
6617:
6482:Inflammation
6467:Alloimmunity
6462:Autoimmunity
6447:Immunity vs.
6399:Autoantibody
6297:Superantigen
5980:
5852:the original
5847:
5821:
5764:
5760:
5750:
5739:. Retrieved
5737:. 2018-08-21
5734:
5725:
5690:
5686:
5676:
5651:
5647:
5640:
5615:
5611:
5605:
5562:
5558:
5548:
5511:
5507:
5497:
5462:
5458:
5447:
5412:
5408:
5398:
5363:
5359:
5348:
5321:
5317:
5307:
5280:
5276:
5266:
5233:
5229:
5216:
5181:
5177:
5167:
5132:
5128:
5118:
5085:
5081:
5075:
5040:
5036:
5026:
4991:
4987:
4977:
4942:
4938:
4888:
4884:
4874:
4839:
4835:
4825:
4790:
4786:
4776:
4741:
4737:
4727:
4692:
4688:
4678:
4641:
4637:
4627:
4597:(6): 492–9.
4594:
4590:
4584:
4549:
4545:
4535:
4500:
4496:
4486:
4449:
4445:
4435:
4400:
4396:
4386:
4351:
4347:
4337:
4300:
4296:
4270:. Retrieved
4257:
4237:
4214:
4175:(4): 153–8.
4172:
4168:
4158:
4123:
4120:Mol. Immunol
4119:
4069:
4065:
4055:
4044:. Retrieved
4040:
4030:
3995:
3991:
3981:
3948:
3944:
3938:
3919:
3875:
3871:
3861:
3852:
3817:
3813:
3803:
3762:
3758:
3752:
3711:
3707:
3701:
3676:
3672:
3666:
3649:
3608:
3604:
3590:
3558:(8): 767–9.
3555:
3551:
3541:
3496:
3492:
3482:
3447:
3443:
3433:
3408:
3404:
3398:
3363:
3359:
3349:
3312:
3308:
3256:
3252:
3242:
3205:
3201:
3191:
3156:
3152:
3142:
3105:
3101:
3049:
3045:
3035:
2998:
2994:
2984:
2951:
2947:
2941:
2917:(5): 591–4.
2914:
2910:
2900:
2868:(4): 307–8.
2865:
2862:Nat. Immunol
2861:
2851:
2816:
2812:
2801:
2769:(2): 50–56.
2766:
2762:
2752:
2717:
2713:
2703:
2666:
2662:
2652:
2617:
2613:
2600:
2565:
2561:
2551:
2510:
2506:
2500:
2465:
2459:
2424:
2420:
2370:
2366:
2356:
2321:
2317:
2307:
2282:
2278:
2272:
2253:
2247:
2212:
2208:
2197:
2164:
2160:
2147:
2112:
2108:
2098:
2073:
2069:
2063:
2018:
2014:
2004:
1985:
1979:
1944:
1940:
1930:
1903:
1899:
1889:
1852:
1848:
1838:
1830:
1826:
1816:
1807:
1782:. Retrieved
1778:the original
1773:
1764:
1717:
1697:
1663:
1630:
1626:
1617:
1606:
1538:
1516:
1510:
1504:
1503:, including
1498:
1451:
1416:
1404:
1400:SpaceX CRS-3
1389:
1385:
1370:
1310:
1277:
1273:
1267:
1235:
1228:
1172:
1107:
1049:
1012:
995:
991:
990:
979:. Recently,
966:
954:
944:
929:
915:
842:(CCR7), and
829:
812:
774:
602:MHC class II
586:
571:plasma cells
557:
529:
520:
512:
485:
474:phagocytosed
469:
458:
449:autoimmunity
446:
441:
436:
432:
430:
414:
404:
393:
376:
368:
352:
330:
325:
322:downregulate
309:
307:
276:
258:immune cells
248:
209:
186:
182:cell surface
157:
156:
97:
6689:Human cells
6605:Lymphocytes
6264:Lymphocytic
6217:Lymphoblast
5915:Plasmablast
5894:Lymphocytes
5693:(7): e330.
4891:(4): R183.
3878:(6): 1–13.
3872:J Autoimmun
3366:(1): 1–12.
3001:: 6633824.
2285:: 529–560.
2209:JCI Insight
1784:21 December
1739:Immunoblast
1358:calcineurin
1241:-bodies or
1060:MHC class I
861:cells and T
852:lymph nodes
796:MHC class I
792:amino acids
724:IL-21, IL-4
587:CD4 T cells
583:macrophages
268:Development
193:bone marrow
174:lymphocytes
87:Identifiers
6699:Immunology
6678:Categories
6646:Substances
6510:Peripheral
6498:Inaction:
6377:Antibodies
6358:Macrophage
6271:complement
6031:Regulatory
6004:Helper CD4
5930:Follicular
5741:2018-09-22
5565:(1): 948.
5514:(1): 116.
4397:Immunology
4272:2008-04-07
4046:2014-04-14
3360:Immunology
2562:J. Immunol
1855:: 925135.
1756:References
1712:See also:
1618:(May 2023)
1584:Exhaustion
1452:Causes of
1431:Deficiency
1343:and AP-1.
1159:See also:
1155:Activation
1129:isoprenoid
1086:, such as
981:Th17 cells
867:L-selectin
844:L-selectin
784:transplant
708:IRF4, PU.1
303:thymocytes
262:autoimmune
256:, whereby
60:(left), a
6663:Cytolysin
6653:Cytokines
6500:Tolerance
6449:tolerance
6368:Immunogen
6190:LTi cells
6145:Null cell
5993:Thymocyte
5654:: 32–40.
5088:: 78–84.
4994:: 33–39.
4644:(1): 50.
4221:eMedicine
3945:BioEssays
2819:: 76–88.
1492:(AT) and
1298:tyrosines
1211:PH domain
1072:cytokines
1068:vitamin B
1024:with the
621:Cell type
610:cytokines
491:apoptotic
372:pathogens
254:tolerance
232:cytokines
228:cytotoxic
6613:Cellular
6457:Immunity
6455:Action:
6438:Paratope
6426:Idiotype
6416:Allotype
6384:Antibody
6338:Mimotope
6302:Allergen
6285:Antigens
6278:Lymphoid
6178:Nuocytes
6127:NK cells
5959:B10 cell
5801:21576466
5717:26230954
5668:29477343
5632:22189042
5597:29507342
5540:27809856
5489:22186141
5439:29197679
5382:25943855
5340:26963287
5299:26170387
5258:33409478
5250:18475193
5208:25377077
5159:11375065
5110:21657071
5102:29689313
5067:27671246
5018:27993215
4969:22187279
4917:21798063
4866:25113973
4817:23947355
4768:19604493
4738:Immunity
4719:17041596
4670:29914540
4619:11052693
4611:21739672
4576:22623779
4478:29483916
4427:20201977
4378:31570879
4329:34555119
4199:24636916
4150:17825415
4098:26471060
4022:21045195
3973:28521713
3965:14579250
3902:25578468
3844:15300249
3795:38040377
3787:12690201
3736:12594515
3693:17129182
3633:23051753
3582:27717815
3574:20733595
3533:19416870
3474:24450998
3425:28119072
3390:26778581
3341:26136743
3285:25339949
3234:26468291
3183:21458588
3134:26217338
3076:17353286
3027:33506055
2976:30992456
2968:26482978
2933:24434314
2892:11294516
2884:23507634
2843:27894837
2793:21288770
2744:23947354
2695:18657274
2669:(6): 6.
2644:16412760
2636:16237082
2592:22340282
2535:10537110
2492:25261209
2451:30867582
2399:32973809
2373:: 2025.
2348:17476341
2299:10837068
2239:28814669
2189:33154019
2181:20431619
2139:15983629
2090:12414722
2055:24927565
1971:17325202
1922:28002722
1900:Immunity
1881:22474485
1723:See also
1521:. Also,
1518:Listeria
1468:(SCID),
1464:such as
1456:include
1239:necrotic
1080:adaptive
977:TGF-beta
823:express
598:antigens
486:class II
433:class II
421:antigens
384:antigens
299:engraft:
62:platelet
6684:T cells
6658:Opsonin
6637:NK cell
6625:Humoral
6505:Central
6472:Allergy
6421:Isotype
6321:Epitope
6292:Antigen
5981:T cells
5910:B1 cell
5902:B cells
5792:3107287
5769:Bibcode
5708:4526784
5588:5838096
5567:Bibcode
5531:5093947
5480:3288154
5430:5826878
5390:5348557
5199:4483591
5150:1088449
5058:5110001
5009:5535083
4960:3361243
4908:3387626
4857:4144726
4808:3748387
4759:3039716
4710:2535582
4661:6006750
4567:3421680
4527:7966595
4469:5816053
4452:: 219.
4418:2842494
4369:7286441
4320:8460019
4190:3989030
4141:2131735
4089:4608155
4013:3035066
3893:4340844
3835:2776074
3767:Bibcode
3759:Science
3716:Bibcode
3641:4419703
3613:Bibcode
3524:2688861
3501:Bibcode
3465:3992039
3411:: 1–7.
3381:4819138
3332:4468870
3315:: 303.
3276:4189401
3259:: 450.
3225:4683245
3174:3130845
3125:4492155
3108:: 344.
3067:1865739
3018:7808823
2924:3928692
2834:6066671
2784:3039080
2735:3748618
2686:2515281
2584:2965180
2543:4378970
2515:Bibcode
2442:6804569
2390:7461801
2339:1857272
2230:5621870
2131:9054502
2046:4078834
2023:Bibcode
1962:2137912
1872:3312336
1701:NK cell
1669:(PD1),
1613:Discuss
1496:(WAS).
1484:(DGS),
1398:on the
1353:calcium
1263:anergic
1226:cells.
1187:peptide
1123:. Some
942:cells.
595:peptide
567:B cells
470:class I
444:cells.
437:class I
407:stage.
291:myeloid
285:during
164:of the
158:T cells
110:D013601
70:Details
6630:B cell
6618:T cell
6363:B cell
6326:Linear
6314:Hapten
5925:Memory
5920:Plasma
5829:
5799:
5789:
5715:
5705:
5666:
5630:
5595:
5585:
5538:
5528:
5487:
5477:
5437:
5427:
5388:
5380:
5338:
5297:
5256:
5248:
5206:
5196:
5157:
5147:
5108:
5100:
5065:
5055:
5016:
5006:
4967:
4957:
4915:
4905:
4864:
4854:
4815:
4805:
4766:
4756:
4717:
4707:
4668:
4658:
4617:
4609:
4574:
4564:
4525:
4518:237269
4515:
4476:
4466:
4425:
4415:
4376:
4366:
4327:
4317:
4245:
4197:
4187:
4148:
4138:
4096:
4086:
4072:: 85.
4020:
4010:
3971:
3963:
3926:
3900:
3890:
3842:
3832:
3793:
3785:
3744:574770
3742:
3734:
3708:Nature
3691:
3639:
3631:
3605:Nature
3580:
3572:
3531:
3521:
3472:
3462:
3423:
3388:
3378:
3339:
3329:
3283:
3273:
3232:
3222:
3181:
3171:
3132:
3122:
3074:
3064:
3025:
3015:
2974:
2966:
2931:
2921:
2890:
2882:
2841:
2831:
2791:
2781:
2742:
2732:
2693:
2683:
2642:
2634:
2590:
2582:
2541:
2533:
2507:Nature
2490:
2480:
2449:
2439:
2397:
2387:
2346:
2336:
2297:
2260:
2237:
2227:
2215:(16).
2187:
2179:
2137:
2129:
2088:
2053:
2043:
1992:
1969:
1959:
1920:
1879:
1869:
1671:CTLA-4
1540:Cancer
1529:Cancer
1472:, and
1306:SLP-76
1294:ZAP-70
1199:anergy
1145:HMB-PP
1125:murine
1113:mucosa
1076:lysing
1056:mucosa
1052:innate
825:CD45RO
741:IL-22
670:GATA-3
646:, IL-2
201:thymus
197:thymus
76:System
33:T cell
6037:Naïve
5945:Pre-B
5940:Naïve
5855:(PDF)
5844:(PDF)
5386:S2CID
5254:S2CID
5226:(PDF)
5106:S2CID
4615:S2CID
4266:(PDF)
3992:Blood
3969:S2CID
3791:S2CID
3740:S2CID
3655:NIAID
3637:S2CID
3601:(PDF)
3578:S2CID
2972:S2CID
2888:S2CID
2640:S2CID
2610:(PDF)
2588:S2CID
2539:S2CID
2185:S2CID
2157:(PDF)
2135:S2CID
1683:TGF-β
1679:IL-10
1654:CD127
1650:CD62L
1603:split
1377:BCL10
1341:NF-κB
1317:PLC-γ
1219:PKC-θ
1181:, or
955:FOXP3
951:FOXP3
738:Th22
727:Bcl-6
689:RORγt
569:into
283:liver
145:[
134:62870
93:Latin
6269:and
5997:αβ (
5954:cell
5827:ISBN
5797:PMID
5713:PMID
5664:PMID
5628:PMID
5593:PMID
5536:PMID
5485:PMID
5435:PMID
5378:PMID
5336:PMID
5295:PMID
5246:PMID
5204:PMID
5155:PMID
5098:PMID
5063:PMID
5014:PMID
4965:PMID
4939:JAMA
4913:PMID
4862:PMID
4813:PMID
4764:PMID
4715:PMID
4666:PMID
4607:PMID
4572:PMID
4523:PMID
4474:PMID
4423:PMID
4374:PMID
4325:PMID
4243:ISBN
4195:PMID
4146:PMID
4094:PMID
4018:PMID
3961:PMID
3924:ISBN
3898:PMID
3840:PMID
3783:PMID
3732:PMID
3689:PMID
3653:The
3629:PMID
3570:PMID
3529:PMID
3470:PMID
3421:PMID
3386:PMID
3337:PMID
3281:PMID
3230:PMID
3179:PMID
3130:PMID
3072:PMID
3023:PMID
2999:2021
2964:PMID
2929:PMID
2880:PMID
2839:PMID
2789:PMID
2740:PMID
2691:PMID
2632:PMID
2580:PMID
2531:PMID
2488:PMID
2478:ISBN
2447:PMID
2395:PMID
2344:PMID
2295:PMID
2258:ISBN
2235:PMID
2177:PMID
2127:PMID
2109:Cell
2086:PMID
2051:PMID
1990:ISBN
1967:PMID
1918:PMID
1877:PMID
1853:2012
1786:2021
1687:Treg
1652:and
1646:CD69
1642:CD43
1638:TNFα
1636:and
1634:IL-2
1566:and
1515:and
1419:pMHC
1381:CARD
1379:via
1362:NFAT
1329:PI3K
1321:VAV1
1304:and
1286:ITAM
1278:TCRβ
1276:and
1274:TCRα
1268:The
1259:OX40
1251:CD86
1249:and
1247:CD80
1223:IL-2
1215:PDK1
1207:PIP3
1203:PI3K
1183:ICOS
1179:CD28
1121:APCs
1034:CD1d
971:and
962:IPEX
875:EMRA
871:CD44
863:EMRA
848:CD44
744:AHR
705:IL-9
682:Th17
650:Tbet
644:IFNγ
581:and
573:and
495:Treg
396:TCRβ
345:CD34
339:and
316:nor
293:and
105:MeSH
6591:HLA
6587:MHC
5952:reg
5787:PMC
5777:doi
5765:108
5703:PMC
5695:doi
5656:doi
5652:190
5620:doi
5616:142
5583:PMC
5575:doi
5526:PMC
5516:doi
5475:PMC
5467:doi
5425:PMC
5417:doi
5368:doi
5326:doi
5285:doi
5281:195
5238:doi
5194:PMC
5186:doi
5145:PMC
5137:doi
5133:356
5090:doi
5086:192
5053:PMC
5045:doi
5041:100
5004:PMC
4996:doi
4992:208
4955:PMC
4947:doi
4943:306
4903:PMC
4893:doi
4852:PMC
4844:doi
4840:211
4803:PMC
4795:doi
4791:255
4754:PMC
4746:doi
4705:PMC
4697:doi
4656:PMC
4646:doi
4599:doi
4562:PMC
4554:doi
4513:PMC
4505:doi
4464:PMC
4454:doi
4413:PMC
4405:doi
4401:129
4364:PMC
4356:doi
4315:PMC
4305:doi
4219:at
4185:PMC
4177:doi
4136:PMC
4128:doi
4084:PMC
4074:doi
4008:PMC
4000:doi
3996:117
3953:doi
3888:PMC
3880:doi
3830:PMC
3822:doi
3775:doi
3763:300
3724:doi
3712:421
3681:doi
3621:doi
3609:491
3560:doi
3519:PMC
3509:doi
3497:106
3460:PMC
3452:doi
3448:176
3413:doi
3409:183
3376:PMC
3368:doi
3364:148
3327:PMC
3317:doi
3271:PMC
3261:doi
3220:PMC
3210:doi
3206:290
3169:PMC
3161:doi
3120:PMC
3110:doi
3062:PMC
3054:doi
3013:PMC
3003:doi
2956:doi
2919:PMC
2915:138
2870:doi
2829:PMC
2821:doi
2779:PMC
2771:doi
2730:PMC
2722:doi
2718:255
2681:PMC
2671:doi
2622:doi
2618:175
2570:doi
2566:140
2523:doi
2511:401
2470:doi
2437:PMC
2429:doi
2385:PMC
2375:doi
2334:PMC
2326:doi
2322:117
2287:doi
2225:PMC
2217:doi
2169:doi
2117:doi
2078:doi
2041:PMC
2031:doi
2019:111
1957:PMC
1949:doi
1945:204
1908:doi
1867:PMC
1857:doi
1681:or
1611:. (
1446:HIV
1345:IP3
1337:IP3
1333:DAG
1325:Itk
1313:LAT
1302:LAT
1290:Lck
1282:CD3
1191:APC
1064:MR1
994:or
973:Th3
969:Tr1
940:reg
936:reg
932:reg
788:CD8
720:Tfh
701:Th9
663:Th2
639:Th1
600:by
591:CD4
476:by
349:CD1
341:CD7
337:CD5
333:CD2
318:CD8
314:CD4
224:CD4
222:or
220:CD8
129:FMA
6680::
6351::
6099:γδ
6073:VM
6065:RM
6057:EM
6049:CM
6029:/
6027:17
6021:/
6013:/
6010:FH
6006:/
5846:.
5795:.
5785:.
5775:.
5763:.
5759:.
5733:.
5711:.
5701:.
5689:.
5685:.
5662:.
5650:.
5626:.
5614:.
5591:.
5581:.
5573:.
5561:.
5557:.
5534:.
5524:.
5510:.
5506:.
5483:.
5473:.
5463:72
5461:.
5457:.
5433:.
5423:.
5413:24
5411:.
5407:.
5384:.
5376:.
5364:15
5362:.
5358:.
5334:.
5322:38
5320:.
5316:.
5293:.
5279:.
5275:.
5252:.
5244:.
5234:85
5232:.
5228:.
5202:.
5192:.
5182:26
5180:.
5176:.
5153:.
5143:.
5131:.
5127:.
5104:.
5096:.
5084:.
5061:.
5051:.
5039:.
5035:.
5012:.
5002:.
4990:.
4986:.
4963:.
4953:.
4941:.
4937:.
4925:^
4911:.
4901:.
4889:15
4887:.
4883:.
4860:.
4850:.
4838:.
4834:.
4811:.
4801:.
4789:.
4785:.
4762:.
4752:.
4742:31
4740:.
4736:.
4713:.
4703:.
4693:12
4691:.
4687:.
4664:.
4654:.
4642:49
4640:.
4636:.
4613:.
4605:.
4595:12
4593:.
4570:.
4560:.
4550:86
4548:.
4544:.
4521:.
4511:.
4501:68
4499:.
4495:.
4472:.
4462:.
4448:.
4444:.
4421:.
4411:.
4399:.
4395:.
4372:.
4362:.
4352:19
4350:.
4346:.
4323:.
4313:.
4301:17
4299:.
4295:.
4281:^
4227:^
4207:^
4193:.
4183:.
4173:35
4171:.
4167:.
4144:.
4134:.
4124:45
4122:.
4118:.
4106:^
4092:.
4082:.
4070:22
4068:.
4064:.
4039:.
4016:.
4006:.
3994:.
3990:.
3967:.
3959:.
3949:25
3947:.
3910:^
3896:.
3886:.
3876:57
3874:.
3870:.
3838:.
3828:.
3816:.
3812:.
3789:.
3781:.
3773:.
3761:.
3738:.
3730:.
3722:.
3710:.
3687:.
3677:25
3675:.
3635:.
3627:.
3619:.
3607:.
3603:.
3576:.
3568:.
3556:88
3554:.
3550:.
3527:.
3517:.
3507:.
3495:.
3491:.
3468:.
3458:.
3446:.
3442:.
3419:.
3407:.
3384:.
3374:.
3362:.
3358:.
3335:.
3325:.
3311:.
3307:.
3293:^
3279:.
3269:.
3255:.
3251:.
3228:.
3218:.
3204:.
3200:.
3177:.
3167:.
3157:13
3155:.
3151:.
3128:.
3118:.
3104:.
3100:.
3084:^
3070:.
3060:.
3050:75
3048:.
3044:.
3021:.
3011:.
2997:.
2993:.
2970:.
2962:.
2952:16
2950:.
2927:.
2913:.
2909:.
2886:.
2878:.
2866:14
2864:.
2860:.
2837:.
2827:.
2817:77
2815:.
2811:.
2787:.
2777:.
2767:32
2765:.
2761:.
2738:.
2728:.
2716:.
2712:.
2689:.
2679:.
2665:.
2661:.
2638:.
2630:.
2616:.
2612:.
2586:.
2578:.
2564:.
2560:.
2537:.
2529:.
2521:.
2509:.
2486:.
2476:.
2445:.
2435:.
2425:16
2423:.
2419:.
2407:^
2393:.
2383:.
2371:11
2369:.
2365:.
2342:.
2332:.
2320:.
2316:.
2293:.
2283:18
2281:.
2233:.
2223:.
2211:.
2207:.
2183:.
2175:.
2165:11
2163:.
2159:.
2133:.
2125:.
2113:88
2111:.
2107:.
2084:.
2074:21
2072:.
2049:.
2039:.
2029:.
2017:.
2013:.
1965:.
1955:.
1943:.
1939:.
1916:.
1904:45
1902:.
1898:.
1875:.
1865:.
1851:.
1847:.
1825:.
1806:.
1794:^
1772:.
1644:,
1615:)
1562::
1509:,
1409:.
1349:ER
1323:,
1319:,
1255:B7
964:.
899:VM
897:(T
889:RM
885:RM
883:(T
859:EM
836:CM
827:.
778:(T
561:(T
335:,
207:.
184:.
117:TH
6589:/
6347:/
6256:e
6249:t
6242:v
6071:T
6063:T
6055:T
6047:T
6033:)
6025:h
6023:T
6019:3
6017:h
6015:T
6008:T
5950:B
5886:e
5879:t
5872:v
5835:.
5803:.
5779::
5771::
5744:.
5719:.
5697::
5691:5
5670:.
5658::
5634:.
5622::
5599:.
5577::
5569::
5563:9
5542:.
5518::
5512:9
5491:.
5469::
5441:.
5419::
5392:.
5370::
5342:.
5328::
5301:.
5287::
5260:.
5240::
5210:.
5188::
5161:.
5139::
5112:.
5092::
5069:.
5047::
5020:.
4998::
4971:.
4949::
4919:.
4895::
4868:.
4846::
4819:.
4797::
4770:.
4748::
4721:.
4699::
4672:.
4648::
4621:.
4601::
4578:.
4556::
4529:.
4507::
4480:.
4456::
4450:9
4429:.
4407::
4380:.
4358::
4331:.
4307::
4275:.
4251:.
4201:.
4179::
4152:.
4130::
4100:.
4076::
4049:.
4024:.
4002::
3975:.
3955::
3932:.
3904:.
3882::
3846:.
3824::
3818:5
3797:.
3777::
3769::
3746:.
3726::
3718::
3695:.
3683::
3661:.
3643:.
3623::
3615::
3584:.
3562::
3535:.
3511::
3503::
3476:.
3454::
3427:.
3415::
3392:.
3370::
3343:.
3319::
3313:6
3287:.
3263::
3257:5
3236:.
3212::
3185:.
3163::
3136:.
3112::
3106:6
3078:.
3056::
3029:.
3005::
2978:.
2958::
2935:.
2894:.
2872::
2845:.
2823::
2795:.
2773::
2746:.
2724::
2697:.
2673::
2667:5
2646:.
2624::
2594:.
2572::
2545:.
2525::
2517::
2494:.
2472::
2453:.
2431::
2401:.
2377::
2350:.
2328::
2301:.
2289::
2266:.
2241:.
2219::
2213:2
2191:.
2171::
2141:.
2119::
2092:.
2080::
2057:.
2033::
2025::
1998:.
1973:.
1951::
1924:.
1910::
1883:.
1859::
1788:.
780:C
563:H
244:H
236:H
149:]
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.