229:. The spin–orbit coupling is achieved by selecting 2 spin states from the manifold of hyperfine states to couple with a two photon process. For weak coupling, the resulting Hamiltonian has a spectrum with a double degenerate ground state in the first band. In this regime, the single particle dispersion relation can host a BEC in each minima. The result is that the BEC has 2 momentum components which can interfere in real space. The interference pattern will appear as fringes in the density of the BEC. The periodicity of the fringes is a result of the Raman coupling beam wavelength modified by the coupling strength and by interactions within the BEC. Spin orbit coupling breaks the gauge symmetry of the system and the time reversal symmetry. The formation of the stripes breaks a continuous translational symmetry.
213:
105:
experimental investigation on local lattice fluctuations have driven the community to the conclusion that it is a problem of quantum physics in complex matter. A growing paradigm for high-temperature superconductivity in superstripes is that a key term is the quantum interference effect between pairing channels, i.e., a resonance in the exchange-like, Josephson-like pair transfer term between different condensates. The quantum configuration interaction between different pairing channels is a particular case of
138:
235:
In 2017, two research groups from ETH Zurich and from MIT reported on the first creation of a supersolid with ultracold quantum gases. The MIT group exposed a Bose-Einstein condensate in a double-well potential to light beams that created an effective spin-orbit coupling. The interference between the
57:
The superstripes show multigap superconductivity near a 2.5 Lifshitz transition where the renormalization of chemical potential at the metal-to-superconductor transition is not negligeable and the self-consistent solution of the gaps equation is required. The superstripes lattice scenario is made of
82:
Superconductivity" held in Rome to describe the particular phase of matter where a broken symmetry appearing at a transition from a phase with higher dimensionality N (3D or 2D) to a phase with lower dimensionality N-1 (2D or 1D) favors the superconducting or superfluid phase and it could increase
177:
In these materials the joint effect of (a) increasing the lattice misfit strain to a critical value, and (b) tuning the chemical potential near a
Lifshitz transition in presence of electron-electron interactions induce a lattice instability with formation of the network of superconducting striped
104:
transition temperatures is rightly considered to be one of the most difficult problems in theoretical physics. The problem remained elusive for many years since these materials have generally a very complex structure making unuseful theoretical modelling for a homogeneous system. The advances in
113:
in atomic and nuclear physics. The critical temperature shows a suppression, due to a Fano antiresonance, when the chemical potential is tuned at a band edge where a new Fermi surface spot appears i.e., an "electronic topological transition" (ETT) or 2.5 Lifshitz transition or, a metal-to-metal
216:
Dispersion relations of a spin–orbit coupled system for different coupling strengths. Box A has no coupling. The dispersion relation shows 2 shifted free space dispersion relations. Box B shows how the gap at k=0 opens for weak coupling. Box C shows the strong coupling limit where the double
91:
was introduced to make the key difference with the stripes scenario where the phase transition from a phase with higher dimensionality N (like a 2D electron gas) to the phase with broken symmetry and lower dimensionality (like a quasi 1D striped fluid) competes and suppresses the transition
128:
can be obtained by changing: the charge density and/or the superlattice structural parameters, and/or the superlattice misfit strain and/or the disorder. Direct evidence for shape resonances in superstripes matter is provided by the anomalous variation of the isotope effect on the critical
123:
is further amplified at the shape resonance if in this range the Fermi surface of the appearing fermi surface spot changes its dimensionality (for example the
Lifshitz transition for opening a neck in a tubular Fermi surface). The tuning of the chemical potential at the
1147:
Caivano, R.; Fratini, M.; Poccia, N.; Ricci, A.; Puri, A.; Ren, Z. A.; Dong, X. L.; Yang, J.; Lu, W.; Zhao, Z. X.; Barba, L.; Bianconi, A. (2009). "Feshbach resonance and mesoscopic phase separation near a quantum critical point in multiband Fe
1532:
Li, Jun-Ru; Lee, Jeongwon; Huang, Wujie; Burchesky, Sean; Shteynas, Boris; Top, Furkan Çağrı; Jamison, Alan O.; Ketterle, Wolfgang (1 March 2017). "A stripe phase with supersolid properties in spin–orbit-coupled Bose–Einstein condensates".
157:
It was known that the high-temperature cuprate superconductors have a complex lattice structure. In 1993 it was proposed that these materials belong to a particular class of materials called heterostructures at atomic limit made of a
169:
All new high-temperature superconducting materials discovered in the years 2001–2013 are heterostructures at atomic limit made of the active atomic layers: honeycomb boron layer in diborides, graphene in intercalated graphite,
437:
Innocenti, D.; Poccia, N.; Ricci, A.; Valletta, A.; Caprara, S.; Perali, A.; Bianconi, A. (2010). "Resonant and crossover phenomena in a multiband superconductor: Tuning the chemical potential near a band edge".
92:
temperature to the superfluid phase and favors modulated striped magnetic ordering. In the broken symmetry of superstripes phase the structural modulation coexists and favors high-temperature superconductivity.
118:
amplification is switched on when the chemical potential is tuned above the band edge in an energy region away from the band edge of the order of 1 or 2 times the energy cut off of the pairing interaction. The
491:
Perali, A.; Innocenti, D.; Valletta, A.; Bianconi, A. (2012). "Anomalous isotope effect near a 2.5 Lifshitz transition in a multi-band multi-condensate superconductor made of a superlattice of stripes".
181:
This complex scenario has been called "superstripes scenario" where the 2D atomic layers show functional lattice inhomogeneities: "ripples puddles" of local lattice distortion have been observed in La
1317:
Poccia, N.; Fratini, M.; Ricci, A.; Campi, G.; Barba, L.; Vittorini-Orgeas, A.; Bianconi, G.; Aeppli, G.; Bianconi, A. (2011). "Evolution and control of oxygen order in a cuprate superconductor".
1205:
Ricci, A.; Poccia, N.; Campi, G.; Joseph, B.; Arrighetti, G.; Barba, L.; Reynolds, M.; Burghammer, M.; Takeya, H.; Mizuguchi, Y.; Takano, Y.; Colapietro, M.; Saini, N. L.; Bianconi, A. (2011).
42:
have been found to favor superconductivity. Before a broken spatial symmetry was expected to compete and suppress the superconducting order. The driving mechanism for the amplification of the
928:
Poccia, N.; Ricci, A.; Campi, G.; Fratini, M.; Puri, A.; Gioacchino, D. D.; Marcelli, A.; Reynolds, M.; Burghammer, M.; Saini, N. L.; Aeppli, G.; Bianconi, A. (2012).
1963:
345:
Perali, A.; Bianconi, A.; Lanzara, A.; Saini, N. L. (1996). "The gap amplification at a shape resonance in a superlattice of quantum stripes: A mechanism for high T
1696:
1633:
678:
Raveau, B. (2007). "The perovskite history: More than 60 years of research from the discovery of ferroelectricity to colossal magnetoresistance via high T
232:
Recent efforts have attempted to observe the stripe phase in a
Rubidium-87 BEC, however the stripes were too small and too low contrast to be detected.
1445:
Li, Yun; Pitaevskii, Lev P.; Stringari, Sandro (2012). "Quantum
Tricriticality and Phase Transitions in Spin-Orbit Coupled Bose-Einstein Condensates".
2086:
58:
puddles of multigap superstripes matter forming a superconducting network where different gaps are not only different in different portions of the
236:
atoms on the two spin-orbit coupled lattice sites gave rise to a density modulation that establishes a stripe phase with supersolid properties.
809:
662:
321:
1671:
825:
Bianconi, A. (1994). "On the possibility of new high Tc superconductors by producing metal heterostructures as in the cuprate perovskites".
2055:
1793:
545:
Hosono, H.; Tanabe, K.; Takayama-Muromachi, E.; Kageyama, H.; Yamanaka, S.; Kumakura, H.; Nohara, M.; Hiramatsu, H.; Fujitsu, S. (2015).
1903:
101:
84:
1991:
784:
759:
629:
197:
and in YBaCuO The network of superconducting striped puddles has been found also in MFeAs pnictides and recently in KFeSe selenides
547:"Exploration of new superconductors and functional materials, and fabrication of superconducting tapes and wires of iron pnictides"
1712:
174:
atomic bbc monolayers in cobaltates, FeAs atomic fluorite monolayers in pnictides, FeSe atomic fluorite monolayers in selenides.
1908:
1626:
110:
1691:
1661:
2032:
1884:
1828:
1803:
1597:
402:
Bianconi, A.; Valletta, A.; Perali, A.; Saini, N. L. (1998). "Superconductivity of a striped phase at the atomic limit".
222:
1934:
1863:
1879:
1798:
1666:
1602:
879:
1986:
1981:
1619:
1078:
Campi, G.; Ricci, A.; Poccia, N.; Barba, L.; Arrighetti, G.; Burghammer, M.; Caporale, A. S.; Bianconi, A. (2013).
1686:
1939:
163:
1722:
1773:
226:
212:
2091:
2065:
1924:
1856:
1976:
1949:
1929:
1851:
1846:
1506:
2050:
189:
in Bi222; striped puddles of ordered dopants in the spacer layers have been seen in superoxygenated La
39:
2006:
1552:
1464:
1400:
1336:
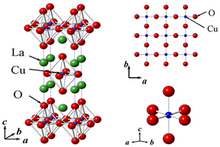
1291:
1240:
1171:
1113:
1036:
959:
902:
844:
722:
568:
511:
457:
411:
368:
264:
1080:"Scanning micro-x-ray diffraction unveils the distribution of oxygen chain nanoscale puddles in YBa
35:
2037:
1788:
1748:
1576:
1542:
1488:
1454:
1424:
1390:
1360:
1326:
1256:
1230:
1187:
1161:
1129:
1103:
1060:
1026:
949:
860:
834:
558:
527:
501:
473:
447:
384:
358:
327:
299:
201:
63:
1005:
Fratini, M.; Poccia, N.; Ricci, A.; Campi, G.; Burghammer, M.; Aeppli, G.; Bianconi, A. (2010).
1813:
1642:
1568:
1480:
1416:
1352:
1052:
987:
805:
780:
755:
658:
625:
594:
317:
291:
43:
2022:
1996:
1768:
1743:
1676:
1560:
1472:
1408:
1344:
1299:
1248:
1179:
1121:
1044:
977:
967:
910:
852:
730:
691:
650:
617:
584:
576:
519:
465:
419:
376:
309:
272:
59:
2045:
62:
but also in different portions of the real space with a complex scale free distribution of
1778:
695:
125:
106:
47:
31:
23:
1381:
Galitski, Victor; Spielman, Ian B. (2013-02-07). "Spin-orbit coupling in quantum gases".
735:
710:
645:
Müller, K. A. (2005). "Essential
Heterogeneities in Hole-Doped Cuprate Superconductors".
523:
1556:
1468:
1404:
1340:
1295:
1244:
1183:
1175:
1117:
1040:
963:
906:
848:
726:
580:
572:
515:
461:
415:
372:
268:
1783:
1727:
1717:
1681:
982:
929:
589:
546:
51:
1303:
423:
2080:
1275:
1260:
1206:
1133:
1079:
864:
856:
531:
477:
380:
331:
1492:
1364:
1191:
1006:
388:
83:
the normal to superconducting transition temperature with the possible emergence of
22:
is a generic name for a phase with spatial broken symmetry that favors the onset of
1808:
1763:
1758:
1580:
1476:
1064:
159:
1428:
1944:
1753:
137:
30:
quantum order. This scenario emerged in the 1990s when non-homogeneous metallic
1252:
1125:
469:
1656:
1607:
914:
276:
27:
313:
78:
was introduced in 2000 at the international conference on "Stripes and High T
972:
621:
296:
Phase
Transitions and Self-Organization in Electronic and Molecular Networks
217:
degenerate minima in the first band merge into a single ground state at k=0.
1572:
1484:
1420:
1356:
1056:
991:
598:
16:
Broken symmetry phase favoring onset of superconducting or superfluid order
1280:
lattice: The second variable for the phase diagram of cuprate perovskites"
1971:
1564:
1412:
1048:
46:
critical temperature in superstripes matter has been proposed to be the
1348:
1207:"Nanoscale phase separation in the iron chalcogenide superconductor K
1611:
654:
1547:
616:. Selected Topics in Superconductivity. Vol. 8. pp. 1–8.
563:
2027:
2001:
1459:
1395:
1331:
1235:
1166:
1108:
1031:
954:
839:
506:
452:
363:
304:
211:
136:
1007:"Scale-free structural organization of oxygen interstitials in La
141:
Crystal structure of the tetragonal (superconductive) phase of La
2060:
1274:
Agrestini, S.; Saini, N. L.; Bianconi, G.; Bianconi, A. (2003).
1615:
777:
Symmetry and heterogeneity in high temperature superconductors
649:. Vol. 114. Berlin/Heidelberg: Springer. pp. 1–11.
647:
Superconductivity in
Complex Systems Structure and Bonding
612:
Müller, K. A. (2002). "From Phase
Separation to Stripes".
200:
Self-organization of lattice defects can be controlled by
930:"Optimum inhomogeneity of local lattice distortions in La
221:
Superstripes (also called stripe phase) can also form in
711:"HTC oxides: A collusion of spin, charge and lattice"
878:
Di Castro, D.; Colapietro, M.; Bianconi, G. (2000).
2015:
1962:
1917:
1893:
1872:
1836:
1827:
1736:
1705:
1649:
1219:
as seen via scanning nanofocused x-ray diffraction"
50:in the energy gap parameters ∆n that is a type of
178:puddles in an insulating or metallic background.
166:by a different material with the role of spacer.
942:Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
754:. New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers.
298:. Fundamental Materials Research. p. 375.
250:
248:
1284:Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and General
129:temperature by tuning the chemical potential.
1627:
8:
551:Science and Technology of Advanced Materials
1507:"MIT researchers create new form of matter"
290:Bianconi, A.; Di Castro, D.; Saini, N. L.;
1833:
1634:
1620:
1612:
1546:
1458:
1394:
1330:
1234:
1165:
1107:
1030:
981:
971:
953:
895:International Journal of Modern Physics B
838:
734:
588:
562:
505:
451:
362:
303:
257:International Journal of Modern Physics B
244:
1440:
1438:
1376:
1374:
1154:Superconductor Science and Technology
779:. Dordrecht Great Britain: Springer.
715:Journal of Physics: Conference Series
696:10.1016/j.progsolidstchem.2007.04.001
494:Superconductor Science and Technology
255:Bianconi, A. (2000). "Superstripes".
7:
880:"Metallic stripes in oxygen doped La
802:Superconductivity in complex systems
102:high-temperature superconductivity
85:high-temperature superconductivity
14:
684:Progress in Solid State Chemistry
162:of superconducting atomic layers
2087:High-temperature superconductors
96:Heterostructures at atomic limit
1477:10.1103/physrevlett.108.225301
736:10.1088/1742-6596/108/1/012027
524:10.1088/0953-2048/25/12/124002
149:: top view (top-right) and CuO
1:
1184:10.1088/0953-2048/22/1/014004
804:. Berlin New York: Springer.
752:Stripes and related phenomena
614:Stripes and Related Phenomena
581:10.1088/1468-6996/16/3/033503
424:10.1016/S0921-4534(97)01825-X
114:topological transition. The T
857:10.1016/0038-1098(94)90354-9
404:Physica C: Superconductivity
381:10.1016/0038-1098(96)00373-0
204:. and photoinduced effects.
54:for coexisting condensates.
1304:10.1088/0305-4470/36/35/302
2108:
1964:Technological applications
1253:10.1103/physrevb.84.060511
1126:10.1103/physrevb.87.014517
827:Solid State Communications
470:10.1103/physrevb.82.184528
351:Solid State Communications
153:octahedron (bottom-right).
109:belonging to the group of
1706:Characteristic parameters
1152:-based superconductors".
915:10.1142/S0217979200003927
277:10.1142/S0217979200003769
223:Bose–Einstein condensates
208:Bose–Einstein condensates
1723:London penetration depth
314:10.1007/0-306-47113-2_24
294:(2002). "Superstripes".
111:Fano Feshbach resonances
2016:List of superconductors
1894:By critical temperature
1447:Physical Review Letters
973:10.1073/pnas.1208492109
622:10.1007/0-306-47100-0_1
1606:Superstripes web page
800:Müller, K. A. (2005).
709:Bishop, A. R. (2008).
218:
154:
1662:Bean's critical state
215:
140:
89:superstripes scenario
1837:By magnetic response
775:Bianconi, A (2006).
750:Bianconi, A (2000).
682:superconductivity".
263:(29n31): 3289–3297.
1789:persistent currents
1774:Little–Parks effect
1565:10.1038/nature21431
1557:2017Natur.543...91L
1469:2012PhRvL.108v5301L
1413:10.1038/nature11841
1405:2013Natur.494...49G
1341:2011NatMa..10..733P
1296:2003JPhA...36.9133A
1245:2011PhRvB..84f0511R
1176:2009SuScT..22a4004C
1118:2013PhRvB..87a4517C
1049:10.1038/nature09260
1041:2010Natur.466..841F
964:2012PNAS..10915685P
948:(39): 15685–15690.
907:2000IJMPB..14.3438D
849:1994SSCom..89..933B
727:2008JPhCS.108a2027B
573:2015STAdM..16c3503H
516:2012SuScT..25l4002P
462:2010PhRvB..82r4528I
416:1998PhyC..296..269B
373:1996SSCom.100..181P
269:2000IJMPB..14.3289B
227:spin–orbit coupling
64:Josephson junctions
1749:Andreev reflection
1744:Abrikosov vortices
1601:Superstripes 2010
1596:Superstripes 2008
1276:"The strain of CuO
219:
202:strain engineering
155:
100:The prediction of
2074:
2073:
1992:quantum computing
1958:
1957:
1814:superdiamagnetism
1643:Superconductivity
1223:Physical Review B
1096:Physical Review B
811:978-3-540-23124-0
664:978-3-540-31499-8
440:Physical Review B
323:978-0-306-46568-0
44:superconductivity
2099:
2023:bilayer graphene
1997:Rutherford cable
1909:room temperature
1904:high temperature
1834:
1794:proximity effect
1769:Josephson effect
1713:coherence length
1636:
1629:
1622:
1613:
1585:
1584:
1550:
1529:
1523:
1522:
1520:
1518:
1503:
1497:
1496:
1462:
1442:
1433:
1432:
1398:
1378:
1369:
1368:
1349:10.1038/nmat3088
1334:
1319:Nature Materials
1314:
1308:
1307:
1271:
1265:
1264:
1238:
1202:
1196:
1195:
1169:
1144:
1138:
1137:
1111:
1075:
1069:
1068:
1034:
1002:
996:
995:
985:
975:
957:
925:
919:
918:
892:
875:
869:
868:
842:
822:
816:
815:
797:
791:
790:
772:
766:
765:
747:
741:
740:
738:
706:
700:
699:
690:(2–4): 171–173.
675:
669:
668:
642:
636:
635:
609:
603:
602:
592:
566:
542:
536:
535:
509:
488:
482:
481:
455:
434:
428:
427:
399:
393:
392:
366:
342:
336:
335:
307:
287:
281:
280:
252:
40:spatial symmetry
32:heterostructures
2107:
2106:
2102:
2101:
2100:
2098:
2097:
2096:
2077:
2076:
2075:
2070:
2041:
2011:
1954:
1913:
1900:low temperature
1889:
1868:
1823:
1779:Meissner effect
1732:
1728:Silsbee current
1701:
1667:Ginzburg–Landau
1645:
1640:
1593:
1588:
1541:(7643): 91–94.
1531:
1530:
1526:
1516:
1514:
1505:
1504:
1500:
1444:
1443:
1436:
1389:(7435): 49–54.
1380:
1379:
1372:
1316:
1315:
1311:
1279:
1273:
1272:
1268:
1218:
1214:
1210:
1204:
1203:
1199:
1146:
1145:
1141:
1091:
1087:
1083:
1077:
1076:
1072:
1025:(7308): 841–4.
1014:
1010:
1004:
1003:
999:
937:
933:
927:
926:
922:
901:(29n31): 3438.
890:
887:
883:
877:
876:
872:
833:(11): 933–936.
824:
823:
819:
812:
799:
798:
794:
787:
774:
773:
769:
762:
749:
748:
744:
708:
707:
703:
681:
677:
676:
672:
665:
655:10.1007/b101015
644:
643:
639:
632:
611:
610:
606:
544:
543:
539:
490:
489:
485:
436:
435:
431:
401:
400:
396:
348:
344:
343:
339:
324:
289:
288:
284:
254:
253:
246:
242:
210:
196:
192:
188:
184:
173:
152:
148:
144:
135:
126:shape resonance
122:
117:
107:shape resonance
98:
81:
72:
48:shape resonance
24:superconducting
17:
12:
11:
5:
2105:
2103:
2095:
2094:
2092:Quantum phases
2089:
2079:
2078:
2072:
2071:
2069:
2068:
2063:
2058:
2053:
2048:
2043:
2039:
2035:
2030:
2025:
2019:
2017:
2013:
2012:
2010:
2009:
2004:
1999:
1994:
1989:
1984:
1979:
1977:electromagnets
1974:
1968:
1966:
1960:
1959:
1956:
1955:
1953:
1952:
1947:
1942:
1937:
1932:
1927:
1921:
1919:
1918:By composition
1915:
1914:
1912:
1911:
1906:
1901:
1897:
1895:
1891:
1890:
1888:
1887:
1885:unconventional
1882:
1876:
1874:
1873:By explanation
1870:
1869:
1867:
1866:
1861:
1860:
1859:
1854:
1849:
1840:
1838:
1831:
1829:Classification
1825:
1824:
1822:
1821:
1816:
1811:
1806:
1801:
1796:
1791:
1786:
1781:
1776:
1771:
1766:
1761:
1756:
1751:
1746:
1740:
1738:
1734:
1733:
1731:
1730:
1725:
1720:
1718:critical field
1715:
1709:
1707:
1703:
1702:
1700:
1699:
1694:
1689:
1687:Mattis–Bardeen
1684:
1679:
1674:
1672:Kohn–Luttinger
1669:
1664:
1659:
1653:
1651:
1647:
1646:
1641:
1639:
1638:
1631:
1624:
1616:
1610:
1609:
1604:
1599:
1592:
1591:External links
1589:
1587:
1586:
1524:
1513:. 2 March 2017
1498:
1453:(22): 225301.
1434:
1370:
1309:
1277:
1266:
1216:
1212:
1208:
1197:
1139:
1089:
1085:
1081:
1070:
1012:
1008:
997:
935:
931:
920:
885:
881:
870:
817:
810:
792:
785:
767:
760:
742:
701:
679:
670:
663:
637:
630:
604:
537:
500:(12): 124002.
483:
446:(18): 184528.
429:
394:
357:(3): 181–186.
346:
337:
322:
282:
243:
241:
238:
209:
206:
194:
190:
186:
182:
171:
150:
146:
142:
134:
131:
120:
115:
97:
94:
79:
71:
68:
52:Fano resonance
38:with a broken
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2104:
2093:
2090:
2088:
2085:
2084:
2082:
2067:
2064:
2062:
2059:
2057:
2054:
2052:
2049:
2047:
2044:
2042:
2036:
2034:
2031:
2029:
2026:
2024:
2021:
2020:
2018:
2014:
2008:
2005:
2003:
2000:
1998:
1995:
1993:
1990:
1988:
1985:
1983:
1980:
1978:
1975:
1973:
1970:
1969:
1967:
1965:
1961:
1951:
1948:
1946:
1943:
1941:
1938:
1936:
1935:heavy fermion
1933:
1931:
1928:
1926:
1923:
1922:
1920:
1916:
1910:
1907:
1905:
1902:
1899:
1898:
1896:
1892:
1886:
1883:
1881:
1878:
1877:
1875:
1871:
1865:
1864:ferromagnetic
1862:
1858:
1855:
1853:
1850:
1848:
1845:
1844:
1842:
1841:
1839:
1835:
1832:
1830:
1826:
1820:
1817:
1815:
1812:
1810:
1809:supercurrents
1807:
1805:
1802:
1800:
1797:
1795:
1792:
1790:
1787:
1785:
1782:
1780:
1777:
1775:
1772:
1770:
1767:
1765:
1762:
1760:
1757:
1755:
1752:
1750:
1747:
1745:
1742:
1741:
1739:
1735:
1729:
1726:
1724:
1721:
1719:
1716:
1714:
1711:
1710:
1708:
1704:
1698:
1695:
1693:
1690:
1688:
1685:
1683:
1680:
1678:
1675:
1673:
1670:
1668:
1665:
1663:
1660:
1658:
1655:
1654:
1652:
1648:
1644:
1637:
1632:
1630:
1625:
1623:
1618:
1617:
1614:
1608:
1605:
1603:
1600:
1598:
1595:
1594:
1590:
1582:
1578:
1574:
1570:
1566:
1562:
1558:
1554:
1549:
1544:
1540:
1536:
1528:
1525:
1512:
1508:
1502:
1499:
1494:
1490:
1486:
1482:
1478:
1474:
1470:
1466:
1461:
1456:
1452:
1448:
1441:
1439:
1435:
1430:
1426:
1422:
1418:
1414:
1410:
1406:
1402:
1397:
1392:
1388:
1384:
1377:
1375:
1371:
1366:
1362:
1358:
1354:
1350:
1346:
1342:
1338:
1333:
1328:
1325:(10): 733–6.
1324:
1320:
1313:
1310:
1305:
1301:
1297:
1293:
1289:
1285:
1281:
1270:
1267:
1262:
1258:
1254:
1250:
1246:
1242:
1237:
1232:
1229:(6): 060511.
1228:
1224:
1220:
1201:
1198:
1193:
1189:
1185:
1181:
1177:
1173:
1168:
1163:
1160:(1): 014004.
1159:
1155:
1151:
1143:
1140:
1135:
1131:
1127:
1123:
1119:
1115:
1110:
1105:
1102:(1): 014517.
1101:
1097:
1093:
1074:
1071:
1066:
1062:
1058:
1054:
1050:
1046:
1042:
1038:
1033:
1028:
1024:
1020:
1016:
1001:
998:
993:
989:
984:
979:
974:
969:
965:
961:
956:
951:
947:
943:
939:
924:
921:
916:
912:
908:
904:
900:
896:
889:
874:
871:
866:
862:
858:
854:
850:
846:
841:
836:
832:
828:
821:
818:
813:
807:
803:
796:
793:
788:
786:9781402039881
782:
778:
771:
768:
763:
761:0-306-46419-5
757:
753:
746:
743:
737:
732:
728:
724:
721:(1): 012027.
720:
716:
712:
705:
702:
697:
693:
689:
685:
674:
671:
666:
660:
656:
652:
648:
641:
638:
633:
631:0-306-46419-5
627:
623:
619:
615:
608:
605:
600:
596:
591:
586:
582:
578:
574:
570:
565:
560:
557:(3): 033503.
556:
552:
548:
541:
538:
533:
529:
525:
521:
517:
513:
508:
503:
499:
495:
487:
484:
479:
475:
471:
467:
463:
459:
454:
449:
445:
441:
433:
430:
425:
421:
417:
413:
409:
405:
398:
395:
390:
386:
382:
378:
374:
370:
365:
360:
356:
352:
341:
338:
333:
329:
325:
319:
315:
311:
306:
301:
297:
293:
286:
283:
278:
274:
270:
266:
262:
258:
251:
249:
245:
239:
237:
233:
230:
228:
224:
214:
207:
205:
203:
198:
179:
175:
167:
165:
161:
139:
132:
130:
127:
112:
108:
103:
95:
93:
90:
86:
77:
69:
67:
65:
61:
55:
53:
49:
45:
41:
37:
33:
29:
25:
21:
1945:oxypnictides
1880:conventional
1819:superstripes
1818:
1764:flux pumping
1759:flux pinning
1754:Cooper pairs
1538:
1534:
1527:
1515:. Retrieved
1511:news.mit.edu
1510:
1501:
1450:
1446:
1386:
1382:
1322:
1318:
1312:
1290:(35): 9133.
1287:
1283:
1269:
1226:
1222:
1200:
1157:
1153:
1149:
1142:
1099:
1095:
1073:
1022:
1018:
1000:
945:
941:
923:
898:
894:
873:
830:
826:
820:
801:
795:
776:
770:
751:
745:
718:
714:
704:
687:
683:
673:
646:
640:
613:
607:
554:
550:
540:
497:
493:
486:
443:
439:
432:
410:(3–4): 269.
407:
403:
397:
354:
350:
340:
295:
292:Bianconi, G.
285:
260:
256:
234:
231:
220:
199:
180:
176:
168:
164:intercalated
160:superlattice
156:
99:
88:
76:superstripes
75:
73:
56:
36:atomic limit
20:Superstripes
19:
18:
1804:SU(2) color
1784:Homes's law
225:(BEC) with
87:. The term
2081:Categories
1940:iron-based
1799:reentrance
1548:1610.08194
564:1505.02240
240:References
28:superfluid
1737:Phenomena
1460:1202.3036
1396:1312.3292
1332:1108.4120
1261:118364960
1236:1107.0412
1167:0809.4865
1134:119233632
1109:1212.2742
1032:1008.2015
955:1208.0101
865:119243248
840:1107.3249
532:118510526
507:1209.1528
478:119232655
453:1007.0510
364:1107.3292
332:118809015
305:1107.4858
133:Materials
74:The term
1972:cryotron
1930:cuprates
1925:covalent
1682:Matthias
1650:Theories
1573:28252062
1493:15680596
1485:23003610
1421:23389539
1365:40563268
1357:21857676
1192:55675041
1057:20703301
992:22961255
599:27877784
389:95957312
2066:more...
1950:organic
1581:4463520
1553:Bibcode
1517:6 March
1465:Bibcode
1401:Bibcode
1337:Bibcode
1292:Bibcode
1241:Bibcode
1172:Bibcode
1114:Bibcode
1065:4405620
1037:Bibcode
983:3465392
960:Bibcode
903:Bibcode
845:Bibcode
723:Bibcode
590:5099821
569:Bibcode
512:Bibcode
458:Bibcode
412:Bibcode
369:Bibcode
265:Bibcode
70:History
60:k-space
34:at the
1843:Types
1677:London
1579:
1571:
1535:Nature
1491:
1483:
1429:240743
1427:
1419:
1383:Nature
1363:
1355:
1259:
1190:
1132:
1063:
1055:
1019:Nature
990:
980:
863:
808:
783:
758:
661:
628:
597:
587:
530:
476:
387:
330:
320:
2056:TBCCO
2028:BSCCO
2007:wires
2002:SQUID
1577:S2CID
1543:arXiv
1489:S2CID
1455:arXiv
1425:S2CID
1391:arXiv
1361:S2CID
1327:arXiv
1257:S2CID
1231:arXiv
1188:S2CID
1162:arXiv
1130:S2CID
1104:arXiv
1061:S2CID
1027:arXiv
950:arXiv
891:(PDF)
861:S2CID
835:arXiv
559:arXiv
528:S2CID
502:arXiv
474:S2CID
448:arXiv
385:S2CID
359:arXiv
328:S2CID
300:arXiv
2061:YBCO
2051:NbTi
2046:NbSn
2033:LBCO
1569:PMID
1519:2017
1481:PMID
1417:PMID
1353:PMID
1090:6.33
1053:PMID
988:PMID
806:ISBN
781:ISBN
756:ISBN
659:ISBN
626:ISBN
595:PMID
318:ISBN
2038:MgB
1987:NMR
1982:MRI
1857:1.5
1697:WHH
1692:RVB
1657:BCS
1561:doi
1539:543
1473:doi
1451:108
1409:doi
1387:494
1345:doi
1300:doi
1249:doi
1213:1.6
1209:0.8
1180:doi
1122:doi
1045:doi
1023:466
1013:4+y
1011:CuO
978:PMC
968:doi
946:109
936:4+y
934:CuO
911:doi
884:CuO
853:doi
731:doi
719:108
692:doi
651:doi
618:doi
585:PMC
577:doi
520:doi
466:doi
420:doi
408:296
377:doi
355:100
349:".
310:doi
273:doi
193:CuO
187:4+y
185:CuO
170:CoO
145:CuO
26:or
2083::
1852:II
1575:.
1567:.
1559:.
1551:.
1537:.
1509:.
1487:.
1479:.
1471:.
1463:.
1449:.
1437:^
1423:.
1415:.
1407:.
1399:.
1385:.
1373:^
1359:.
1351:.
1343:.
1335:.
1323:10
1321:.
1298:.
1288:36
1286:.
1282:.
1255:.
1247:.
1239:.
1227:84
1225:.
1221:.
1215:Se
1211:Fe
1186:.
1178:.
1170:.
1158:22
1156:.
1150:As
1128:.
1120:.
1112:.
1100:87
1098:.
1094:.
1084:Cu
1059:.
1051:.
1043:.
1035:.
1021:.
1017:.
986:.
976:.
966:.
958:.
944:.
940:.
909:.
899:14
897:.
893:.
859:.
851:.
843:.
831:89
829:.
729:.
717:.
713:.
688:35
686:.
657:.
624:.
593:.
583:.
575:.
567:.
555:16
553:.
549:.
526:.
518:.
510:.
498:25
496:.
472:.
464:.
456:.
444:82
442:.
418:.
406:.
383:.
375:.
367:.
353:.
326:.
316:.
308:.
271:.
261:14
259:.
247:^
66:.
2040:2
1847:I
1635:e
1628:t
1621:v
1583:.
1563::
1555::
1545::
1521:.
1495:.
1475::
1467::
1457::
1431:.
1411::
1403::
1393::
1367:.
1347::
1339::
1329::
1306:.
1302::
1294::
1278:2
1263:.
1251::
1243::
1233::
1217:2
1194:.
1182::
1174::
1164::
1136:.
1124::
1116::
1106::
1092:"
1088:O
1086:3
1082:2
1067:.
1047::
1039::
1029::
1015:"
1009:2
994:.
970::
962::
952::
938:"
932:2
917:.
913::
905::
888:"
886:4
882:2
867:.
855::
847::
837::
814:.
789:.
764:.
739:.
733::
725::
698:.
694::
680:C
667:.
653::
634:.
620::
601:.
579::
571::
561::
534:.
522::
514::
504::
480:.
468::
460::
450::
426:.
422::
414::
391:.
379::
371::
361::
347:C
334:.
312::
302::
279:.
275::
267::
195:4
191:2
183:2
172:2
151:6
147:4
143:2
121:c
119:T
116:c
80:c
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.