36:
613:
784:
One caveat to this calculation is that the original work was concerned with the hydrography of the East China Sea, where cooling plays the dominant role in the formation of dense shelf water, and that this mechanism may not apply in other regions. However, it has been suggested that other processes
842:
over the last de-glacial transition on the global carbon cycle. During the last glacial maximum sea level was some 120 m (390 ft) lower than today. As sea level rose the surface area of the shelf seas grew and in consequence the strength of the shelf sea pump should increase.
967:
Orr, J. C.; Maier-Reimer, E.; Mikolajewicz, U.; Monfray, P.; Sarmiento, J. L.; Toggweiler, J. R.; Taylor, N. K.; Palmer, J.; Gruber, N.; Sabine, Christopher L.; Le Quéré, Corinne; Key, Robert M.; Boutin, Jacqueline; et al. (2001).
776:
estimates suggest that the ocean is currently responsible for the uptake of approximately 2 Gt C y, and that these estimates are poor for the shelf regions, the continental shelf pump may play an important role in the ocean's
772:(1999) estimated that the continental shelf pump could be responsible for an air-to-sea flux of approximately 1 Gt C y over the world's shelf areas. Given that observational and modelling of anthropogenic emissions of CO
808:(1999) was later confirmed in the Gulf of Biscay, the Middle Atlantic Bight and the North Sea. On the other hand, in the sub-tropical South Atlantic Bight reported a source of CO
906:
Wollast, R. (1998). Evaluation and comparison of the global carbon cycle in the coastal zone and in the open ocean, p. 213-252. In K. H. Brink and A. R. Robinson (eds.),
123:
408:
81:
581:
108:
644:
462:
586:
1471:
51:
1441:
1451:
831:(+11.1 mol C m y; +0.40 Gt C y) from the ensemble of near-shore coastal ecosystems, mostly related to the emission of CO
511:
1466:
516:
501:
181:
868:
Tsunogai, S.; Watanabe, S.; Sato, T. (1999). "Is there a "continental shelf pump" for the absorption of atmospheric CO
571:
469:
175:
169:
751:
the dense, carbon-rich shelf waters sink to the shelf floor and enter the sub-surface layer of the open ocean via
576:
196:
637:
1461:
1436:
1362:"Impact of sea-level rise over the last deglacial transition on the strength of the continental shelf CO2 pump"
551:
479:
474:
457:
302:
163:
61:
676:(as either dissolved or particulate material) from surface waters to the interior of the adjacent deep ocean.
823:
sink (-1.6 mol C m y; -0.45 Gt C y) in agreement with previous estimates. However, the global sink of CO
561:
76:
785:
may drive the pump under different climatic conditions. For instance, in polar regions, the formation of
157:
118:
86:
735:
as a consequence, cooling is greater for continental shelf waters than for neighbouring open ocean waters
1456:
630:
617:
566:
297:
748:
this extra carbon storage is augmented by the increased biological production characteristic of shelves
1190:
969:
1373:
1316:
1238:
1169:
1123:
1082:
1041:
984:
941:
881:
493:
395:
151:
56:
1416:
442:
258:
113:
1391:
1342:
1203:
1010:
521:
289:
273:
268:
191:
1195:
712:, and the observation that, averaged over the year, its surface waters represented a sink for
669:
452:
231:
66:
1150:
819:
fluxes in coastal environments, and shown that globally marginal seas act as a significant CO
1381:
1332:
1324:
1283:
1246:
1185:
1177:
1131:
1090:
1049:
1000:
992:
949:
889:
418:
312:
307:
1030:"An examination of the "continental shelf pump" in an open ocean general circulation model"
893:
35:
1446:
1421:
1411:
970:"Estimates of anthropogenic carbon uptake from four three-dimensional global ocean models"
742:
693:
689:
661:
546:
413:
346:
334:
263:
137:
1377:
1320:
1303:
Borges, A. V.; Delille, B.; Frankignoulle, M. (2005). "Budgeting sinks and sources of CO
1242:
1173:
1127:
1086:
1045:
988:
945:
885:
839:
713:
709:
556:
526:
506:
447:
361:
244:
239:
100:
1135:
953:
1430:
1207:
1014:
1005:
920:
Takahashi, T.; Sutherland, S. C.; Sweeney, C.; et al. (2002). "Global sea-air CO
1346:
1395:
778:
339:
253:
207:
145:
27:
1223:"The role of marsh-dominated heterotrophic continental margins in transport of CO
1071:"European continental shelf as a significant sink for atmospheric carbon dioxide"
1110:
DeGrandpre, M. D.; Olbu, G. J.; Beatty, C. M.; Hammar, T. R. (2002). "Air-sea CO
794:
701:
697:
403:
376:
371:
366:
356:
326:
212:
71:
729:
721:
716:. This observation was combined with others of the distribution of dissolved
351:
793:
of salt that may increase seawater density. Similarly, in tropical regions,
1181:
790:
752:
738:
this leads to the production of relatively cool and dense water on the shelf
717:
1199:
1386:
1361:
1328:
1251:
1222:
1095:
1070:
1054:
1029:
996:
838:
An interesting application of this work has been examining the impact of
827:
in marginal seas could be almost fully compensated by the emission of CO
1288:
1267:
786:
700:
that feeds dense water from the shelf floor into sub-surface (at least
434:
217:
1337:
673:
596:
658:
591:
1360:
Rippeth, T. P.; Scourse, J. D.; Uehara, K.; McKeown, S. (2008).
1149:
Thomas, H.; Bozec, Y.; Elkalay, K.; Baar, H. J. W. De (2004).
745:
and lead to an increased storage of dissolved inorganic carbon
1227:
between the atmosphere, the land-sea interface and the ocean"
815:
Recently, work has compiled and scaled available data on CO
1221:
Cai, Wei-Jun; Wang, Zhaohui Aleck; Wang, Yongchen (2003).
1307:
in the coastal ocean: Diversity of ecosystems counts".
1268:"Do we have enough pieces of the jigsaw to integrate CO
932:, and seasonal biological and temperature effects".
768:
flux over the East China Sea (35 g C m y), Tsunogai
668:
is proposed to operate in the shallow waters of the
728:the shallowness of the continental shelf restricts
704:) waters in the neighbouring deep ocean. Tsunogai
797:may increase local salinity and seawater density.
688:(1999), the pump is believed to occur where the
638:
8:
804:at temperate latitudes reported by Tsunogai
924:flux based on climatological surface ocean
1191:11370/e821600e-4560-49e8-aeec-18eeb17549e3
645:
631:
18:
1385:
1336:
1287:
1250:
1189:
1114:fluxes on the US Middle Atlantic Bight".
1094:
1069:Frankignoulle, M.; Borges, A. V. (2001).
1053:
1004:
863:
861:
859:
857:
855:
851:
582:Territorialisation of carbon governance
26:
16:Transport of carbon from shallow waters
894:10.1034/j.1600-0889.1999.t01-2-00010.x
708:s (1999) original work focused on the
764:Based on their measurements of the CO
672:, acting as a mechanism to transport
587:Total Carbon Column Observing Network
7:
1028:Yool, A.; Fasham, M. J. R. (2001).
1151:"Enhanced open ocean storage of CO
684:Originally formulated by Tsunogai
14:
724:and explained as follows :
612:
611:
34:
835:from estuaries (0.34 Gt C y).
741:the cooler waters promote the
547:Climate reconstruction proxies
1:
1272:fluxes in the Coastal Ocean?"
1136:10.1016/S0967-0645(02)00122-4
954:10.1016/S0967-0645(02)00003-6
1309:Geophysical Research Letters
1231:Geophysical Research Letters
1075:Global Biogeochemical Cycles
696:pumps interact with a local
517:Carbonate compensation depth
182:Particulate inorganic carbon
1472:Oceanographical terminology
1488:
572:Carbon capture and storage
176:Particulate organic carbon
170:Dissolved inorganic carbon
1116:Deep-Sea Research Part II
1034:Global Biogeochem. Cycles
1006:21.11116/0000-0004-ECB6-5
977:Global Biogeochem. Cycles
934:Deep-Sea Research Part II
577:Carbon cycle re-balancing
910:. John Wiley & Sons.
908:The Global Coastal Ocean
552:Carbon-to-nitrogen ratio
512:Carbonate–silicate cycle
480:Carbon dioxide clathrate
475:Clathrate gun hypothesis
303:Net ecosystem production
164:Dissolved organic carbon
1442:Biological oceanography
1182:10.1126/science.1095491
1155:from shelf sea pumping"
562:Deep Carbon Observatory
22:Part of a series on the
1266:Borges, A. V. (2005).
666:continental shelf pump
382:Continental shelf pump
158:Total inorganic carbon
124:Satellite measurements
1452:Chemical oceanography
800:The strong sink of CO
567:Global Carbon Project
298:Ecosystem respiration
1387:10.1029/2008GL035880
1329:10.1029/2005GL023053
1252:10.1029/2003GL017633
1096:10.1029/2000GB001307
1055:10.1029/2000GB001359
997:10.1029/2000GB001273
396:Carbon sequestration
152:Total organic carbon
1467:Continental shelves
1417:Ocean acidification
1378:2008GeoRL..3524604R
1321:2005GeoRL..3214601B
1243:2003GeoRL..30.1849C
1174:2004Sci...304.1005T
1168:(5673): 1005–1008.
1128:2002DSR....49.4355D
1087:2001GBioC..15..569F
1046:2001GBioC..15..831Y
989:2001GBioC..15...43O
946:2002DSR....49.1601T
940:(9–10): 1601–1622.
886:1999TellB..51..701T
812:to the atmosphere.
670:continental shelves
443:Atmospheric methane
409:Soil carbon storage
259:Reverse Krebs cycle
114:Ocean acidification
1366:Geophys. Res. Lett
1289:10.1007/BF02732750
522:Great Calcite Belt
470:Aerobic production
290:Carbon respiration
232:Metabolic pathways
192:Primary production
1122:(20): 4355–4367.
655:
654:
453:Methane emissions
109:In the atmosphere
1479:
1400:
1399:
1389:
1357:
1351:
1350:
1340:
1300:
1294:
1293:
1291:
1263:
1257:
1256:
1254:
1218:
1212:
1211:
1193:
1159:
1146:
1140:
1139:
1107:
1101:
1100:
1098:
1066:
1060:
1059:
1057:
1025:
1019:
1018:
1008:
974:
964:
958:
957:
917:
911:
904:
898:
897:
865:
732:of cooling water
647:
640:
633:
620:
615:
614:
419:pelagic sediment
313:Soil respiration
308:Photorespiration
38:
19:
1487:
1486:
1482:
1481:
1480:
1478:
1477:
1476:
1462:Biogeochemistry
1437:Aquatic ecology
1427:
1426:
1422:Solubility pump
1412:Biological pump
1408:
1403:
1359:
1358:
1354:
1306:
1302:
1301:
1297:
1271:
1265:
1264:
1260:
1226:
1220:
1219:
1215:
1157:
1154:
1148:
1147:
1143:
1113:
1109:
1108:
1104:
1068:
1067:
1063:
1027:
1026:
1022:
972:
966:
965:
961:
931:
923:
919:
918:
914:
905:
901:
871:
867:
866:
853:
849:
834:
830:
826:
822:
818:
811:
803:
789:results in the
775:
767:
762:
743:solubility pump
682:
662:biogeochemistry
651:
610:
603:
602:
601:
541:
533:
532:
531:
496:
486:
485:
484:
437:
427:
426:
425:
414:Marine sediment
398:
388:
387:
386:
347:Solubility pump
335:Biological pump
329:
319:
318:
317:
292:
282:
281:
280:
264:Carbon fixation
249:
234:
224:
223:
222:
203:
187:
140:
138:Forms of carbon
130:
129:
128:
103:
93:
92:
91:
46:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1485:
1483:
1475:
1474:
1469:
1464:
1459:
1454:
1449:
1444:
1439:
1429:
1428:
1425:
1424:
1419:
1414:
1407:
1404:
1402:
1401:
1372:(24): L24604.
1352:
1315:(14): L14601.
1304:
1295:
1269:
1258:
1224:
1213:
1152:
1141:
1111:
1102:
1081:(3): 569–576.
1061:
1040:(4): 831–844.
1020:
959:
929:
921:
912:
899:
880:(3): 701–712.
869:
850:
848:
845:
840:sea level rise
832:
828:
824:
820:
816:
809:
801:
773:
765:
761:
758:
757:
756:
749:
746:
739:
736:
733:
714:carbon dioxide
710:East China Sea
702:subthermocline
681:
678:
653:
652:
650:
649:
642:
635:
627:
624:
623:
622:
621:
605:
604:
600:
599:
594:
589:
584:
579:
574:
569:
564:
559:
557:Deep biosphere
554:
549:
543:
542:
539:
538:
535:
534:
530:
529:
527:Redfield ratio
524:
519:
514:
509:
507:Nutrient cycle
504:
498:
497:
494:Biogeochemical
492:
491:
488:
487:
483:
482:
477:
472:
467:
466:
465:
460:
450:
448:Methanogenesis
445:
439:
438:
433:
432:
429:
428:
424:
423:
422:
421:
411:
406:
400:
399:
394:
393:
390:
389:
385:
384:
379:
374:
369:
364:
362:Microbial loop
359:
354:
349:
344:
343:
342:
331:
330:
325:
324:
321:
320:
316:
315:
310:
305:
300:
294:
293:
288:
287:
284:
283:
279:
278:
277:
276:
271:
261:
256:
250:
248:
247:
245:Chemosynthesis
242:
240:Photosynthesis
236:
235:
230:
229:
226:
225:
221:
220:
215:
210:
204:
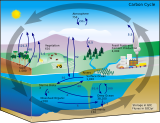
202:
201:
200:
199:
188:
186:
185:
179:
173:
167:
161:
155:
149:
142:
141:
136:
135:
132:
131:
127:
126:
121:
116:
111:
105:
104:
101:Carbon dioxide
99:
98:
95:
94:
90:
89:
84:
79:
74:
69:
64:
59:
54:
48:
47:
44:
43:
40:
39:
31:
30:
24:
23:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1484:
1473:
1470:
1468:
1465:
1463:
1460:
1458:
1455:
1453:
1450:
1448:
1445:
1443:
1440:
1438:
1435:
1434:
1432:
1423:
1420:
1418:
1415:
1413:
1410:
1409:
1405:
1397:
1393:
1388:
1383:
1379:
1375:
1371:
1367:
1363:
1356:
1353:
1348:
1344:
1339:
1334:
1330:
1326:
1322:
1318:
1314:
1310:
1299:
1296:
1290:
1285:
1281:
1277:
1273:
1262:
1259:
1253:
1248:
1244:
1240:
1236:
1232:
1228:
1217:
1214:
1209:
1205:
1201:
1197:
1192:
1187:
1183:
1179:
1175:
1171:
1167:
1163:
1156:
1145:
1142:
1137:
1133:
1129:
1125:
1121:
1117:
1106:
1103:
1097:
1092:
1088:
1084:
1080:
1076:
1072:
1065:
1062:
1056:
1051:
1047:
1043:
1039:
1035:
1031:
1024:
1021:
1016:
1012:
1007:
1002:
998:
994:
990:
986:
982:
978:
971:
963:
960:
955:
951:
947:
943:
939:
935:
927:
916:
913:
909:
903:
900:
895:
891:
887:
883:
879:
875:
864:
862:
860:
858:
856:
852:
846:
844:
841:
836:
813:
807:
798:
796:
792:
788:
782:
780:
771:
759:
754:
750:
747:
744:
740:
737:
734:
731:
727:
726:
725:
723:
719:
715:
711:
707:
703:
699:
695:
691:
687:
679:
677:
675:
671:
667:
663:
660:
648:
643:
641:
636:
634:
629:
628:
626:
625:
619:
609:
608:
607:
606:
598:
595:
593:
590:
588:
585:
583:
580:
578:
575:
573:
570:
568:
565:
563:
560:
558:
555:
553:
550:
548:
545:
544:
537:
536:
528:
525:
523:
520:
518:
515:
513:
510:
508:
505:
503:
502:Marine cycles
500:
499:
495:
490:
489:
481:
478:
476:
473:
471:
468:
464:
461:
459:
456:
455:
454:
451:
449:
446:
444:
441:
440:
436:
431:
430:
420:
417:
416:
415:
412:
410:
407:
405:
402:
401:
397:
392:
391:
383:
380:
378:
375:
373:
370:
368:
365:
363:
360:
358:
355:
353:
350:
348:
345:
341:
338:
337:
336:
333:
332:
328:
323:
322:
314:
311:
309:
306:
304:
301:
299:
296:
295:
291:
286:
285:
275:
272:
270:
267:
266:
265:
262:
260:
257:
255:
252:
251:
246:
243:
241:
238:
237:
233:
228:
227:
219:
216:
214:
211:
209:
206:
205:
198:
195:
194:
193:
190:
189:
183:
180:
177:
174:
171:
168:
165:
162:
159:
156:
153:
150:
147:
144:
143:
139:
134:
133:
125:
122:
120:
117:
115:
112:
110:
107:
106:
102:
97:
96:
88:
85:
83:
82:Boreal forest
80:
78:
75:
73:
70:
68:
65:
63:
60:
58:
55:
53:
50:
49:
42:
41:
37:
33:
32:
29:
25:
21:
20:
1457:Geochemistry
1369:
1365:
1355:
1312:
1308:
1298:
1279:
1275:
1261:
1237:(16): 1849.
1234:
1230:
1216:
1165:
1161:
1144:
1119:
1115:
1105:
1078:
1074:
1064:
1037:
1033:
1023:
983:(1): 43–60.
980:
976:
962:
937:
933:
925:
915:
907:
902:
877:
873:
837:
814:
805:
799:
783:
779:carbon cycle
769:
763:
760:Significance
705:
685:
683:
665:
656:
381:
340:Martin curve
327:Carbon pumps
254:Calvin cycle
208:Black carbon
146:Total carbon
87:Geochemistry
28:Carbon cycle
795:evaporation
698:hydrography
404:Carbon sink
367:Viral shunt
357:Marine snow
213:Blue carbon
67:Deep carbon
62:Atmospheric
52:Terrestrial
1431:Categories
847:References
730:convection
722:alkalinity
694:biological
690:solubility
377:Whale pump
372:Jelly pump
352:Lipid pump
77:Permafrost
45:By regions
1338:2268/2118
1276:Estuaries
1208:129790522
1015:129094847
791:extrusion
753:isopycnal
718:carbonate
1406:See also
1347:45272714
1282:: 3–27.
1200:15143279
874:Tellus B
680:Overview
618:Category
1396:1049049
1374:Bibcode
1317:Bibcode
1239:Bibcode
1170:Bibcode
1162:Science
1124:Bibcode
1083:Bibcode
1042:Bibcode
985:Bibcode
942:Bibcode
882:Bibcode
787:sea-ice
706:et al.'
659:oceanic
463:Wetland
435:Methane
218:Kerogen
119:Removal
1447:Carbon
1394:
1345:
1206:
1198:
1013:
806:et al.
770:et al.
755:mixing
686:et al.
674:carbon
664:, the
616:
597:CO2SYS
458:Arctic
197:marine
57:Marine
1392:S2CID
1343:S2CID
1204:S2CID
1158:(PDF)
1011:S2CID
973:(PDF)
592:C4MIP
540:Other
184:(PIC)
178:(POC)
172:(DIC)
166:(DOC)
160:(TIC)
154:(TOC)
1196:PMID
720:and
692:and
148:(TC)
72:Soil
1382:doi
1333:hdl
1325:doi
1284:doi
1247:doi
1186:hdl
1178:doi
1166:304
1132:doi
1091:doi
1050:doi
1001:hdl
993:doi
950:doi
890:doi
872:".
657:In
1433::
1390:.
1380:.
1370:35
1368:.
1364:.
1341:.
1331:.
1323:.
1313:32
1311:.
1280:28
1278:.
1274:.
1245:.
1235:30
1233:.
1229:.
1202:.
1194:.
1184:.
1176:.
1164:.
1160:.
1130:.
1120:49
1118:.
1089:.
1079:15
1077:.
1073:.
1048:.
1038:15
1036:.
1032:.
1009:.
999:.
991:.
981:15
979:.
975:.
948:.
938:49
936:.
928:CO
888:.
878:51
876:.
854:^
781:.
274:C4
269:C3
1398:.
1384::
1376::
1349:.
1335::
1327::
1319::
1305:2
1292:.
1286::
1270:2
1255:.
1249::
1241::
1225:2
1210:.
1188::
1180::
1172::
1153:2
1138:.
1134::
1126::
1112:2
1099:.
1093::
1085::
1058:.
1052::
1044::
1017:.
1003::
995::
987::
956:.
952::
944::
930:2
926:p
922:2
896:.
892::
884::
870:2
833:2
829:2
825:2
821:2
817:2
810:2
802:2
774:2
766:2
646:e
639:t
632:v
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.