Portal maintenance status: (June 2018)
|
The Classical Music Portal


Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical music, as the term "classical music" can also be applied to non-Western art musics. Classical music is often characterized by formality and complexity in its musical form and harmonic organization, particularly with the use of polyphony. Since at least the ninth century it has been primarily a written tradition, spawning a sophisticated notational system, as well as accompanying literature in analytical, critical, historiographical, musicological and philosophical practices. A foundational component of Western culture, classical music is frequently seen from the perspective of individual or groups of composers, whose compositions, personalities and beliefs have fundamentally shaped its history. (Full article...)
Selected articles - load new batch
-
Image 1A countertenor (also contra tenor) is a type of classical male singing voice whose vocal range is equivalent to that of the female contralto or mezzo-soprano voice types, generally extending from around G3 to D5 or E5, although a sopranist (a specific kind of countertenor) may match the soprano's range of around C4 to C6. Countertenors often have tenor or baritone chest voices, but sing in falsetto or head voice much more often than they do in their chest voice.
The nature of the countertenor voice has radically changed throughout musical history, from a modal voice, to a modal and falsetto voice, to the primarily falsetto voice that is denoted by the term today. This is partly because of changes in human physiology (increase in body height) and partly because of fluctuations in pitch. (Full article...) -
Image 2

Antonio Vivaldi (engraving by François Morellon de La Cave, from Michel-Charles Le Cène's edition of Vivaldi's Op. 8, 1725)
The Four Seasons (Italian: Le quattro stagioni) is a group of four violin concerti by Italian composer Antonio Vivaldi, each of which gives musical expression to a season of the year. These were composed around 1718–1720, when Vivaldi was the court chapel master in Mantua. They were published in 1725 in Amsterdam, together with eight additional concerti, as Il cimento dell'armonia e dell'inventione (The Contest Between Harmony and Invention).
The Four Seasons is the best known of Vivaldi's works. Though three of the concerti are wholly original, the first, "Spring", borrows patterns from a sinfonia in the first act of Vivaldi's contemporaneous opera Il Giustino. The inspiration for the concertos is not the countryside around Mantua, as initially supposed, where Vivaldi was living at the time, since according to Karl Heller they could have been written as early as 1716–1717, while Vivaldi was engaged with the court of Mantua only in 1718. (Full article...) -
Image 3
Petrushka (French: Pétrouchka; ‹See Tfd›Russian: Петрушка) is a ballet by Russian composer Igor Stravinsky. It was written for the 1911 Paris season of Sergei Diaghilev's Ballets Russes company; the original choreography was by Michel Fokine and stage designs and costumes by Alexandre Benois, who assisted Stravinsky with the libretto. The ballet premiered at the Théâtre du Châtelet on 13 June 1911 with Vaslav Nijinsky as Petrushka, Tamara Karsavina as the lead ballerina, Alexander Orlov as the Moor, and Enrico Cecchetti the charlatan.
Petrushka tells the story of the loves and jealousies of three puppets. The three are brought to life by the Charlatan during the 1830 Shrovetide Fair (Maslenitsa) in Saint Petersburg. Petrushka is in love with the Ballerina, but she rejects him as she prefers the Moor. Petrushka is angry and hurt, and curses the Charlatan for bringing him into the world with only pain and suffering in his miserable life. Because of his anger, he challenges the Moor as a result. The Moor, who is both bigger and stronger than Petrushka, kills him with his sword (scimitar). The crowd watching is horrified, and the Charlatan is called to the scene as well as a police officer. The Charlatan reminds everyone that Petrushka is nothing but a puppet made of straw and cloth, and that he has no real emotion nor 'life'. As the crowd disperses, the Charlatan is left alone on the stage. At that moment, Petrushka's ghost rises above the puppet theatre as night falls. He shakes his fist and thumbs his nose at the Charlatan, making him flee, terrified. Petrushka then collapses in a second death. (Full article...) -
Image 4

Harpsichord with double keyboard. The inside of the lid is decorated with two original paintings depicting the battle between Apollo and Pan based on The Judgment of Midas by Hendrick Goltzius (1590). The front cover shows Apollo and the Muses on Mount Helicon. The exterior was repainted with red chinoiserie decoration in the 18th century.
A harpsichord (Italian: clavicembalo, French: clavecin, ‹See Tfd›German: Cembalo; Spanish: clavecín, Portuguese: cravo, ‹See Tfd›Russian: клавеси́н (tr. klavesín or klavesin), Dutch: klavecimbel, Polish: klawesyn) is a musical instrument played by means of a keyboard. This activates a row of levers that turn a trigger mechanism that plucks one or more strings with a small plectrum made from quill or plastic. The strings are under tension on a soundboard, which is mounted in a wooden case; the soundboard amplifies the vibrations from the strings so that the listeners can hear it. Like a pipe organ, a harpsichord may have more than one keyboard manual, and even a pedal board. Harpsichords may also have stop buttons which add or remove additional octaves. Some harpsichords may have a buff stop, which brings a strip of buff leather or other material in contact with the strings, muting their sound to simulate the sound of a plucked lute.
The term denotes the whole family of similar plucked-keyboard instruments, including the smaller virginals, muselar, and spinet. The harpsichord was widely used in Renaissance and Baroque music, both as an accompaniment instrument and as a soloing instrument. During the Baroque era, the harpsichord was a standard part of the continuo group. The basso continuo part acted as the foundation for many musical pieces in this era. During the late 18th century, with the development of the fortepiano (and then the increasing use of the piano in the 19th century) the harpsichord gradually disappeared from the musical scene (except in opera, where it continued to be used to accompany recitative). In the 20th century, it made a resurgence, being used in historically informed performances of older music, in new compositions, and, in rare cases, in certain styles of popular music (e.g., Baroque pop). (Full article...) -
Image 5Cover of the symphony, with the dedication to Prince J. F. M. Lobkowitz and Count Rasumovsky
The Symphony No. 5 in C minor, Op. 67, also known as the Fate Symphony (‹See Tfd›German: Schicksalssinfonie), is a symphony composed by Ludwig van Beethoven between 1804 and 1808. It is one of the best-known compositions in classical music and one of the most frequently played symphonies, and it is widely considered one of the cornerstones of western music. First performed in Vienna's Theater an der Wien in 1808, the work achieved its prodigious reputation soon afterward. E. T. A. Hoffmann described the symphony as "one of the most important works of the time". As is typical of symphonies during the Classical period, Beethoven's Fifth Symphony has four movements.
It begins with a distinctive four-note "short-short-short-long" motif, often characterized as "fate knocking at the door", the Schicksals-Motiv (fate motif): (Full article...) -
Image 6

Fauré in 1907
Gabriel Urbain Fauré (12 May 1845 – 4 November 1924) was a French composer, organist, pianist and teacher. He was one of the foremost French composers of his generation, and his musical style influenced many 20th-century composers. Among his best-known works are his Pavane, Requiem, Sicilienne, nocturnes for piano and the songs "Après un rêve" and "Clair de lune". Although his best-known and most accessible compositions are generally his earlier ones, Fauré composed many of his most highly regarded works in his later years, in a more harmonically and melodically complex style.
Fauré was born into a cultured but not especially musical family. His talent became clear when he was a young boy. At the age of nine, he was sent to the École Niedermeyer music college in Paris, where he was trained to be a church organist and choirmaster. Among his teachers was Camille Saint-Saëns, who became a lifelong friend. After graduating from the college in 1865, Fauré earned a modest living as an organist and teacher, leaving him little time for composition. When he became successful in his middle age, holding the important posts of organist of the Église de la Madeleine and director of the Paris Conservatoire, he still lacked time for composing; he retreated to the countryside in the summer holidays to concentrate on composition. By his last years, he was recognised in France as the leading French composer of his day. An unprecedented national musical tribute was held for him in Paris in 1922, headed by the president of the French Republic. Outside France, Fauré's music took decades to become widely accepted, except in Britain, where he had many admirers during his lifetime. (Full article...) -
Image 7Otello and Desdemona
by Alexandre-Marie Colin, 1829
Otello (Italian pronunciation: [oˈtɛllo]) is an opera in four acts by Giuseppe Verdi to an Italian libretto by Arrigo Boito, based on Shakespeare's play Othello. It was Verdi's penultimate opera, first performed at the Teatro alla Scala, Milan, on 5 February 1887.
The composer was reluctant to write anything new after the success of Aida in 1871, and he retreated into retirement. It took his Milan publisher Giulio Ricordi the next ten years, first to encourage the revision of Verdi's 1857 Simon Boccanegra by introducing Boito as librettist and then to begin the arduous process of persuading and cajoling Verdi to see Boito's completed libretto for Otello in July/August 1881. However, the process of writing the first drafts of the libretto and the years of their revision, with Verdi all along not promising anything, dragged on. It wasn't until 1884, five years after the first drafts of the libretto, that composition began, with most of the work finishing in late 1885. When it finally premiered in Milan on 5 February 1887, it proved to be a resounding success, and further stagings of Otello soon followed at leading theatres throughout Europe and America. (Full article...) -
Image 8Mendelssohn in 1846 by Eduard Magnus
Felix Mendelssohn's Violin Concerto in E minor, Op. 64, MWV O 14, is his last concerto. Well received at its premiere, it has remained among the most prominent and highly-regarded violin concertos. It holds a central place in the violin repertoire and has developed a reputation as an essential concerto for all aspiring concert violinists to master, and usually one of the first Romantic era concertos they learn. A typical performance lasts just under half an hour.
Mendelssohn originally proposed the idea of the violin concerto to Ferdinand David, a close friend and then concertmaster of the Leipzig Gewandhaus Orchestra. Although conceived in 1838, the work took another six years to complete and was not premiered until 1845. During this time, Mendelssohn maintained a regular correspondence with David, who gave him many suggestions. The work itself was one of the foremost violin concertos of the Romantic era and was influential on many other composers. (Full article...) -
Image 9Original 1904 poster by Adolfo Hohenstein
Madama Butterfly (Italian pronunciation: [maˈdaːmaˈbatterflai]; Madame Butterfly) is an opera in three acts (originally two) by Giacomo Puccini, with an Italian libretto by Luigi Illica and Giuseppe Giacosa.
It is based on the short story "Madame Butterfly" (1898) by John Luther Long, which in turn was based on stories told to Long by his sister Jennie Correll and on the semi-autobiographical 1887 French novel Madame Chrysanthème by Pierre Loti. Long's version was dramatized by David Belasco as the one-act play Madame Butterfly: A Tragedy of Japan, which, after premiering in New York in 1900, moved to London, where Puccini saw it in the summer of that year. (Full article...) -
Image 10The Royal Academy of Music (RAM) in London, England, is one of the oldest music schools in the UK, founded in 1822 by John Fane and Nicolas-Charles Bochsa. It received its royal charter in 1830 from King George IV with the support of the first Duke of Wellington.
The academy provides undergraduate and postgraduate training across instrumental performance, composition, jazz, musical theatre and opera, and recruits musicians from around the world, with a student community representing more than 50 nationalities. It is committed to lifelong learning, from Junior Academy, which trains musicians up to the age of 18, through Open Academy community music projects, to performances and educational events for all ages. (Full article...) -
Image 11Nixon in China is an opera in three acts by John Adams with a libretto by Alice Goodman. Adams's first opera, it was inspired by U.S. president Richard Nixon's 1972 visit to the People's Republic of China. The work premiered at the Houston Grand Opera on October 22, 1987, in a production by Peter Sellars with choreography by Mark Morris. When Sellars approached Adams with the idea for the opera in 1983, Adams was initially reluctant, but eventually decided that the work could be a study in how myths come to be, and accepted the project. Goodman's libretto was the result of considerable research into Nixon's visit, though she disregarded most sources published after the 1972 trip.
To create the sounds he sought, Adams augmented the orchestra with a large saxophone section, additional percussion, and electronic synthesizer. Although sometimes described as minimalist, the score displays a variety of musical styles, embracing minimalism after the manner of Philip Glass alongside passages echoing 19th-century composers such as Wagner and Johann Strauss. With these ingredients, Adams mixes Stravinskian 20th-century neoclassicism, jazz references, and big band sounds reminiscent of Nixon's youth in the 1930s. The combination of these elements varies frequently, to reflect changes in the onstage action. (Full article...) -
Image 12Drawing by Dora Stock, 1789
Eine kleine Nachtmusik (Serenade No. 13 for strings in G major), K. 525, is a 1787 composition for a chamber ensemble by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (1756–1791). The German title means "a little night music". The work is written for an ensemble of two violins, viola, cello and double bass, but is often performed by string orchestras. The serenade is one of Mozart's most famous works. (Full article...)
General images - load new batch
-
Image 6Wanderer above the Sea of Fog, by Caspar David Friedrich, is an example of Romantic painting. (from Romantic music)
-
Image 7Hummel in 1814 (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 8Musicians from 'Procession in honour of Our Lady of Sablon in Brussels.' Early 17th-century Flemish alta cappella. From left to right: bass dulcian, alto shawm, treble cornett, soprano shawm, alto shawm, tenor sackbut. (from Renaissance music)
-
Image 9Individual sheet music for a seventeenth-century harp. (from Baroque music)
-
Image 11Gluck, detail of a portrait by Joseph Duplessis, dated 1775 (Kunsthistorisches Museum, Vienna) (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 12Painting by Evaristo Baschenis of Baroque instruments, including a cittern, viola da gamba, violin, and two lutes (from Baroque music)
-
Image 13A modern string quartet. In the 2000s, string quartets from the Classical era are the core of the chamber music literature. From left to right: violin 1, violin 2, cello, viola (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 14Richard Wagner in Paris, 1861
-
Image 15Josef Danhauser's 1840 painting of Franz Liszt at the piano surrounded by (from left to right) Alexandre Dumas, Hector Berlioz, George Sand, Niccolò Paganini, Gioachino Rossini and Marie d'Agoult, with a bust of Ludwig van Beethoven on the piano (from Romantic music)
-
Image 19The Mozart family c. 1780. The portrait on the wall is of Mozart's mother. (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 20A group of Renaissance musicians in The Concert (1623) by Gerard van Honthorst (from Renaissance music)
-
Image 22Balakirev (top), Cui (upper left), Mussorgsky (upper right), Rimsky-Korsakov (lower left), and Borodin (lower right). (from Romantic music)
-
Image 24Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, posthumous painting by Barbara Krafft in 1819 (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 25Gustav Mahler, photographed in 1907 by Moritz Nähr at the end of his period as director of the Vienna Hofoper (from Romantic music)
-
Image 26A large instrumental ensemble's performance in the lavish Teatro Argentina, as depicted by Panini (1747) (from Baroque music)
-
Image 27A young Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, a representative composer of the Classical period, seated at a keyboard. (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 29Fortepiano by Paul McNulty after Walter & Sohn, c. 1805 (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 30Bernhard Crusell, a Swedish-Finnish composer and clarinetist, in 1826 (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 32Portion of Du Fay's setting of Ave maris stella, in fauxbourdon. The top line is a paraphrase of the chant; the middle line, designated "fauxbourdon", (not written) follows the top line but exactly a perfect fourth below. The bottom line is often, but not always, a sixth below the top line; it is embellished, and reaches cadences on the octave.Play (from Renaissance music)
-
Image 33Double-manual harpsichord by Vital Julian Frey, after Jean-Claude Goujon (1749) (from Baroque music)
-
Image 34Marc-Antoine Charpentier (from Baroque music)
-
Image 35The opening bars of the Commendatore's aria in Mozart's opera Don Giovanni. The orchestra starts with a dissonant diminished seventh chord (G# dim7 with a B in the bass) moving to a dominant seventh chord (A7 with a C# in the bass) before resolving to the tonic chord (D minor) at the singer's entrance. (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 361875 oil painting of Franz Schubert by Wilhelm August Rieder, after his own 1825 watercolor portrait (from Classical period (music))
Quotes - show another
| “ | My faith is the grand drama of my life. I'm a believer, so I sing words of God to those who have no faith. | ” |
| — Olivier Messiaen | ||
Related portals
WikiProjects
 Selected composers - load new batch
Selected composers - load new batch 
-
Image 1

Nikolai Andreyevich Rimsky-Korsakov (18 March 1844 – 21 June 1908) was a Russian composer, a member of the group of composers known as The Five. He was a master of orchestration. His best-known orchestral compositions—Capriccio Espagnol, the Russian Easter Festival Overture, and the symphonic suite Scheherazade—are staples of the classical music repertoire, along with suites and excerpts from some of his fifteen operas. Scheherazade is an example of his frequent use of fairy-tale and folk subjects.
Rimsky-Korsakov believed in developing a nationalistic style of classical music, as did his fellow composer Mily Balakirev and the critic Vladimir Stasov. This style employed Russian folk song and lore along with exotic harmonic, melodic and rhythmic elements in a practice known as musical orientalism, and eschewed traditional Western compositional methods. Rimsky-Korsakov appreciated Western musical techniques after he became a professor of musical composition, harmony, and orchestration at the Saint Petersburg Conservatory in 1871. He undertook a rigorous three-year program of self-education and became a master of Western methods, incorporating them alongside the influences of Mikhail Glinka and fellow members of The Five. Rimsky-Korsakov's techniques of composition and orchestration were further enriched by his exposure to the works of Richard Wagner. (Full article...) -
Image 2
Kaikhosru Shapurji Sorabji (born Leon Dudley Sorabji; 14 August 1892 – 15 October 1988) was an English composer, music critic, pianist and writer whose music, written over a period of seventy years, ranges from sets of miniatures to works lasting several hours. One of the most prolific 20th-century composers, he is best known for his piano pieces, notably nocturnes such as Gulistān and Villa Tasca, and large-scale, technically intricate compositions, which include seven symphonies for piano solo, four toccatas, Sequentia cyclica and 100 Transcendental Studies. He felt alienated from English society by reason of his homosexuality and mixed ancestry, and had a lifelong tendency to seclusion.
Sorabji was educated privately. His mother was English and his father a Parsi businessman and industrialist from India, who set up a trust fund that freed his family from the need to work. Although Sorabji was a reluctant performer and not a virtuoso, he played some of his music publicly between 1920 and 1936. In the late 1930s, his attitude shifted and he imposed restrictions on performance of his works, which he lifted in 1976. His compositions received little exposure in those years and he remained in public view mainly through his writings, which include the books Around Music and Mi contra fa: The Immoralisings of a Machiavellian Musician. During this time, he also left London and eventually settled in the village of Corfe Castle, Dorset. Information on Sorabji's life, especially his later years, is scarce, with most of it coming from the letters he exchanged with his friends. (Full article...) -
Image 3

Andrieu's Armes, amours/O flour des flours, recto 52 in the Chantilly Codex
F. Andrieu (fl. late 14th century; possibly François or Franciscus Andrieu) was a French composer in the ars nova style of late medieval music. Nothing is known for certain about him except that he wrote Armes, amours/O flour des flours (Weapons, loves/O flower of flowers), a double ballade déploration, for the death of Guillaume de Machaut in 1377. The work has been widely praised and analyzed; it is notable for being one of two extant medieval double ballades for four voices, the only known contemporary musical setting of Eustache Deschamps and the earliest representative of the longstanding medieval and Renaissance lamentation tradition between composers.
Andrieu may be the same person as Magister Franciscus, although the scholarly consensus on this identification is unclear. With P. des Molins, Jehan Vaillant and Grimace, Andrieu was one of the "post-Machaut" generation whose pieces retain enough ars nova qualities to be differentiated from composers of ars subtilior. (Full article...) -
Image 4Zhou Bangyan (Chinese: 周邦彥; 1056–1121) was a Chinese musician, poet, and politician of the Northern Song dynasty. He was from Qiantang (in modern Hangzhou). His courtesy name was Meicheng (Chinese: 美成; pinyin: Měichéng), and his art name was Qingzhen Jushi (Chinese: 清真居士; pinyin: Qīngzhēn Jūshì). He left a two-volume poetry anthology called either the Qingzhen-ji or the Pianyu-ci. (Full article...)
-
Image 5

Poulenc in the early 1920s
Francis Jean Marcel Poulenc (French: [fʁɑ̃sisʒɑ̃maʁsɛlpulɛ̃k]; 7 January 1899 – 30 January 1963) was a French composer and pianist. His compositions include songs, solo piano works, chamber music, choral pieces, operas, ballets, and orchestral concert music. Among the best-known are the piano suite Trois mouvements perpétuels (1919), the ballet Les biches (1923), the Concert champêtre (1928) for harpsichord and orchestra, the Organ Concerto (1938), the opera Dialogues des Carmélites (1957), and the Gloria (1959) for soprano, choir, and orchestra.
As the only son of a prosperous manufacturer, Poulenc was expected to follow his father into the family firm, and he was not allowed to enrol at a music college. He studied with the pianist Ricardo Viñes, who became his mentor after the composer's parents died. Poulenc also made the acquaintance of Erik Satie, under whose tutelage he became one of a group of young composers known collectively as Les Six. In his early works Poulenc became known for his high spirits and irreverence. During the 1930s a much more serious side to his nature emerged, particularly in the religious music he composed from 1936 onwards, which he alternated with his more light-hearted works. (Full article...) -
Image 6Ellis Gibbons (bapt. 30 November 1573 – 14? May 1603) was an English composer of the late Renaissance who was associated with the English Madrigal School. Born in Cambridge to a musical family, Gibbons was the second surviving son of William Gibbons, a town wait. By 1598 he was known to be living in Cambridge's High ward, and later the Market ward. He owned property in Cambridge and London and probably spent much time there, presumably as a musician of some kind (although this has never been verified). At the age of 28 he became one of only two composers to contribute two pieces to The Triumphs of Oriana, a collection of 25 madrigals published in 1601. These madrigals were Long live faire Oriana and Round about her Charret; modern commentators generally favor the latter. No other compositions by Gibbons survive, and some scholars have doubted his authorship of these works, ascribing them to his brothers. Two months after his mother's death, his career was cut short by his early death in May 1603, leaving behind his brothers Edward, Ferdinando and Orlando, who would become the most famous musician of the family. Orlando's son, Christopher, was also a noted composer. (Full article...)
-
Image 7Nobuo Uematsu (植松 伸夫, Uematsu Nobuo, born March 21, 1959) is a Japanese composer and keyboardist best known for his contributions to the Final Fantasy video game series by Square Enix. A self-taught musician, he began playing the piano at the age of twelve, with English singer-songwriter Elton John as one of his biggest influences.
Uematsu joined Square in 1986, where he first met Final Fantasy creator Hironobu Sakaguchi. The two later worked together on many games at the company, most notably in the Final Fantasy series. After nearly two decades with Square, Uematsu left in 2004 to create his own production company and music label, Dog Ear Records. He has since composed music as a freelancer for other games, including ones developed by Square Enix and Sakaguchi's studio Mistwalker. (Full article...) -
Image 8
 Debussy c. 1900 by Atelier Nadar
Debussy c. 1900 by Atelier Nadar
(Achille) Claude Debussy (French: [aʃilkloddəbysi]; 22 August 1862 – 25 March 1918) was a French composer. He is sometimes seen as the first Impressionist composer, although he vigorously rejected the term. He was among the most influential composers of the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Born to a family of modest means and little cultural involvement, Debussy showed enough musical talent to be admitted at the age of ten to France's leading music college, the Conservatoire de Paris. He originally studied the piano, but found his vocation in innovative composition, despite the disapproval of the Conservatoire's conservative professors. He took many years to develop his mature style, and was nearly 40 when he achieved international fame in 1902 with the only opera he completed, Pelléas et Mélisande. (Full article...) -
Image 9Yasunori Mitsuda (光田 康典, Mitsuda Yasunori, born January 21, 1972) is a Japanese composer and musician. He is best known for his work in video games, primarily for the Chrono, Xeno, Shadow Hearts, and Inazuma Eleven franchises, among various others. Mitsuda began composing music for his own games in high school, later attending a music college in Tokyo. While still a student, he was granted an intern position at the game development studio Wolf Team.
Mitsuda joined Square upon graduation in 1992 and worked there as a sound effects designer for two years before telling Square's vice president Hironobu Sakaguchi he would quit unless he could write music for their games. Shortly after, Sakaguchi assigned him to work on the soundtrack for Chrono Trigger (1995), whose music has since been cited as among the best in video games. (Full article...) -
Image 10

Imogen Clare Holst CBE (née von Holst; 12 April 1907 – 9 March 1984) was a British composer, arranger, conductor, teacher, musicologist, and festival administrator. The only child of the composer Gustav Holst, she is particularly known for her educational work at Dartington Hall in the 1940s, and for her 20 years as joint artistic director of the Aldeburgh Festival. In addition to composing music, she wrote composer biographies, much educational material, and several books on the life and works of her father.
From a young age, Holst showed precocious talent in composing and performance. After attending Eothen School and St Paul's Girls' School, she entered the Royal College of Music, where she developed her skills as a conductor and won several prizes for composing. Unable to follow her initial ambitions to be a pianist or a dancer for health reasons, Holst spent most of the 1930s teaching, and as a full-time organiser for the English Folk Dance and Song Society. These duties reduced her compositional activities, although she made many arrangements of folksongs. After serving as an organiser for the Council for the Encouragement of Music and the Arts at the start of the Second World War, in 1942 she began working at Dartington. In her nine years there she established Dartington as a major centre of music education and activity. (Full article...) -
Image 11

Stockhausen in the Electronic Music Studio of the WDR, 1994
Karlheinz Stockhausen (German: [kaʁlˈhaɪntsˈʃtɔkhaʊzn̩] ; 22 August 1928 – 5 December 2007) was a German composer, widely acknowledged by critics as one of the most important but also controversial composers of the 20th and early 21st centuries. He is known for his groundbreaking work in electronic music, having been called the "father of electronic music", for introducing controlled chance (aleatory techniques) into serial composition, and for musical spatialization.
He was educated at the Hochschule für Musik Köln and the University of Cologne, later studying with Olivier Messiaen in Paris and with Werner Meyer-Eppler at the University of Bonn. As one of the leading figures of the Darmstadt School, his compositions and theories were and remain widely influential, not only on composers of art music, but also on jazz and popular music. His works, composed over a period of nearly sixty years, eschew traditional forms. In addition to electronic music—both with and without live performers—they range from miniatures for musical boxes through works for solo instruments, songs, chamber music, choral and orchestral music, to a cycle of seven full-length operas. His theoretical and other writings comprise ten large volumes. He received numerous prizes and distinctions for his compositions, recordings, and for the scores produced by his publishing company. (Full article...) -
Image 12

Britten in 1968, by Hans Wild
Edward Benjamin Britten, Baron Britten OM CH (22 November 1913 – 4 December 1976) was an English composer, conductor, and pianist. He was a central figure of 20th-century British music, with a range of works including opera, other vocal music, orchestral and chamber pieces. His best-known works include the opera Peter Grimes (1945), the War Requiem (1962) and the orchestral showpiece The Young Person's Guide to the Orchestra (1945).
Britten was born in Lowestoft, Suffolk, the son of a dentist. He showed talent from an early age. He studied at the Royal College of Music in London and privately with the composer Frank Bridge. Britten first came to public attention with the a cappella choral work A Boy Was Born in 1934. With the premiere of Peter Grimes in 1945, he leapt to international fame. Over the next 28 years, he wrote 14 more operas, establishing himself as one of the leading 20th-century composers in the genre. In addition to large-scale operas for Sadler's Wells and Covent Garden, he wrote chamber operas for small forces, suitable for performance in venues of modest size. Among the best known of these is The Turn of the Screw (1954). Recurring themes in his operas include the struggle of an outsider against a hostile society and the corruption of innocence. (Full article...) -
Image 13
Top: Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky. Bottom (left to right): Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov, Alexander Glazunov and Anatoly Lyadov
Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky's relations with the group of composers known as the Belyayev circle, which lasted from 1887 until Tchaikovsky's death in 1893, influenced all of their music and briefly helped shape the next generation of Russian composers. This group was named after timber merchant Mitrofan Belyayev, an amateur musician who became an influential music patron and publisher after he had taken an interest in Alexander Glazunov's work. By 1887, Tchaikovsky was firmly established as one of the leading composers in Russia. A favorite of Tsar Alexander III, he was widely regarded as a national treasure. He was in demand as a guest conductor in Russia and Western Europe, and in 1890 visited the United States in the same capacity. By contrast, the fortunes of the nationalistic group of composers known as The Five, which preceded the Belyayev circle, had waned, and the group had long since dispersed; of its members, only Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov remained fully active as a composer. Now a professor of musical composition and orchestration at the Saint Petersburg Conservatory, Rimsky-Korsakov had become a firm believer in the Western-based compositional training that had been once frowned upon by the group.
As a result of the time Tchaikovsky spent with the Belyayev circle's leading composers—Glazunov, Anatoly Lyadov and Rimsky-Korsakov—the somewhat fraught relationship he had previously endured with The Five would eventually meld into something more harmonious. Tchaikovsky's friendship with these men gave him increased confidence in his own abilities as a composer, while his music encouraged Glazunov to broaden his artistic outlook past the nationalist agenda and to compose along more universal themes. This influence grew to the point that Glazunov's Third Symphony became known as the "anti-kuchist" symphony of his oeuvre ("kuchist" refers to "kuchka", the shortened Russian name for The Five) and shared several stylistic fingerprints with Tchaikovsky's later symphonies. Nor was Glazunov the only composer so influenced. Rimsky-Korsakov wrote about the Belyayev composers' "worship of Tchaikovsky and ... tendency toward eclecticism" that became prevalent during this period, along with a predilection toward "Italian-French music of the time of wig and farthingale" (that is, of the 18th Century) typified in Tchaikovsky's late operas The Queen of Spades and Iolanta. (Full article...) -
Image 14

Bizet photographed by Étienne Carjat (1875)
Georges Bizet (né Alexandre César Léopold Bizet; 25 October 1838 – 3 June 1875) was a French composer of the Romantic era. Best known for his operas in a career cut short by his early death, Bizet achieved few successes before his final work, Carmen, which has become one of the most popular and frequently performed works in the entire opera repertoire.
During a brilliant student career at the Conservatoire de Paris, Bizet won many prizes, including the prestigious Prix de Rome in 1857. He was recognised as an outstanding pianist, though he chose not to capitalise on this skill and rarely performed in public. Returning to Paris after almost three years in Italy, he found that the main Parisian opera theatres preferred the established classical repertoire to the works of newcomers. His keyboard and orchestral compositions were likewise largely ignored; as a result, his career stalled, and he earned his living mainly by arranging and transcribing the music of others. Restless for success, he began many theatrical projects during the 1860s, most of which were abandoned. Neither of his two operas that reached the stage in this time—Les pêcheurs de perles and La jolie fille de Perth—were immediately successful. (Full article...) -
Image 15Tōru Takemitsu (武満 徹, pronounced [takeꜜmitsɯ̥toːɾɯ]; 8 October 1930 – 20 February 1996) was a Japanese composer and writer on aesthetics and music theory. Largely self-taught, Takemitsu was admired for the subtle manipulation of instrumental and orchestral timbre. He is known for combining elements of oriental and occidental philosophy and for fusing sound with silence and tradition with innovation.
He composed several hundred independent works of music, scored more than ninety films and published twenty books. He was also a founding member of the Jikken Kōbō (Experimental Workshop) in Japan, a group of avant-garde artists who distanced themselves from academia and whose collaborative work is often regarded among the most influential of the 20th century. (Full article...)
Did you know (auto-generated) - load new batch

- ... that the choral music of Artemy Vedel, who is regarded as one of the Golden Three composers of 18th-century Ukrainian classical music, was censored but performed from handwritten copies?
- ... that WFMT classical music radio host Don Tait owned such a large collection of recordings that he had to buy a house and have its floor reinforced to accommodate the weight?
- ... that opera singer Charles Holland spent much of his career in Europe as opportunities in classical music for African Americans were limited?
- ... that in 1994, Anthony Pople created two computer programs to analyse classical music?
- ... that, according to its owner, KLEF in Anchorage, Alaska, was one of just three remaining commercially operated classical-music radio stations in the United States, as of 2013?
- ... that gas lighting inspired Stephen Gunzenhauser to start a classical music festival?
Selected image
-
Image 1Photograph: David IliffThe Royal Albert Hall is a concert hall, seating a maximum of 5,272, on the northern edge of South Kensington, London. Constructed beginning in 1867, the hall was inaugurated on 29 March 1871. Since 1941 it has held The Proms, an eight-week summer season of daily orchestral classical music concerts and other events.
-
Image 2

A picture of the first theatre drawn shortly before it burned down in 1808.
The Royal Opera House is an opera house and major performing arts venue in the London district of Covent Garden. The large building, often referred to as simply "Covent Garden", is the home of The Royal Opera, The Royal Ballet and the Orchestra of the Royal Opera House. -
Image 3
 The Teatro alla Scala (or La Scala, as it is known), in Milan, Italy, is one of the world's most famous opera houses. The theatre was inaugurated on 3 August 1778, under the name Nuovo Regio Ducal Teatro alla Scala with Salieri's Europa riconosciuta.
The Teatro alla Scala (or La Scala, as it is known), in Milan, Italy, is one of the world's most famous opera houses. The theatre was inaugurated on 3 August 1778, under the name Nuovo Regio Ducal Teatro alla Scala with Salieri's Europa riconosciuta. -
Image 4Painting: Thomas GainsboroughJohann Christian Bach (5 September 1735 – 1 January 1782) was a composer of the Classical era, the eighteenth child of Johann Sebastian Bach, and the youngest of his eleven sons. Bach was taught by his father and then, after the latter's death, by his half-brother C. P. E. Bach. Bach moved to Italy in 1754, and then to London in 1762, where he became known as the "London Bach". Bach's compositions include eleven operas, as well as chamber music, orchestral music and compositions for keyboard music. In 1764 Bach met Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, who was eight at the time, and spent five months teaching him composition. He had considerable influence on Mozart, and was later described by scholars as his "only, true teacher".
This portrait of Bach was painted in 1776 by Thomas Gainsborough, as part of a collection started by Bach's former teacher Padre Martini. It now hangs in the National Portrait Gallery, London. -
Image 5Photograph credit: Eugène Pirou; restored by Adam CuerdenJules Massenet (12 May 1842 – 13 August 1912) was a French composer of the Romantic era, best known for his operas. Between 1867 and his death, he wrote more than forty stage works in a wide variety of styles, from opéra comique to grand depictions of classical myths, romantic comedies and lyric dramas, as well as oratorios, cantatas and ballets. Massenet had a good sense of the theatre and of what would succeed with the Parisian public. Despite some miscalculations, he produced a series of successes that made him the leading opera composer in France in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. By the time of his death, he was regarded as old-fashioned; his works, however, began to be favourably reassessed during the mid-20th century, and many have since been staged and recorded. This photograph of Massenet was taken by French photographer Eugène Pirou in 1875.
-
Image 6Photograph credit: William P. Gottlieb; restored by Adam CuerdenBilly Strayhorn (November 29, 1915 – May 31, 1967) was an American jazz composer, pianist, lyricist, and arranger, best remembered for his long-time collaboration with bandleader and composer Duke Ellington that lasted nearly three decades. Though classical music was Strayhorn's first love, his ambition to become a classical composer went unrealized because of the harsh reality of a black man trying to make his way in the world of classical music, which at that time was almost completely white. He was introduced to the music of pianists like Art Tatum and Teddy Wilson at age 19, and the artistic influence of these musicians guided him into the realm of jazz, where he remained for the rest of his life. This photograph of Strayhorn was taken by William P. Gottlieb in the 1940s.
-
Image 7Photo: W. J. Mayer; Restoration: Lise BroerA bust of the German composer and pianist Ludwig van Beethoven (1770–1827), made from his death mask. He was a crucial figure in the transitional period between the Classical and Romantic eras in Western classical music, and remains one of the most acclaimed and influential composers of all time. Born in Bonn, of the Electorate of Cologne and a part of the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation in present-day Germany, he moved to Vienna in his early twenties and settled there, studying with Joseph Haydn and quickly gaining a reputation as a virtuoso pianist. His hearing began to deteriorate in the late 1790s, yet he continued to compose, conduct, and perform, even after becoming completely deaf.
-
Image 8
 Ballet is a formalized form of dance with its origins in the French court, further developed in France and Russia as a concert dance form.
Ballet is a formalized form of dance with its origins in the French court, further developed in France and Russia as a concert dance form. -
Image 9Photo: Guillaume PiolleThe anatomy of a Périnet piston valve, this one taken from a B♭ trumpet. When depressed, the valve diverts the air stream through additional tubing, thus lengthening the instrument and lowering the harmonic series on which the instrument is vibrating (i.e., it lowers the pitch). Trumpets generally use three valves, with some variations, such as a piccolo trumpet, having four. When used singly or in combination, the valves make the instrument fully chromatic, or capable of playing all twelve pitches of classical music. Trumpets may also use rotary valves instead.
-
Image 10Sheet music for the Polonaise in A-flat major, Op. 53, a solo piano piece written by Frédéric Chopin in 1842. This work is one of Chopin's most admired compositions and has long been a favorite of the classical piano repertoire. The piece, which is very difficult, requires exceptional pianistic skills and great virtuosity to be interpreted. A typical performance of the polonaise lasts seven minutes.
-
Image 11
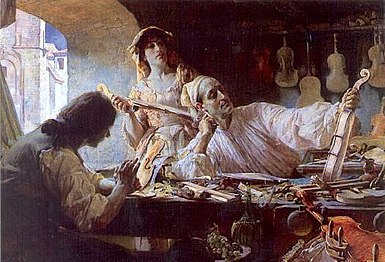 Stradivarius is one of the violins, violas, cellos and other string instruments built by members of the Italian Stradivari family, particularly Antonio Stradivari.
Stradivarius is one of the violins, violas, cellos and other string instruments built by members of the Italian Stradivari family, particularly Antonio Stradivari.
Topics
Things you can do
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus










































































