Portal maintenance status: (July 2018)
|
The Medicine Portal

Medicine is the science and practice of caring for patients, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others.
Medicine has been practiced since prehistoric times, and for most of this time it was an art (an area of creativity and skill), frequently having connections to the religious and philosophical beliefs of local culture. For example, a medicine man would apply herbs and say prayers for healing, or an ancient philosopher and physician would apply bloodletting according to the theories of humorism. In recent centuries, since the advent of modern science, most medicine has become a combination of art and science (both basic and applied, under the umbrella of medical science). For example, while stitching technique for sutures is an art learned through practice, knowledge of what happens at the cellular and molecular level in the tissues being stitched arises through science.
Prescientific forms of medicine, now known as traditional medicine or folk medicine, remain commonly used in the absence of scientific medicine and are thus called alternative medicine. Alternative treatments outside of scientific medicine with ethical, safety and efficacy concerns are termed quackery. (Full article...)
 Featured articles - load new batch
Featured articles - load new batch
-
Image 1Ray Fletcher Farquharson MBE (4 August 1897 – 1 June 1965) was a Canadian medical doctor, university professor, and medical researcher. Born in Claude, Ontario, he attended and taught at the University of Toronto for most of his life, and was trained and employed at Toronto General Hospital. With co-researcher Arthur Squires, Farquharson was responsible for the discovery of the Farquharson phenomenon, an important principle of endocrinology, which is that administering external hormones suppresses the natural production of that hormone.
He served in the First and Second World Wars, earning appointment as a Member of the Order of the British Empire for his medical work during the latter. He chaired the Penicillin Committee of Canada and served as a medical consultant for the Royal Canadian Air Force. He was awarded the Queen's Coronation Medal in 1953 for his work for the Defence Review Board. Farquharson was also a charter member of the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada. (Full article...) -
Image 2
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, intense headache, vomiting and neck stiffness and occasionally photophobia.
Other symptoms include confusion or altered consciousness, nausea, and an inability to tolerate light or loud noises. Young children often exhibit only nonspecific symptoms, such as irritability, drowsiness, or poor feeding. A non-blanching rash (a rash that does not fade when a glass is rolled over it) may also be present. (Full article...) -
Image 3
Buruli ulcer (/bəˈruːli/) is an infectious disease characterized by the development of painless open wounds. The disease is limited to certain areas of the world, most cases occurring in Sub-Saharan Africa and Australia. The first sign of infection is a small painless nodule or area of swelling, typically on the arms or legs. The nodule grows larger over days to weeks, eventually forming an open ulcer. Deep ulcers can cause scarring of muscles and tendons, resulting in permanent disability.
Buruli ulcer is caused by skin infection with bacteria called Mycobacterium ulcerans. The mechanism by which M. ulcerans is transmitted from the environment to humans is not known, but may involve the bite of an aquatic insect or the infection of open wounds. Once in the skin, M. ulcerans grows and releases the toxin mycolactone, which blocks the normal function of cells, resulting in tissue death and immune suppression at the site of the ulcer. (Full article...) -
Image 4Cartoon in Punch, November 1858
In 1858 a batch of sweets in Bradford, England, was accidentally adulterated with poisonous arsenic trioxide. About five pounds (two kilograms) of sweets were sold to the public, leading to around 20 deaths and over 200 people suffering the effects of arsenic poisoning.
The adulteration of food had been practised in Britain since before the Middle Ages, but from 1800, with increasing urbanisation and the rise in shop-purchased food, adulterants became a growing problem. With the cost of sugar high, replacing it with substitutes was common. For the sweets produced in Bradford, the confectioner was supposed to purchase powdered gypsum, but a mistake at the wholesale chemist meant arsenic was purchased instead. (Full article...) -
Image 5Liver histology is altered in HRS while kidney histology is normal. The upper image is a trichrome stain (chicken wire appearance) cirrhosis of the liver, the most common cause of HRS. The lower image is a PAS stain of normal kidney histology.
Hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) is a life-threatening medical condition that consists of rapid deterioration in kidney function in individuals with cirrhosis or fulminant liver failure. HRS is usually fatal unless a liver transplant is performed, although various treatments, such as dialysis, can prevent advancement of the condition.
HRS can affect individuals with cirrhosis, severe alcoholic hepatitis, or liver failure, and usually occurs when liver function deteriorates rapidly because of a sudden insult such as an infection, bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, or overuse of diuretic medications. HRS is a relatively common complication of cirrhosis, occurring in 18% of people within one year of their diagnosis, and in 39% within five years of their diagnosis. Deteriorating liver function is believed to cause changes in the circulation that supplies the intestines, altering blood flow and blood vessel tone in the kidneys. The kidney failure of HRS is a consequence of these changes in blood flow, rather than direct damage to the kidney. The diagnosis of hepatorenal syndrome is based on laboratory tests of individuals susceptible to the condition. Two forms of hepatorenal syndrome have been defined: Type 1 HRS entails a rapidly progressive decline in kidney function, while type 2 HRS is associated with ascites (fluid accumulation in the abdomen) that does not improve with standard diuretic medications. (Full article...) -
Image 6
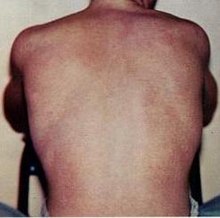
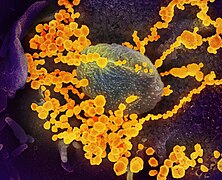
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne disease caused by dengue virus, prevalent in tropical and subtropical areas. It is frequently asymptomatic; if symptoms appear they typically begin 3 to 14 days after infection. These may include a high fever, headache, vomiting, muscle and joint pains, and a characteristic skin itching and skin rash. Recovery generally takes two to seven days. In a small proportion of cases, the disease develops into severe dengue (previously known as dengue hemorrhagic fever or dengue shock syndrome) with bleeding, low levels of blood platelets, blood plasma leakage, and dangerously low blood pressure.
Dengue virus has four confirmed serotypes; infection with one type usually gives lifelong immunity to that type, but only short-term immunity to the others. Subsequent infection with a different type increases the risk of severe complications. The symptoms of dengue resemble many other diseases including malaria, influenza, and Zika. Blood tests are available to confirm the diagnosis including detecting viral RNA, or antibodies to the virus. (Full article...) -
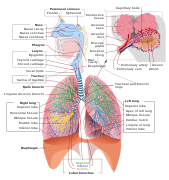
Image 7A chest X-ray showing a tumor in the lung (marked by arrow)
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma, is a malignant tumor that begins in the lung. Lung cancer is caused by genetic damage to the DNA of cells in the airways, often caused by cigarette smoking or inhaling damaging chemicals. Damaged airway cells gain the ability to multiply unchecked, causing the growth of a tumor. Without treatment, tumors spread throughout the lung, damaging lung function. Eventually lung tumors metastasize, spreading to other parts of the body.
Early lung cancer often has no symptoms and can only be detected by medical imaging. As the cancer progresses, most people experience nonspecific respiratory problems: coughing, shortness of breath, or chest pain. Other symptoms depend on the location and size of the tumor. Those suspected of having lung cancer typically undergo a series of imaging tests to determine the location and extent of any tumors. Definitive diagnosis of lung cancer requires a biopsy of the suspected tumor be examined by a pathologist under a microscope. In addition to recognizing cancerous cells, a pathologist can classify the tumor according to the type of cells it originates from. Around 15% of cases are small-cell lung cancer (SCLC), and the remaining 85% (the non-small-cell lung cancers or NSCLC) are adenocarcinomas, squamous-cell carcinomas, and large-cell carcinomas. After diagnosis, further imaging and biopsies are done to determine the cancer's stage based on how far it has spread. (Full article...) -
Image 8

Golding Bird, 1840
Golding Bird (9 December 1814 – 27 October 1854) was a British medical doctor and a Fellow of the Royal College of Physicians. He became a great authority on kidney diseases and published a comprehensive paper on urinary deposits in 1844. He was also notable for his work in related sciences, especially the medical uses of electricity and electrochemistry. From 1836, he lectured at Guy's Hospital, a well-known teaching hospital in London and now part of King's College London, and published a popular textbook on science for medical students called Elements of Natural Philosophy.
Having developed an interest in chemistry while still a child, largely through self-study, Bird was far enough advanced to deliver lectures to his fellow pupils at school. He later applied this knowledge to medicine and did much research on the chemistry of urine and of kidney stones. In 1842, he was the first to describe oxaluria, a condition which leads to the formation of a particular kind of stone. (Full article...) -
Image 9

Amphetamine (contracted from alpha-methylphenethylamine) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity. Amphetamine was discovered as a chemical in 1887 by Lazăr Edeleanu, and then as a drug in the late 1920s. It exists as two enantiomers: levoamphetamine and dextroamphetamine. Amphetamine properly refers to a specific chemical, the racemic free base, which is equal parts of the two enantiomers in their pure amine forms. The term is frequently used informally to refer to any combination of the enantiomers, or to either of them alone. Historically, it has been used to treat nasal congestion and depression. Amphetamine is also used as an athletic performance enhancer and cognitive enhancer, and recreationally as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant. It is a prescription drug in many countries, and unauthorized possession and distribution of amphetamine are often tightly controlled due to the significant health risks associated with recreational use.
The first amphetamine pharmaceutical was Benzedrine, a brand which was used to treat a variety of conditions. Currently, pharmaceutical amphetamine is prescribed as racemic amphetamine, Adderall, dextroamphetamine, or the inactive prodrug lisdexamfetamine. Amphetamine increases monoamine and excitatory neurotransmission in the brain, with its most pronounced effects targeting the norepinephrine and dopamine neurotransmitter systems. (Full article...) -
Image 10Taare Zameen Par (lit. 'Stars on Earth'), also known as Like Stars on Earth in English, is a 2007 Indian Hindi-language psychological drama film produced and directed by Aamir Khan. It stars Khan himself, with Darsheel Safary, Tanay Chheda, Vipin Sharma and Tisca Chopra. It explores the life and imagination of Ishaan (Safary), an artistically gifted 8-year-old boy whose poor academic performance leads his parents to send him to a boarding school, where a new art teacher Nikumbh (Khan) suspects that he is dyslexic and helps him to overcome his reading disorder.
Creative director and writer Amole Gupte developed the idea with his wife Deepa Bhatia, who was the film's editor. Shankar–Ehsaan–Loy composed the score, and Prasoon Joshi wrote the lyrics for many of the songs. Principal photography took place in Mumbai, and in Panchgani's New Era High School, where some of the school's students participated in the filming. (Full article...) -
Image 11
In 1984, 751 people suffered food poisoning in The Dalles, Oregon, United States, due to the deliberate contamination of salad bars at ten local restaurants with Salmonella. A group of prominent followers of Rajneesh (later known as Osho) led by Ma Anand Sheela had hoped to incapacitate the voting population of the city so that their own candidates would win the 1984 Wasco County elections. The incident was the first and is still the single largest bioterrorist attack in U.S. history.
Rajneesh's followers had previously gained political control of Antelope, Oregon, as they were based in the nearby intentional community of Rajneeshpuram, and they now sought election to two of the three seats on the Wasco County Circuit Court that were up for election in November 1984. Some Rajneeshpuram officials feared that they would not get enough votes, so they decided to incapacitate voters in The Dalles, the largest population center in Wasco County. The chosen biological agent was Salmonella enterica Typhimurium, which was first delivered through glasses of water to two county commissioners and then at salad bars and in salad dressing. (Full article...) -
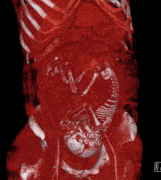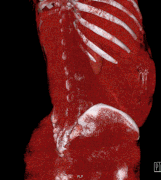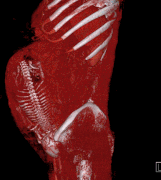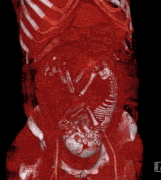
Image 12A CT scan showing a pulmonary contusion (red arrow) accompanied by a rib fracture (purple arrow)
A pulmonary contusion, also known as lung contusion, is a bruise of the lung, caused by chest trauma. As a result of damage to capillaries, blood and other fluids accumulate in the lung tissue. The excess fluid interferes with gas exchange, potentially leading to inadequate oxygen levels (hypoxia). Unlike pulmonary laceration, another type of lung injury, pulmonary contusion does not involve a cut or tear of the lung tissue.
A pulmonary contusion is usually caused directly by blunt trauma but can also result from explosion injuries or a shock wave associated with penetrating trauma. With the use of explosives during World Wars I and II, pulmonary contusion resulting from blasts gained recognition. In the 1960s its occurrence in civilians began to receive wider recognition, in which cases it is usually caused by traffic accidents. The use of seat belts and airbags reduces the risk to vehicle occupants. (Full article...) -
Image 13
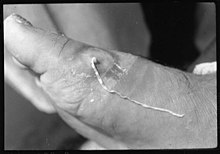
Dracunculiasis, also called Guinea-worm disease, is a parasitic infection by the Guinea worm, Dracunculus medinensis. A person becomes infected by drinking water contaminated with Guinea-worm larvae that reside inside copepods (a type of small crustacean). Stomach acid digests the copepod and releases the Guinea worm, which penetrates the digestive tract and escapes into the body. Around a year later, the adult female migrates to an exit site – usually the lower leg – and induces an intensely painful blister on the skin. Eventually, the blister bursts, creating a painful wound from which the worm gradually emerges over several weeks. The wound remains painful throughout the worm's emergence, disabling the affected person for the three to ten weeks it takes the worm to emerge.
There is no medication to treat or prevent dracunculiasis. Instead, the mainstay of treatment is the careful wrapping of the emerging worm around a small stick or gauze to encourage and speed up its exit. Each day, a few more centimeters of the worm emerge, and the stick is turned to maintain gentle tension. Too much tension can break and kill the worm in the wound, causing severe pain and swelling. Dracunculiasis is a disease of extreme poverty, occurring in places with poor access to clean drinking water. Prevention efforts center on filtering drinking water to remove copepods, as well as public education campaigns to discourage people from soaking affected limbs in sources of drinking water, as this allows the worms to spread their larvae. (Full article...) -
Image 14
John Rolph (4 March 1793 – 19 October 1870) was a Canadian physician, lawyer, and political figure. As a politician, he was considered the leader of the Reform faction in the 1820s and helped plan the Upper Canada Rebellion. As a doctor, he founded several medical schools and incorporated new teaching techniques and medical procedures into his lectures. However, his actions against rival medical schools decreased public confidence in the ability of medical professionals to regulate themselves.
Rolph grew up in England and was educated in medicine and law. He immigrated to Upper Canada in 1813 and lived on his father's farm in Port Talbot, where he practiced law and medicine concurrently and opened a medical school called the Talbot Dispensary. In 1824, Rolph was elected to the Parliament of Upper Canada and returned to England to petition the Colonial Office to allow the naturalization of American citizens in Canada. He was elected as an alderman to Toronto's first city council, though he resigned after his council colleagues did not select him to be the city's mayor. (Full article...) -
Image 15Cloth embroidered by a person diagnosed with schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, disorganized thinking and behavior, and flat or inappropriate affect. Symptoms develop gradually and typically begin during young adulthood and are never resolved. There is no objective diagnostic test; diagnosis is based on observed behavior, a psychiatric history that includes the person's reported experiences, and reports of others familiar with the person. For a diagnosis of schizophrenia, the described symptoms need to have been present for at least six months (according to the DSM-5) or one month (according to the ICD-11). Many people with schizophrenia have other mental disorders, especially mood disorders, anxiety disorders, and obsessive–compulsive disorder.
About 0.3% to 0.7% of people are diagnosed with schizophrenia during their lifetime. In 2017, there were an estimated 1.1 million new cases and in 2022 a total of 24 million cases globally. Males are more often affected and on average have an earlier onset than females. The causes of schizophrenia may include genetic and environmental factors. Genetic factors include a variety of common and rare genetic variants. Possible environmental factors include being raised in a city, childhood adversity, cannabis use during adolescence, infections, the age of a person's mother or father, and poor nutrition during pregnancy. (Full article...)
Selected image – show another
Photo credit: Molecule of the Month by www.pdb.org
WikiProject

Get involved by joining WikiProject Medicine. We discuss collaborations and all manner of issues on our talk page.
Related portals
 Good articles - load new batch
Good articles - load new batch
-
Image 1
Barend Joseph Stokvis (Dutch pronunciation: [ˈbaːrəɲˈcoːsəfˈstɔkfɪs]; 16 August 1834 – 29 September 1902) was a physician and professor of physiology and pharmacology at the University of Amsterdam. He is mainly remembered for his description of acute porphyria in 1889. As a researcher in chemical pathology he made contributions to the understanding of a number of diseases, such as diabetes. He was also considered an expert in tropical medicine and a celebrated medical educator. He authored an influential pharmacology textbook. Stokvis was one of a number of prominent 19th century Jewish physicians in the Netherlands. (Full article...) -
Image 2
XYYY syndrome, also known as 48,XYYY, is a chromosomal disorder in which a male has two extra copies of the Y chromosome. The syndrome is exceptionally rare, with only twelve recorded cases. The presentation of the syndrome is heterogeneous, but appears to be more severe than its counterpart XYY syndrome. Common traits include borderline to mild intellectual disability, infertility, radioulnar synostosis (the fusion of the long bones in the forearm), and in some cases tall stature. (Full article...) -
Image 3
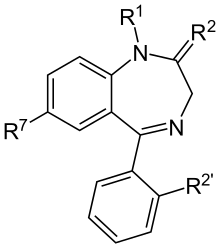
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), colloquially called "benzos", are a class of depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizures. The first benzodiazepine, chlordiazepoxide (Librium), was discovered accidentally by Leo Sternbach in 1955, and was made available in 1960 by Hoffmann–La Roche, which followed with the development of diazepam (Valium) three years later, in 1963. By 1977, benzodiazepines were the most prescribed medications globally; the introduction of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), among other factors, decreased rates of prescription, but they remain frequently used worldwide.
Benzodiazepines are depressants that enhance the effect of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) at the GABAA receptor, resulting in sedative, hypnotic (sleep-inducing), anxiolytic (anti-anxiety), anticonvulsant, and muscle relaxant properties. High doses of many shorter-acting benzodiazepines may also cause anterograde amnesia and dissociation. These properties make benzodiazepines useful in treating anxiety, panic disorder, insomnia, agitation, seizures, muscle spasms, alcohol withdrawal and as a premedication for medical or dental procedures. Benzodiazepines are categorized as short, intermediate, or long-acting. Short- and intermediate-acting benzodiazepines are preferred for the treatment of insomnia; longer-acting benzodiazepines are recommended for the treatment of anxiety. (Full article...) -
Image 4

Launch of the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations, CEPI in 2017 at the World Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland.
The Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI) is a foundation that takes donations from public, private, philanthropic, and civil society organisations, to finance independent research projects to develop vaccines against emerging infectious diseases (EID).
CEPI is focused on the World Health Organization's (WHO) "blueprint priority diseases", which include: the Middle East respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus (MERS-CoV), the Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the Nipah virus, the Lassa fever virus, and the Rift Valley fever virus, as well as the Chikungunya virus and the hypothetical, unknown pathogen "Disease X". CEPI investment also requires "equitable access" to the vaccines during outbreaks, although subsequent CEPI policy changes may have compromised this criterion. In 2022, CEPI adopted a vision for the world to be able to respond to a pandemic threat with a new vaccine within 100 days. (Full article...) -
Image 5
Fish allergy is an immune hypersensitivity to proteins found in fish. Symptoms can be either rapid or gradual in onset. The latter can take hours to days to appear. The former may include anaphylaxis, a potentially life-threatening condition which requires treatment with epinephrine. Other presentations may include atopic dermatitis or inflammation of the esophagus. Fish is one of the eight common food allergens which are responsible for 90% of allergic reactions to foods: cow's milk, eggs, wheat, shellfish, peanuts, tree nuts, fish, and soy beans.
Unlike early childhood allergic reactions to milk and eggs, which often lessen as the children age, fish allergy tends to first appear in school-age children and persist in adulthood. Strong predictors for adult-persistence are anaphylaxis, high fish-specific serum immunoglobulin E (IgE) and robust response to the skin prick test. It is unclear if the early introduction of fish to the diet of babies aged 4–6 months decreases the risk of later development of fish allergy. Adult onset of fish allergy is common in workers in the fish catching and processing industry. (Full article...) -
Image 6Iodine is a chemical element; it has symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists at standard conditions as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid that melts to form a deep violet liquid at 114 °C (237 °F), and boils to a violet gas at 184 °C (363 °F). The element was discovered by the French chemist Bernard Courtois in 1811 and was named two years later by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, after the Ancient Greek Ιώδης, meaning 'violet'.
Iodine occurs in many oxidation states, including iodide (I), iodate (IO
3), and the various periodate anions. As the heaviest essential mineral nutrient, iodine is required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Iodine deficiency affects about two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disabilities. (Full article...) -
Image 7
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection period, people often have mild or no symptoms. Early symptoms can include fever, dark urine, abdominal pain, and yellow tinged skin. The virus persists in the liver, becoming chronic, in about 70% of those initially infected. Early on, chronic infection typically has no symptoms. Over many years however, it often leads to liver disease and occasionally cirrhosis. In some cases, those with cirrhosis will develop serious complications such as liver failure, liver cancer, or dilated blood vessels in the esophagus and stomach.
HCV is spread primarily by blood-to-blood contact associated with injection drug use, poorly sterilized medical equipment, needlestick injuries in healthcare, and transfusions. In regions where blood screening has been implemented, the risk of contracting HCV from a transfusion has dropped substantially to less than one per two million. HCV may also be spread from an infected mother to her baby during birth. It is not spread through breast milk, food, water or casual contact such as hugging, kissing and sharing food or drinks with an infected person. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.
Diagnosis is by blood testing to look for either antibodies to the virus or viral RNA. In the United States, screening for HCV infection is recommended in all adults age 18 to 79 years old.
There is no vaccine against hepatitis C. Prevention includes harm reduction efforts among people who inject drugs, testing donated blood, and treatment of people with chronic infection. Chronic infection can be cured more than 95% of the time with antiviral medications such as sofosbuvir or simeprevir. Peginterferon and ribavirin were earlier generation treatments that proved successful in <50% of cases and caused greater side effects. While access to the newer treatments was expensive, by 2022 prices had dropped dramatically in many countries (primarily low-income and lower-middle-income countries) due to the introduction of generic versions of medicines. Those who develop cirrhosis or liver cancer may require a liver transplant. Hepatitis C is one of the leading reasons for liver transplantation, though the virus usually recurs after transplantation. (Full article...) -
Image 8Long COVID or long-haul COVID is a group of health problems persisting or developing after an initial period of COVID-19 infection. Symptoms can last weeks, months or years and are often debilitating. The World Health Organization defines long COVID as starting three months after the initial COVID-19 infection, but other agencies define it as starting at four weeks after the initial infection.
Long COVID is characterised by a large number of symptoms that sometimes disappear and then reappear. Commonly reported symptoms of long COVID are fatigue, memory problems, shortness of breath, and sleep disorder. Several other symptoms, including headaches, mental health issues, loss of smell or taste, muscle weakness, fever, and cognitive dysfunction may also present. Symptoms often get worse after mental or physical effort, a process called post-exertional malaise. There is a large overlap in symptoms with myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS). (Full article...) -
Image 9Late onset congenital adrenal hyperplasia (LOCAH), also known as nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia (NCCAH or NCAH), is a milder form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH), a group of autosomal recessive disorders characterized by impaired cortisol synthesis that leads to variable degrees of postnatal androgen excess.
The causes of LOCAH are the same as of classic CAH, and in the majority of the cases are the mutations in the CYP21A2 gene resulting in corresponding activity changes in the associated P450c21 (21-hydroxylase) enzyme which ultimately leads to excessive androgen production. Other causes, albeit less frequent, are mutations in genes affecting other enzymes involved in steroid metabolism, like 11β-hydroxylase or 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. It has a prevalence between 0.1% and 2% depending on population, and is one of the most common autosomal recessive genetic diseases in humans. The pathophysiology is complex and not all individuals are symptomatic. (Full article...) -
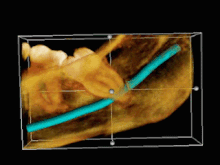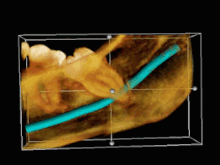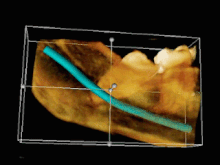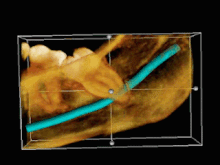
Image 103D CT of an impacted wisdom tooth adjacent the inferior alveolar nerve prior to removal of wisdom tooth
Impacted wisdom teeth is a condition where the third molars (wisdom teeth) are prevented from erupting into the mouth. This can be caused by a physical barrier, such as other teeth, or when the tooth is angled away from a vertical position. Completely unerupted wisdom teeth usually result in no symptoms, although they can sometimes develop cysts or neoplasms. Partially erupted wisdom teeth or wisdom teeth that are not erupted but are exposed to oral bacteria through deep periodontal pocket, can develop cavities or pericoronitis. Removal of impacted wisdom teeth is advised for the future prevention of or in the current presence of certain pathologies, such as caries (dental decay), periodontal disease or cysts. Prophylactic (preventative) extraction of wisdom teeth is preferred to be done at a younger age (middle to late teenage years) to take advantage of incomplete root development, which is associated with an easier surgical procedure and less probability of complications.
Impacted wisdom teeth are classified by their direction of impaction, their depth compared to the biting surface of adjacent teeth and the amount of the tooth's crown that extends through gum tissue or bone. Impacted wisdom teeth can also be classified by the presence or absence of symptoms and disease. Screening for the presence of wisdom teeth often begins in late adolescence when a partially developed tooth may become impacted. Screening commonly includes a clinical examination as well as x-rays such as panoramic radiographs. (Full article...) -
Image 11
Egg allergy is an immune hypersensitivity to proteins found in chicken eggs, and possibly goose, duck, or turkey eggs. Symptoms can be either rapid or gradual in onset. The latter can take hours to days to appear. The former may include anaphylaxis, a potentially life-threatening condition which requires treatment with epinephrine. Other presentations may include atopic dermatitis or inflammation of the esophagus.
In the United States, 90% of allergic responses to foods are caused by cow's milk, eggs, wheat, shellfish, peanuts, tree nuts, fish, soybeans, and sesame seeds. The declaration of the presence of trace amounts of allergens in foods is not mandatory in any country, with the exception of Brazil. (Full article...) -
Image 12
Wilson's disease (also called Hepatolenticular degeneration) is a genetic disorder characterized by the excess build-up of copper in the body. Symptoms are typically related to the brain and liver. Liver-related symptoms include vomiting, weakness, fluid build-up in the abdomen, swelling of the legs, yellowish skin, and itchiness. Brain-related symptoms include tremors, muscle stiffness, trouble in speaking, personality changes, anxiety, and psychosis.
Wilson's disease is caused by a mutation in the Wilson disease protein (ATP7B) gene. This protein transports excess copper into bile, where it is excreted in waste products. The condition is autosomal recessive; for people to be affected, they must inherit a mutated copy of the gene from both parents. Diagnosis may be difficult and often involves a combination of blood tests, urine tests, and a liver biopsy. Genetic testing may be used to screen family members of those affected. (Full article...) -
Image 133D structure of major prion protein
A prion /ˈpriːɒn/ is a misfolded protein that induces misfolding in normal variants of the same protein, leading to cellular death. Prions are responsible for prion diseases, known as transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs), which are fatal and transmissible neurodegenerative diseases affecting both humans and animals. These proteins can misfold sporadically, due to genetic mutations, or by exposure to an already misfolded protein, leading to an abnormal three-dimensional structure that can propagate misfolding in other proteins.
The term prion comes from "proteinaceous infectious particle". Unlike other infectious agents such as viruses, bacteria, and fungi, prions do not contain nucleic acids (DNA or RNA). Prions are mainly twisted isoforms of the major prion protein (PrP), a naturally occurring protein with an uncertain function. They are the hypothesized cause of various TSEs, including scrapie in sheep, chronic wasting disease (CWD) in deer, bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) in cattle (mad cow disease), and Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD) in humans. (Full article...) -
Image 14Horace Gilbert Smithy Jr. (July 19, 1914 – October 28, 1948) was an American cardiac surgeon who in 1948 performed the first successful mitral valve repair (mitral valvulotomy) since the 1920s. Smithy's work was complicated because it predated heart-lung machines or open heart surgery. Though his procedure did not become a definitive treatment for valvular heart disease, he introduced the technique of injecting novocaine into the heart to avoid arrhythmias during surgery, and he showed that it was feasible to access and operate on the heart's valves.
A graduate of the University of Virginia School of Medicine, Smithy completed a surgical residency in Charleston, South Carolina, and then practiced surgery at Roper Hospital in Charleston. He also began working with a colleague in a dog laboratory to devise a valvulotomy (surgical treatment for diseased heart valves). Smithy's interest in heart valve dysfunction was also personal; he suffered from narrowing of the aortic valve related to rheumatic heart disease. (Full article...) -
Image 15
Friedreich's ataxia (FRDA) is a rare, inherited, autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects the nervous system, causing progressive damage to the spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and cerebellum, leading to impaired muscle coordination (ataxia). The condition typically manifests in childhood or adolescence, with initial symptoms including difficulty walking, loss of balance, and poor coordination. As the disease progresses, it can also impact speech, vision, and hearing. Many individuals with Friedreich's ataxia develop scoliosis, diabetes, and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a serious heart condition that is a leading cause of mortality in patients.
Friedreich's ataxia is caused by mutations in the FXN gene, which result in reduced production of frataxin, a protein essential for mitochondrial function, particularly in iron-sulfur cluster biogenesis. The deficiency of frataxin disrupts cellular energy production and leads to oxidative stress, contributing to the neurological and systemic symptoms associated with the disorder. (Full article...)
Did you know – show different entries
- ... that in Prehistoric medicine, a hole was cut into the skull to release evil spirits (Trepanning) and that there is evidence that many people survived the operation?
- ...Empty nose syndrome is caused by excess surgical removal of turbinate tissue, e.g. because of severe chronic congestion, and may severely impact quality of life?
- ...hair transplantation is a surgical baldness treatment?
General images – load new batch
-
Image 3The plinthios brochos as described by Greek physician Heraklas, a sling for binding a fractured jaw. These writings were preserved in one of Oribasius' collections. (from History of medicine)
-
Image 4An American billing clerk preparing a detailed invoice. (1992) (from Medical billing)
-
Image 5Seven named physicians and botanists of the Classical world from Vienna Dioscurides. Clockwise from top center: Galen, Dioscorides, Nicander, Rufus of Ephesus, Andreas of Carystus, Apollonius Mus or of Pergamon, Crateuas (from History of medicine)
-
Image 7AMA Code of Medical Ethics (from Medical ethics)
-
Image 8Infographic showing how healthcare data flows within the billing process (from Medical billing)
-
Image 9A cuneiform terracotta tablet describing a medicinal recipe for poisoning (c. 18th century BCE). Discovered in Nippur, Iraq.
-
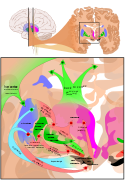
Image 10"Diagram of the causes of mortality in the army in the East" by Florence Nightingale. (from History of medicine)
-
Image 11Statue of Robert Koch, father of medical bacteriology, at Robert-Koch-Platz (Robert Koch square) in Berlin (from History of medicine)
-
Image 12Sometimes traditional medicines include parts of endangered species, such as the slow loris in Southeast Asia. (from Traditional medicine)
-
Image 13A Neo-Assyrian cuneiform tablet fragment describing medical text (c. 9th to 7th century BCE). (from History of medicine)
-
Image 15Emil Kraepelin (1856–1926), the founder of modern scientific psychiatry, psychopharmacology and psychiatric genetics. (from History of medicine)
-
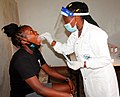
Image 16COVID-19 swab testing in Rwanda (2021). (from History of medicine)
-
Image 17Magical stela or cippus of Horus inscribed with healing encantations (c. 332 to 280 BCE). (from History of medicine)
-
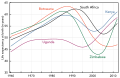
Image 19Most countries have seen a tremendous increase in life expectancy since 1945. However, in southern Africa, the HIV epidemic beginning around 1990 has eroded national health. (from History of medicine)
-
Image 20The Edwin Smith Surgical Papyrus, written in the 17th century BCE, contains the earliest recorded reference to the brain. New York Academy of Medicine. (from History of medicine)
-
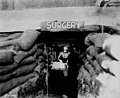
Image 21Medicine during the First World War - Medical Transport. (from History of medicine)
-
Image 22healthcare expenditure in Japan by age group (from Health insurance)
-
Image 23National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery in London, United Kingdom is a specialist neurological hospital. (from Health care)
-
Image 24Mandrake (written 'ΜΑΝΔΡΑΓΟΡΑ' in Greek capitals). Naples Dioscurides, 7th century (from History of medicine)
-
Image 25A doctor checks a patient's pulse in Meiji-era Japan. (from History of medicine)
-
Image 26Total healthcare cost per person. Public and private spending. US dollars PPP. For example: $6,319 for Canada in 2022. $12,555 for the US in 2022. (from Health care)
-
Image 27A 12th-century manuscript of the Hippocratic Oath in Greek, one of the most famous aspects of classical medicine that carried into later eras (from History of medicine)
-
Image 30Primary care may be provided in community health centers. (from Health care)
-
Image 31The numbers of Americans lacking health insurance and the uninsured rate from 1987 to 2008 (from Health insurance)
-
Image 32Life Expectancy of the total population at birth among several OECD member nations. Data source: OECD's iLibrary (from Health insurance)
-
Image 33Zhang Zhongjing – a Chinese pharmacologist, physician, inventor, and writer of the Eastern Han dynasty. (from History of medicine)
-
Image 35Yarrow, a medicinal plant found in human-occupied caves in the Upper Palaeolithic period. (from History of medicine)
-
Image 36The Quaker-run York Retreat, founded in 1796, gained international prominence as a centre for moral treatment and a model of asylum reform following the publication of Samuel Tuke's Description of the Retreat (1813). (from History of medicine)
-
Image 37The emergency room is often a frontline venue for the delivery of primary medical care. (from Health care)
-
Image 38Life expectancy vs healthcare spending of rich OECD countries. US average of $10,447 in 2018. (from Health care)
-
Image 39Botánicas such as this one in Jamaica Plain, Boston, cater to the Latino community and sell folk medicine alongside statues of saints, candles decorated with prayers, lucky bamboo, and other items. (from Traditional medicine)
-
Image 40Smallpox vaccination in Niger, 1969. A decade later, this was the first infectious disease to be eradicated. (from History of medicine)
-
Image 42Global concentrations of health care resources, as depicted by the number of physicians per 10,000 individuals, by country. Data is sourced from a World Health Statistics 2010, a WHO report. (from Health care)
-
Image 44Jackson Memorial Hospital in Miami, the primary teaching hospital of the University of Miami's Miller School of Medicine and the largest hospital in the United States with 1,547 beds (from Health care)
-
Image 45Ethical prayer for medical wisdom by Dr Edmond Fernandes (from Medical ethics)
-
Image 47A Ukrainian monument to the HIV pandemic. (from History of medicine)
-
Image 4818th-century medical remedies collected by a British Gentry family (from History of medicine)
-
Image 49Health spending by country. Percent of GDP (Gross domestic product). For example: 11.2% for Canada in 2022. 16.6% for the United States in 2022. (from Health care)
-
Image 50Health Expenditure per capita (in PPP-adjusted US$) among several OECD member nations. Data source: OECD's iLibrary (from Health insurance)
-
Image 51Patient, Surrey County Lunatic Asylum, c. 1850–58. The asylum population in England and Wales rose from 1,027 in 1827 to 74,004 in 1900. (from History of medicine)
-
Image 52A cochlear implant is a common kind of neural prosthesis, a device replacing part of the human nervous system. (from History of medicine)
-
Image 53"More Doctors Smoke Camels than Any Other Cigarette" advertisement for Camel cigarettes in the 1940s (from Medical ethics)
-
Image 54Mexico City epidemic of 1737, with elites calling on the Virgin of Guadalupe (from History of medicine)
-
Image 55Taoist symbol of Yin and Yang (from Medical ethics)
-
Image 58Depiction of smallpox in Franciscan Bernardino de Sahagún's history of the conquest of Mexico, Book XII of the Florentine Codex, from the defeated Aztecs' point of view (from History of medicine)
-
Image 59Medical personnel place sterilized covers on the arms of the daVinci Xi surgical system, a minimally-invasive robotic surgery system, at the William Beaumont Army Medical Center. (from History of medicine)
More Did you know (auto generated)

- ... that Indian gynaecologist and reproductive medicine pioneer Baidyanath Chakrabarty, who performed over 4,000 IVF procedures, was a cricket fan who thought Virat Kohli and Ashwin were "such good boys"?
- ... that the Noongar used the Eucalyptus wandoo tree as a medicine and ointment?
- ... that Constance Fozzard was told during her surgical training that women with children could not become consultants?
- ... that the Anglo-Saxons may have used a mixture of garlic, another Allium, wine, and bovine bile as an eye medicine?
- ... that fourteenth-century Buddhist monk Tuệ Tĩnh is referred to as a founding father of traditional Vietnamese medicine?
- ... that Margaret C. Roberts was encouraged to study medicine by LDS Church leader Brigham Young to reduce mortality rates during childbirth?
Topics
Categories
Recognized content
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus